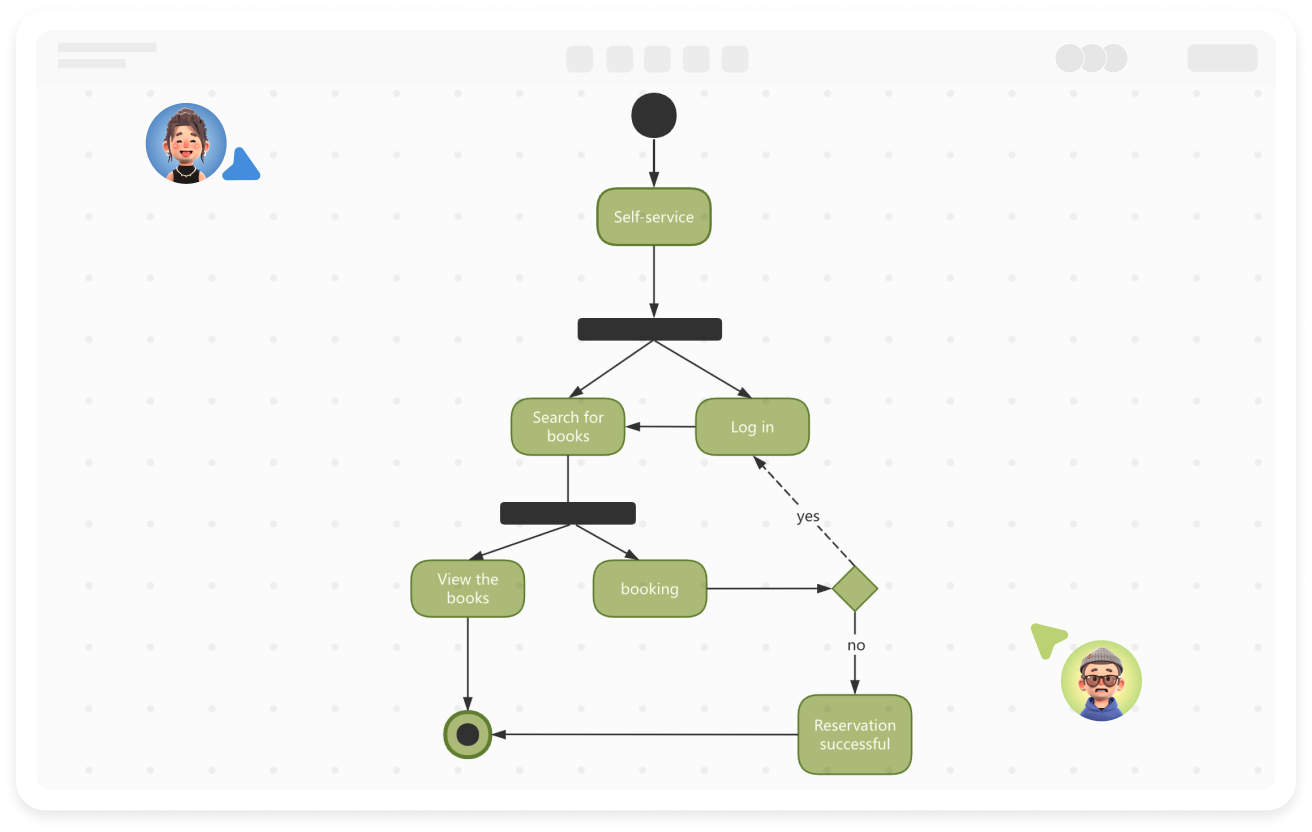
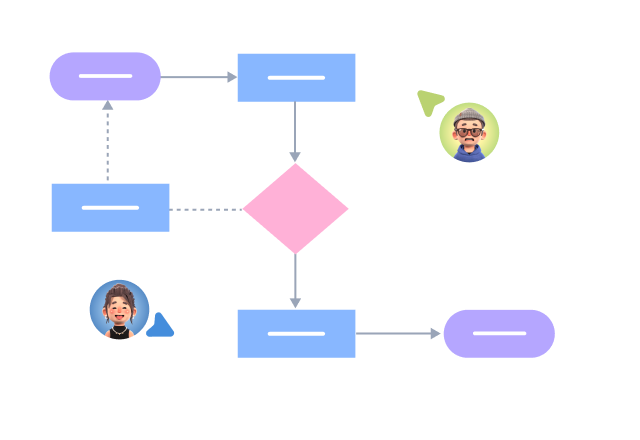
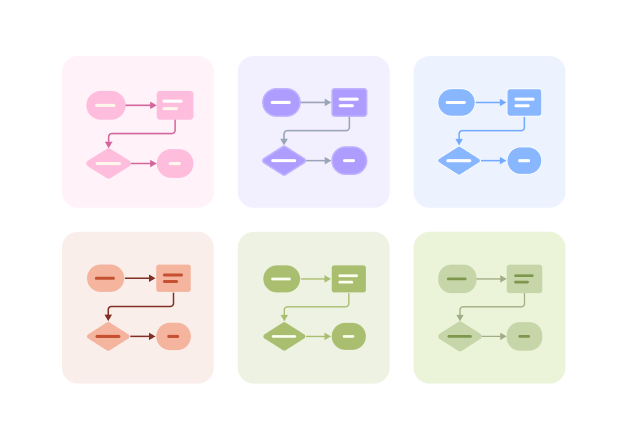
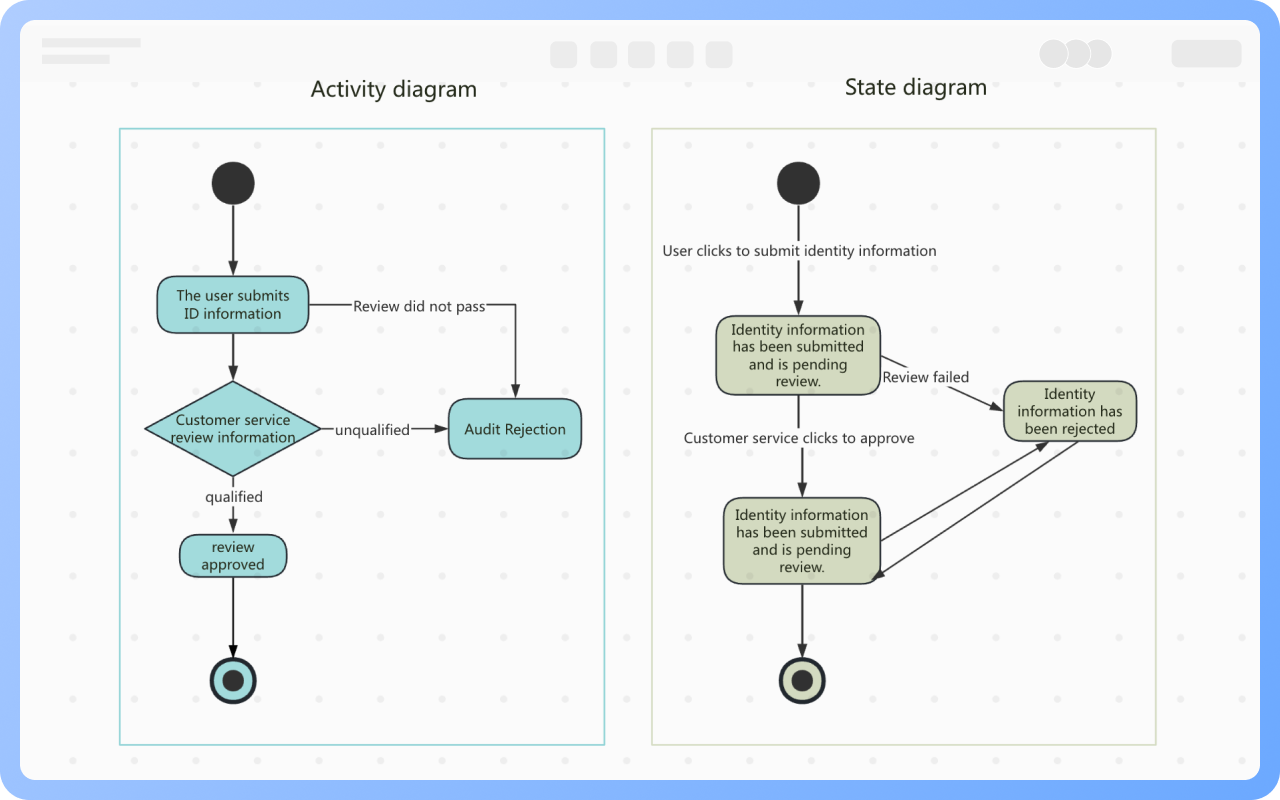
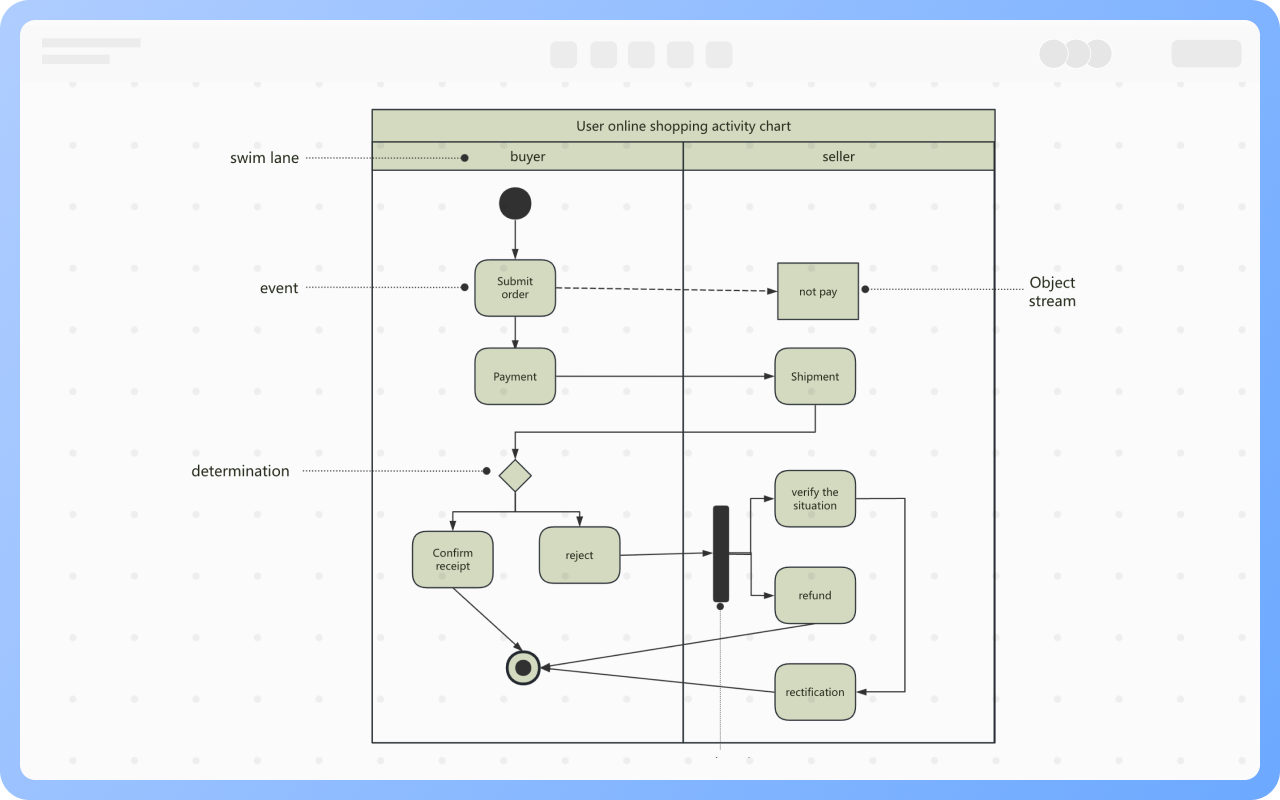
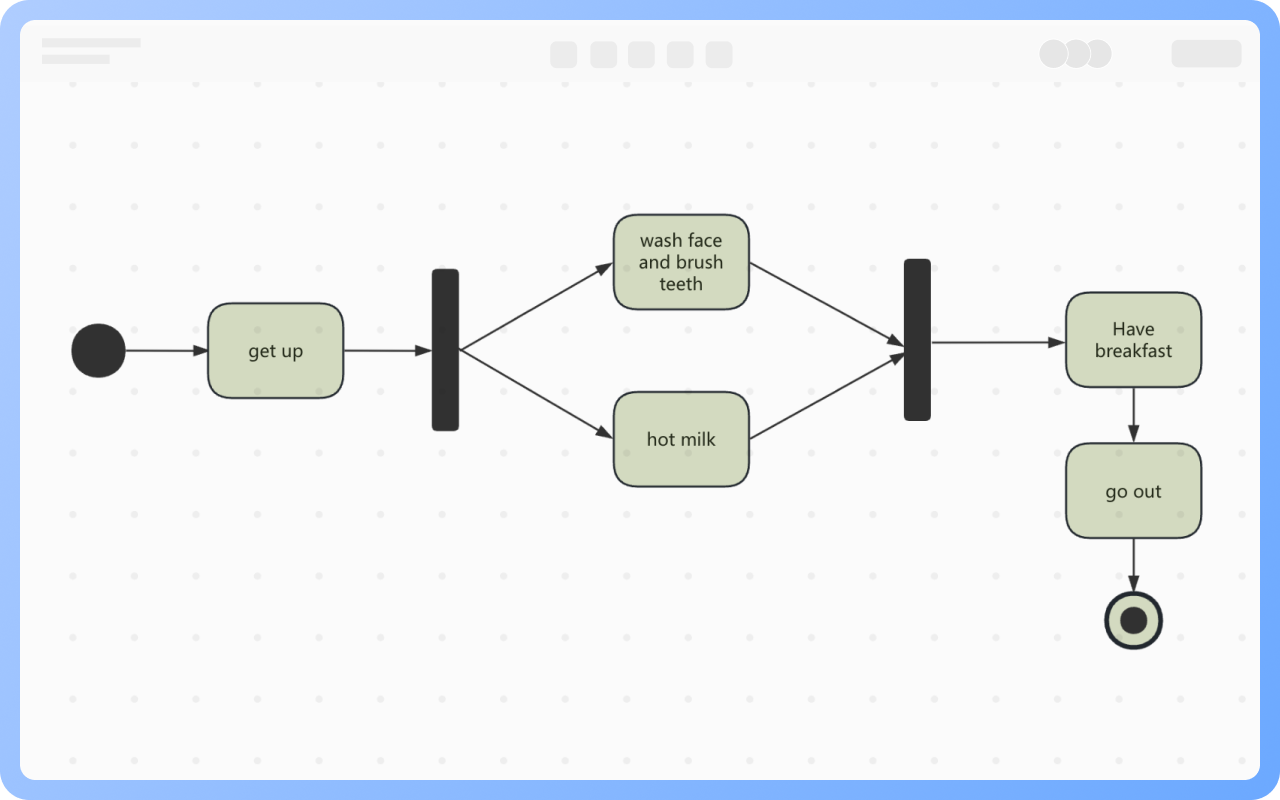
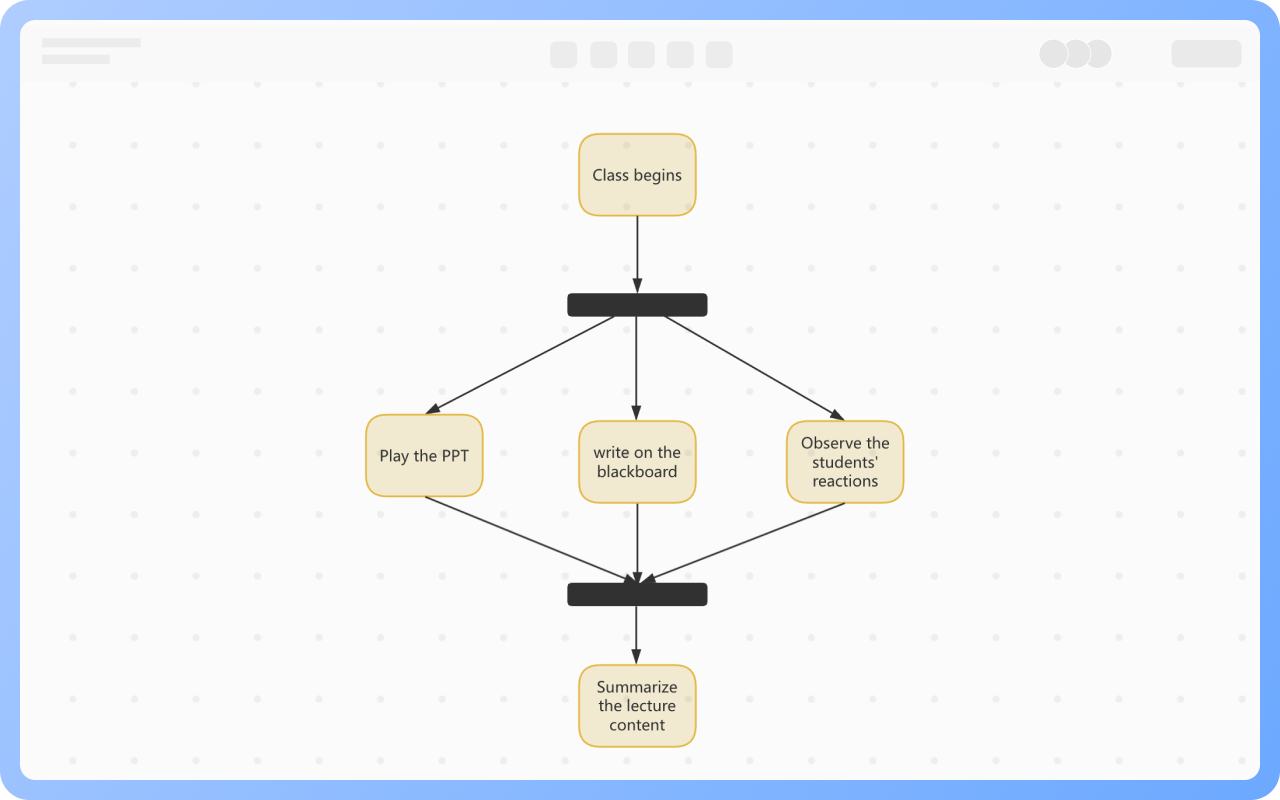
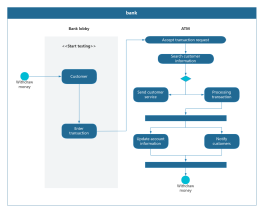
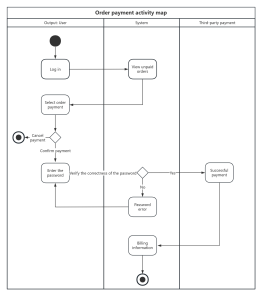
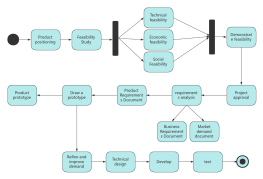
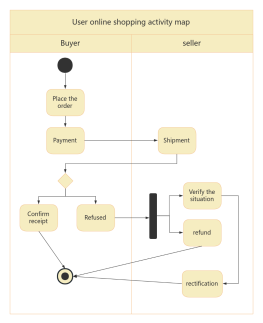
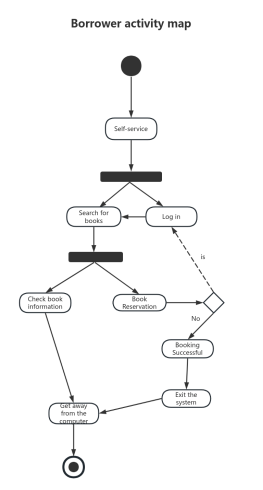
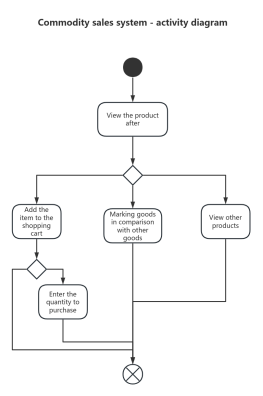
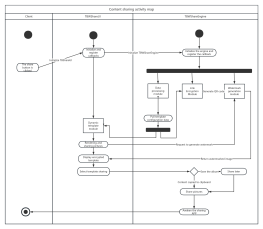
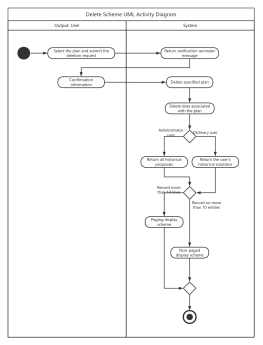
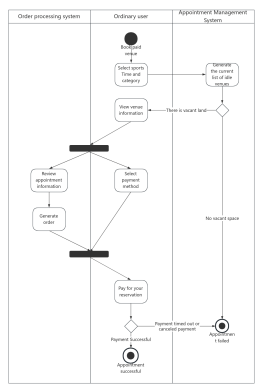
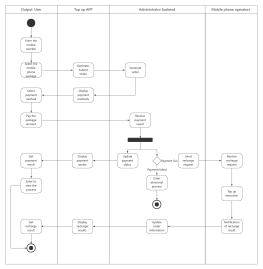
Components of Activity Diagram
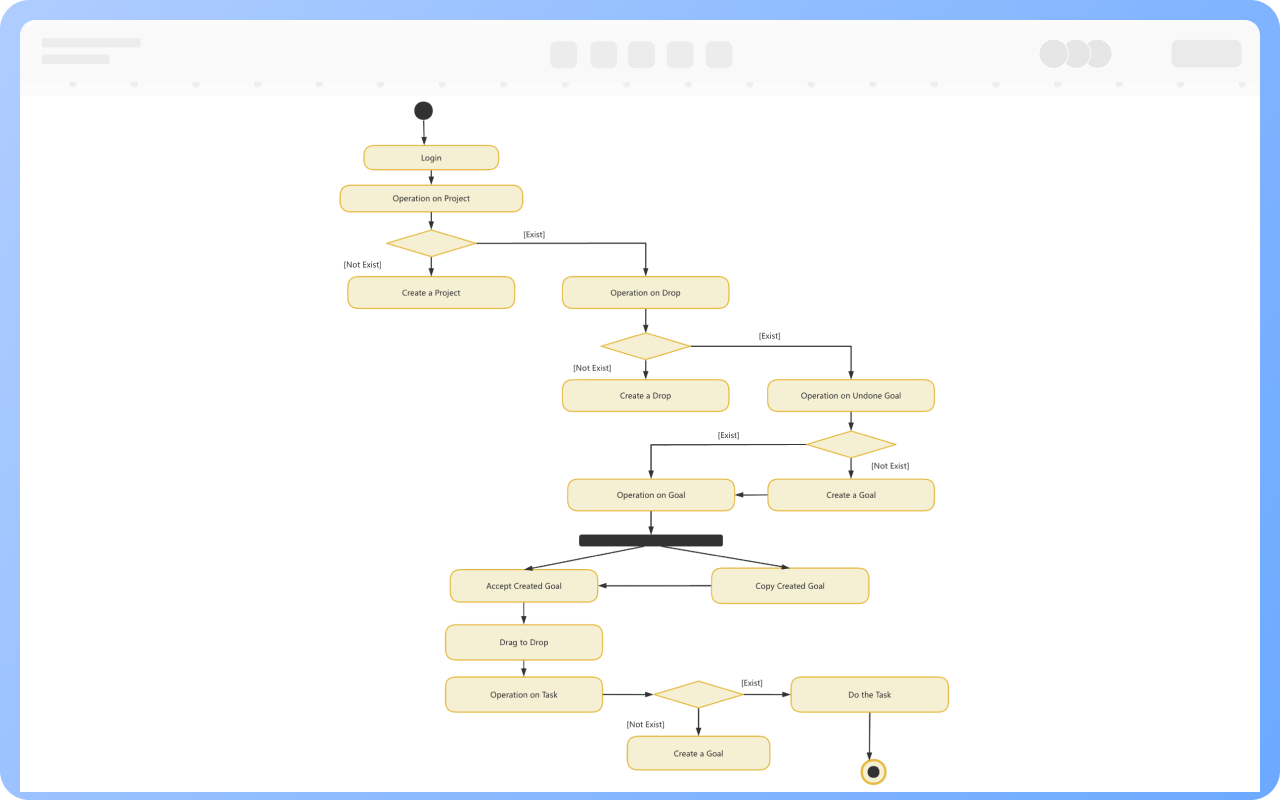
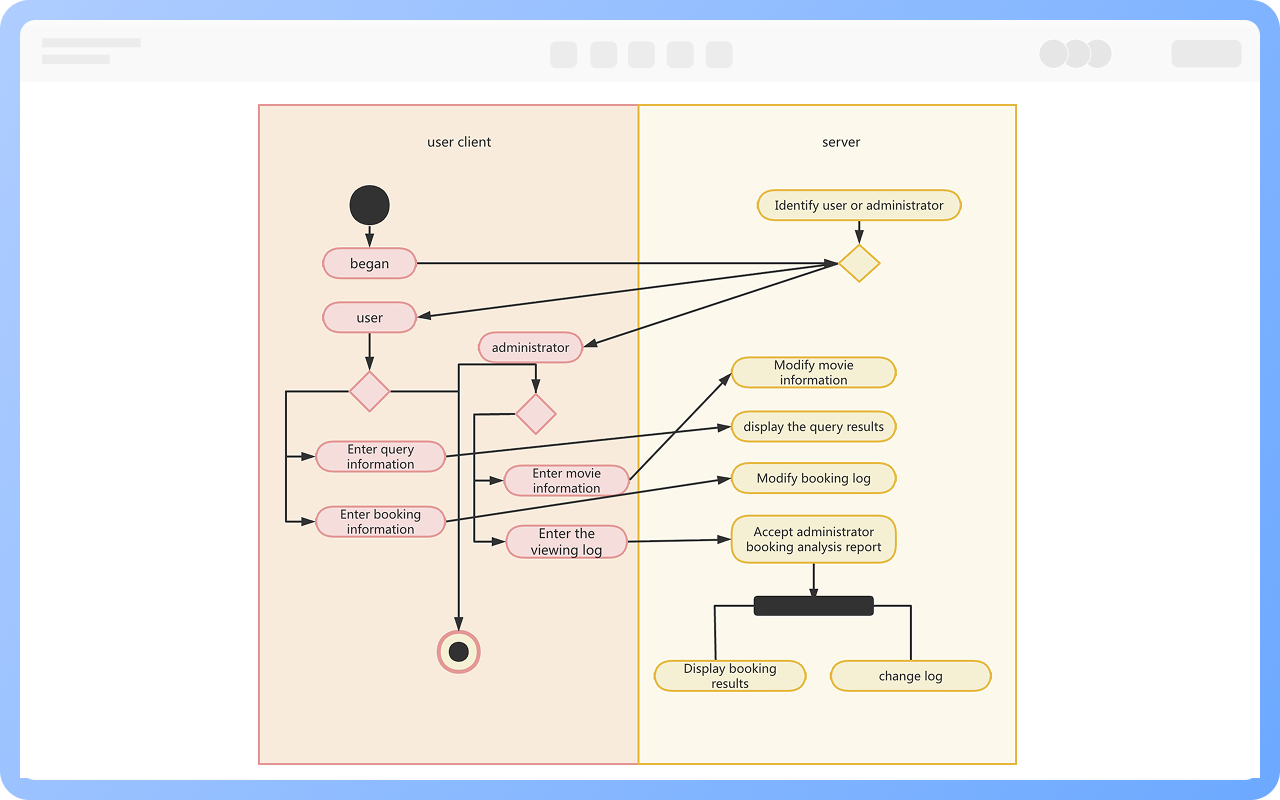
Starting Point: An activity diagram begins with a starting point, represented by a solid circle.
Activity: Represents a step or task in the system or business process, indicated by a rounded rectangle with the activity name inside.
Decision: Represented by a diamond shape, also known as branching and merging. A decision has one incoming path and two or more outgoing paths.
Synchronization: Represented by a solid narrow rectangle, also known as fork and join, used to describe parallel processes. A fork indicates the start of parallel activities, while a join indicates the end of parallel activities.
Swimlane: Swimlanes group activities or actions by the executing entity, with each group separated by swimlanes. This clearly describes the transfer of activities or actions and clarifies who completes them.
Object Flow: Represented by a rectangular box for an object, with dashed arrows indicating the dependency between activities and objects.