A class diagram primarily consists of classes, interfaces, and various relationships, mainly including generalization, dependency, association, and realization relationships.

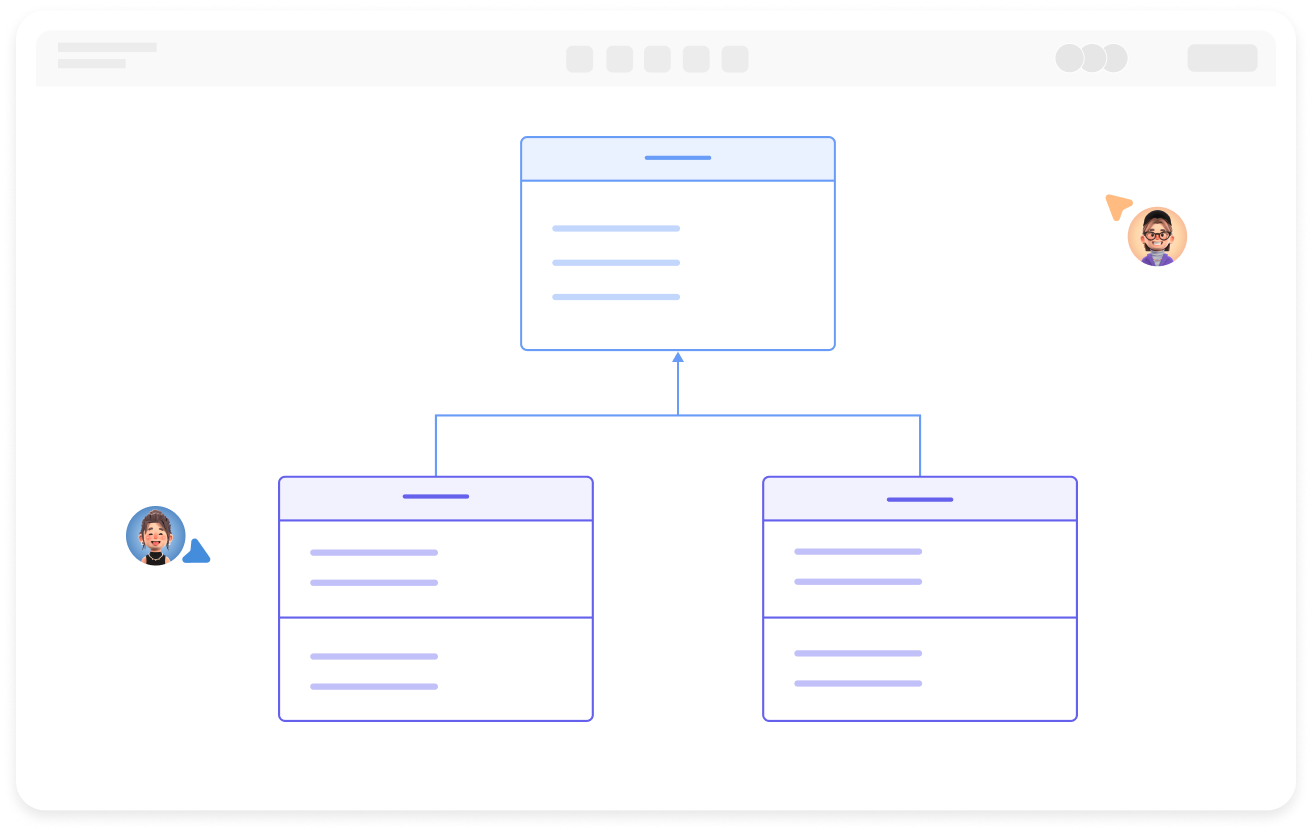
Class diagrams are a type of static view in UML modeling used to describe classes, interfaces, collaborations, and their relationships, showing the static structure of these concepts in a system. They are widely used in the system analysis and design phases of software engineering.
Class diagrams are a major component of object-oriented modeling and define the foundation for other UML diagrams. Based on class diagrams, state diagrams, collaboration diagrams, component diagrams, and configuration diagrams can be drawn.
Class diagrams are mainly used to display the static model of classes, interfaces, and their static structure and relationships within a system. Once a software designer designs a class diagram, programmers can implement the contents of the class diagram using code.
Supports real-time multi-user co-creation with shareable links for instant information transfer
Automatically generates graphics from text input and applies style enhancements
Prebuilt themes with full customization for personalized designs
Supports icons, images, labels, LaTeX formulas, code blocks, links, attachments and more

Export: PNG, VISIO, PDF, SVG | Import: VISIO, Mermaid
Real-time cloud storage, multi-device sync, version history, and secure data protection
A class diagram primarily consists of classes, interfaces, and various relationships, mainly including generalization, dependency, association, and realization relationships.
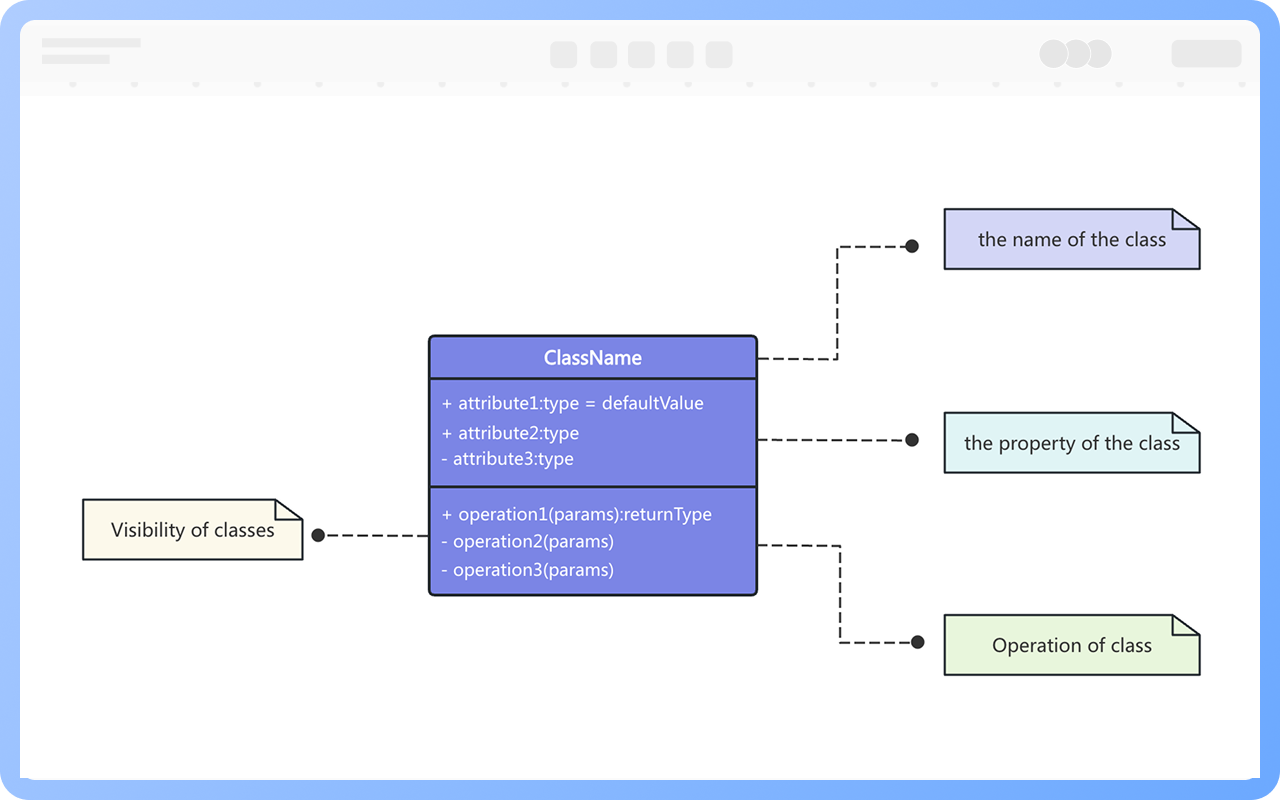
A class typically consists of a name, attributes, and operations. In addition, class composition also includes the class's responsibilities, constraints, and annotations.
In a class diagram, a class is represented by a rectangular box divided into three layers: the first layer is the class name, the second layer is the class attributes, and the third layer is the class operations.
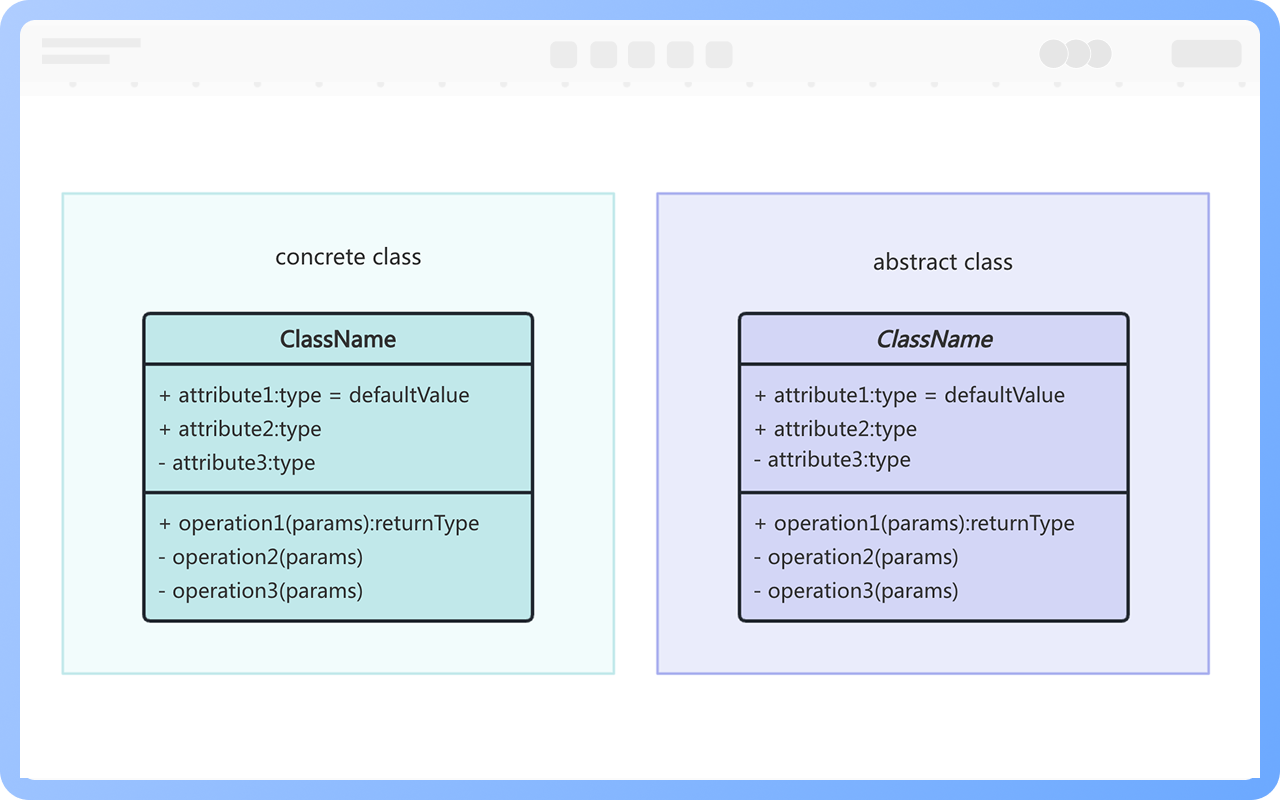
The name of a class should be a noun and should accurately and clearly reflect a concept in the problem domain. According to UML conventions, each word in the class name should start with a capital letter, using regular font to represent concrete classes and italic font to represent abstract classes.
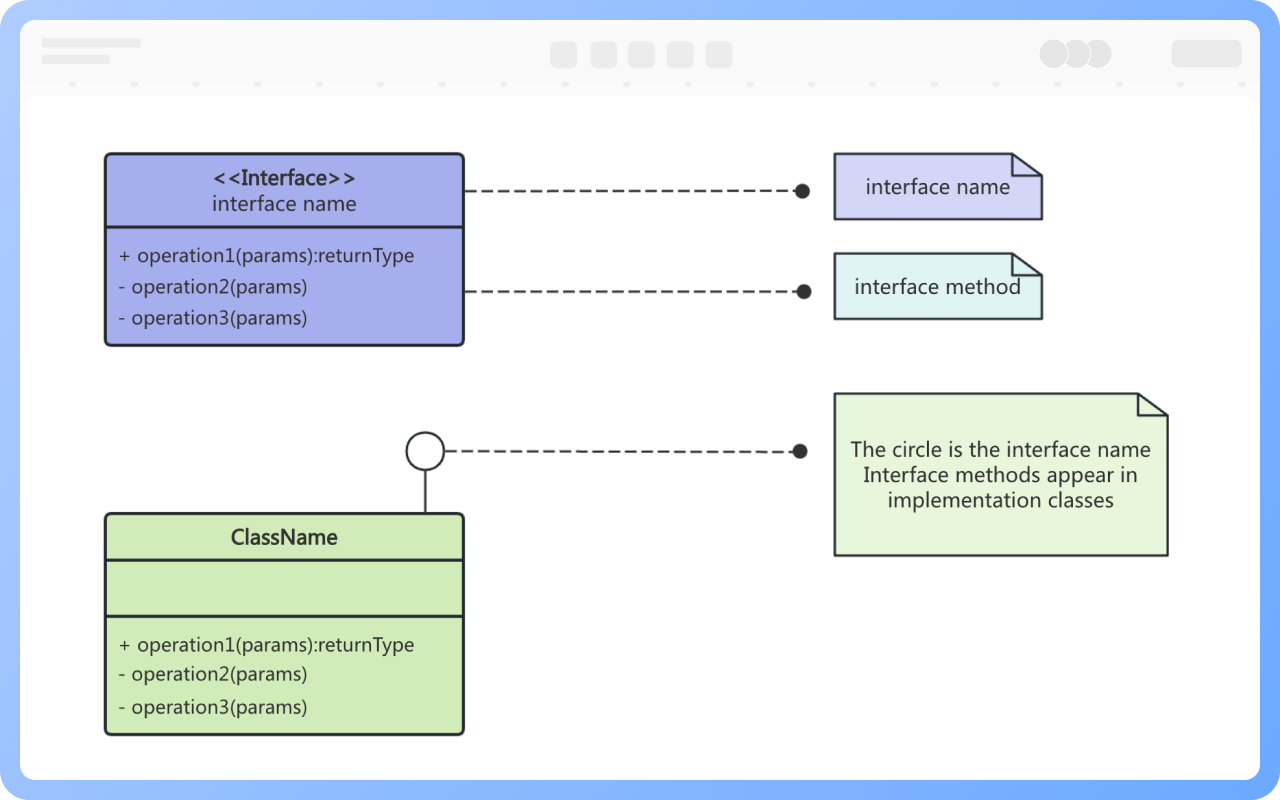
Interfaces are also represented by rectangular boxes in class diagrams, but unlike classes, the top layer of an interface in a class diagram is marked with the stereotype <<interface>>, followed by the interface name, and the second layer contains the interface methods.
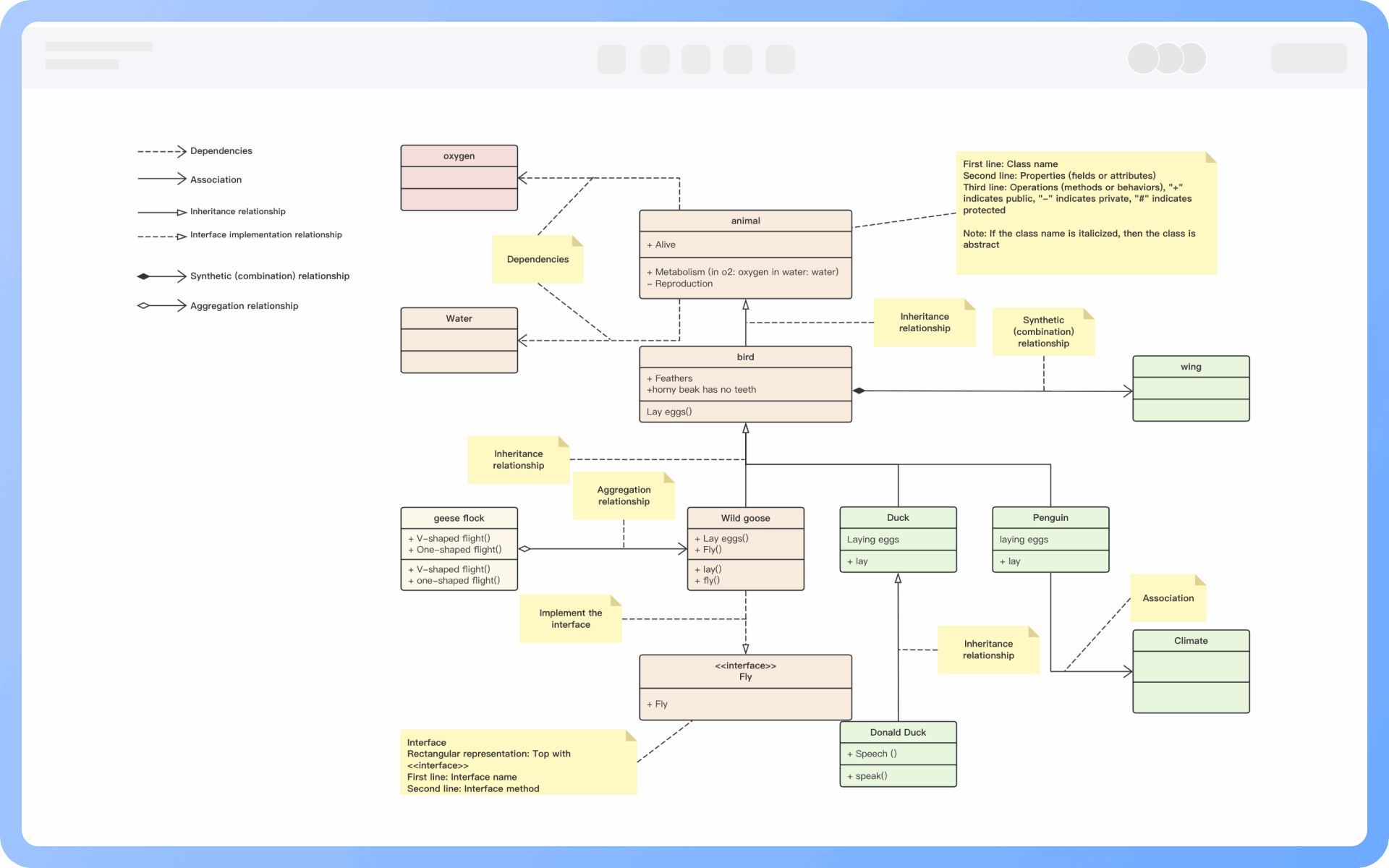
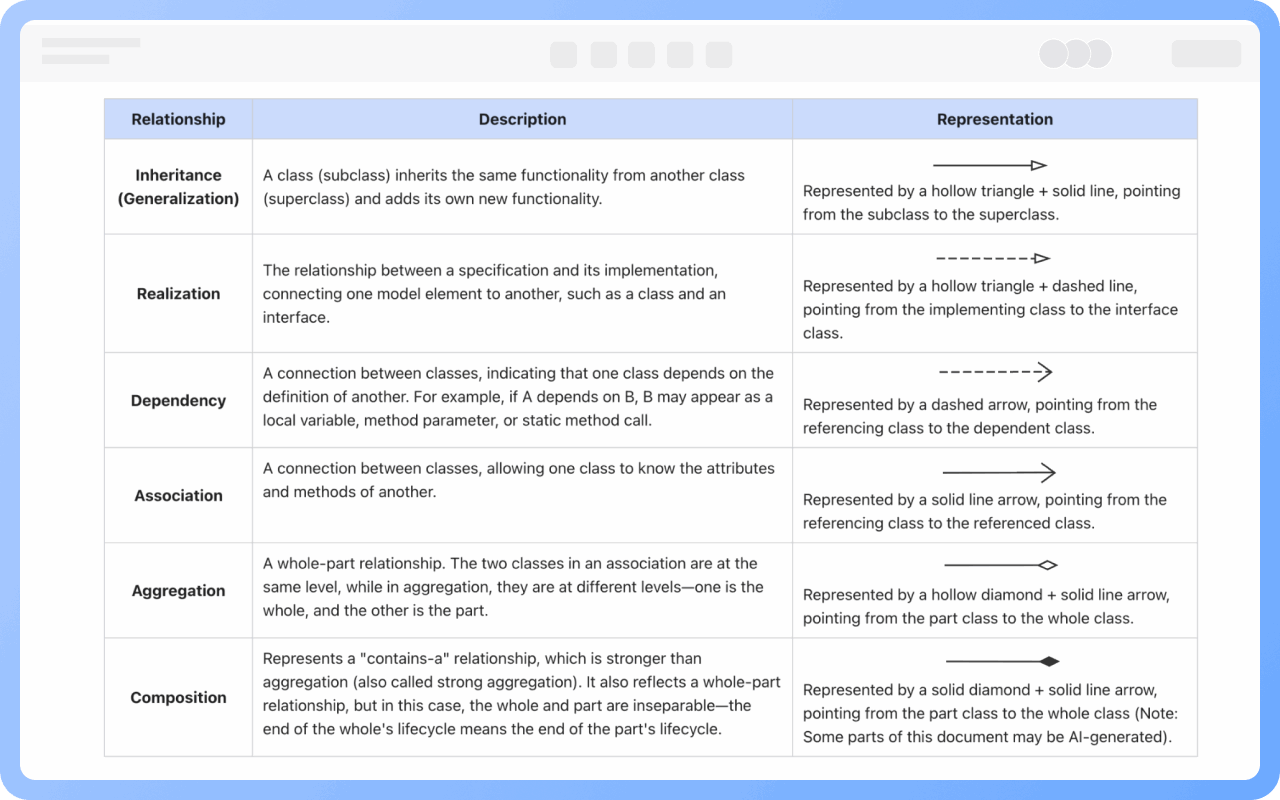
There are certain relationships between classes and classes, classes and interfaces, and interfaces and interfaces. UML class diagrams usually have lines indicating these relationships. There are six types of relationships: realization, generalization, association, dependency, aggregation, and composition.
1. The model established by a class diagram describes a general situation, whereas the model established by an object diagram describes a specific situation.
2. A class diagram can completely describe the object structure of a system, whereas an object diagram cannot.
3. A class in a class diagram may correspond to multiple objects in an object diagram.
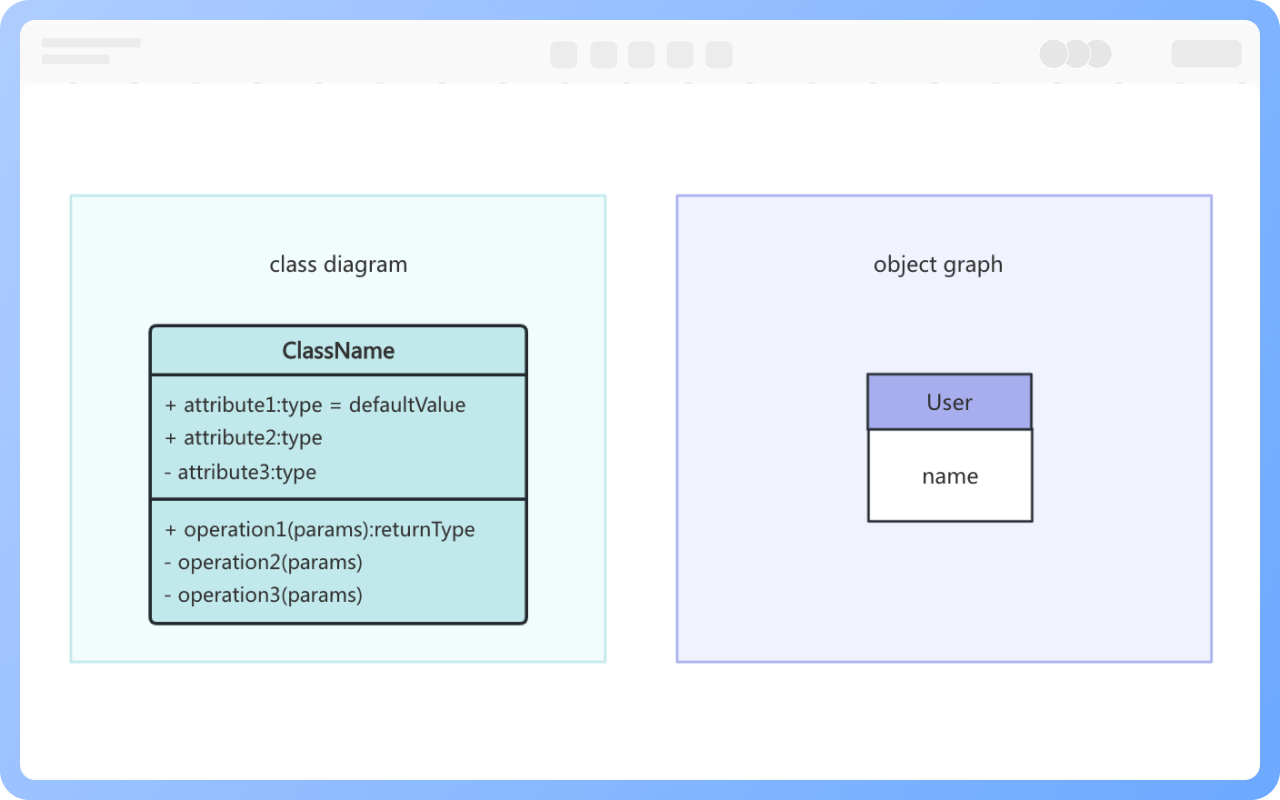
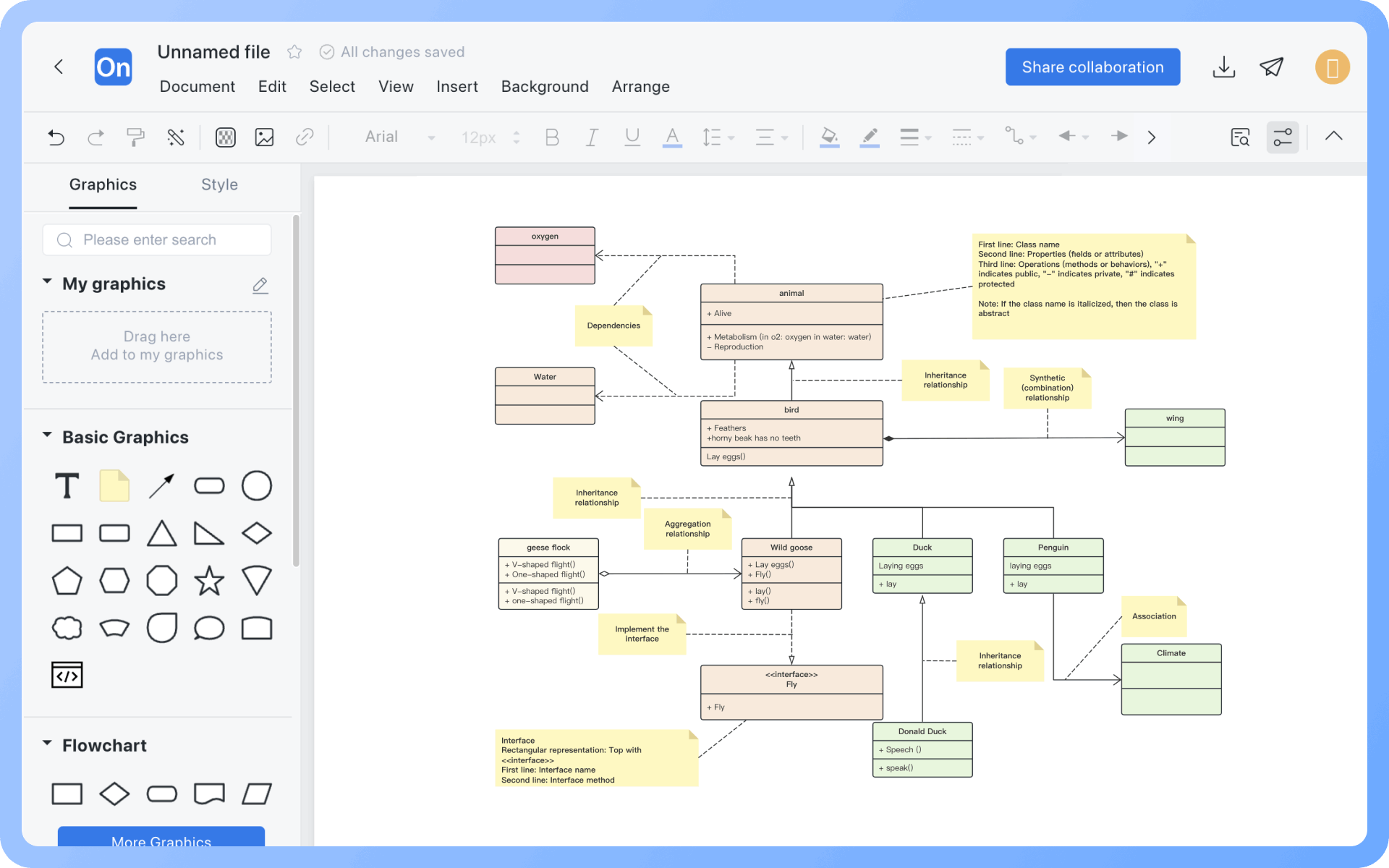
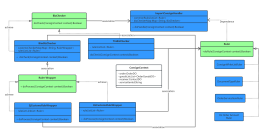
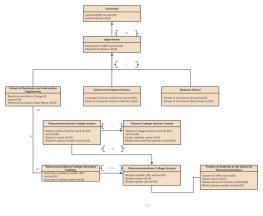
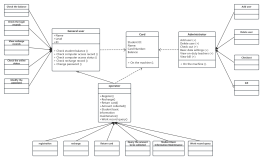
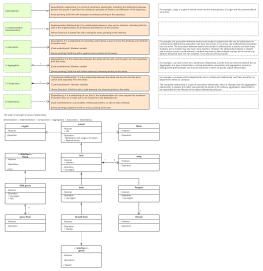
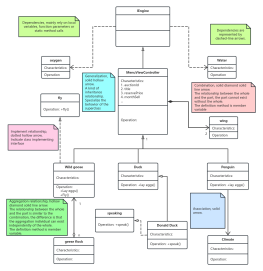
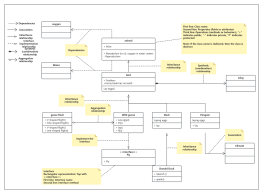
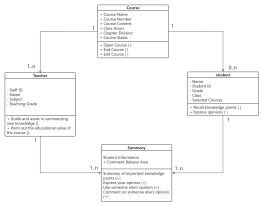
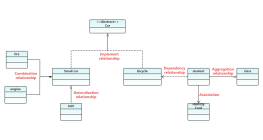
Classes are usually composed of names, attributes, and operations, represented by a rectangular box divided into three layers: the first layer is the class name, the second layer is the class attributes, and the third layer is the class operations.
However, in practical use, there are three representations: "class name", "class name" + "class attributes", and "class name" + "class operations".
The name of a class should be a noun, with the first letter of each word capitalized. Italic font is used for abstract classes, while regular font is used for instantiable classes.
The syntax for defining class attributes is: [visibility] attribute name [:data type] [=initial value] [{property string}]
The content in [] indicates optional elements.
Class constraints specify one or more rules that the class must satisfy. In UML, constraints are represented by text information enclosed in curly braces.
Implementation relationship: Represented by an open triangle + dashed line, pointing from the implementing class to the interface class.
Generalization relationship: Represented by an open triangle + solid line, pointing from the subclass to the parent class.
Association relationship: Represented by a solid line arrow, pointing from the referencing class to the referenced class.
Aggregation relationship: Represented by an open diamond + solid line, pointing from the part class to the whole class.
Composition relationship: Represented by a solid diamond + solid line, pointing from the part class to the whole class.
Dependency relationship: Represented by a dashed line arrow, pointing from the referencing class to the dependent class.
Class diagrams are not completely independent. They should abstract entities, control, and boundary classes from use case diagrams and maintain semantic coordination with use case diagrams, activity diagrams, sequence diagrams, etc.
Classes should maintain a single responsibility. Large classes can be split, responsibilities reasonably distributed among multiple classes, avoiding high coupling, clarifying boundaries, and adhering to object-oriented design principles.