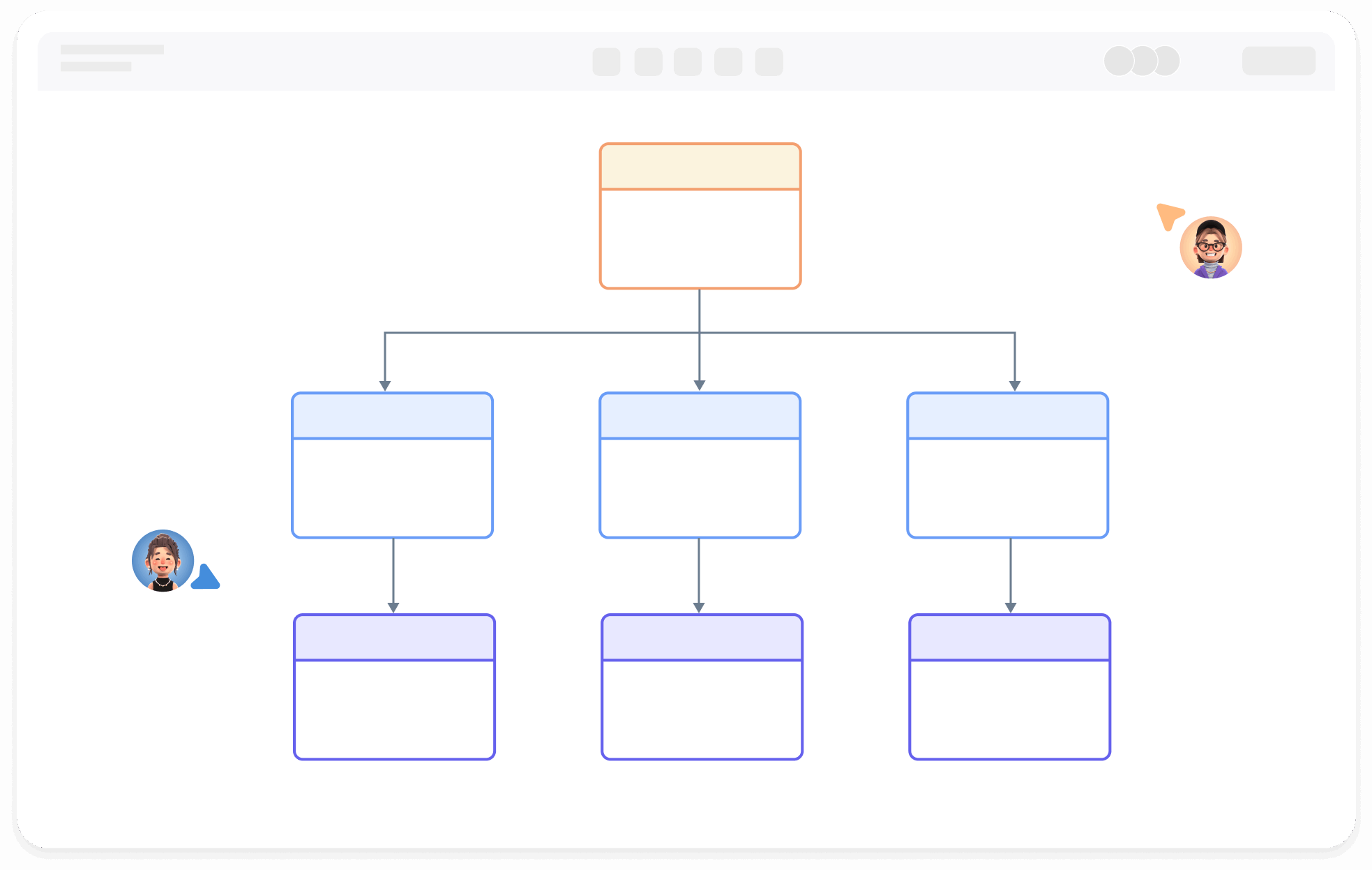
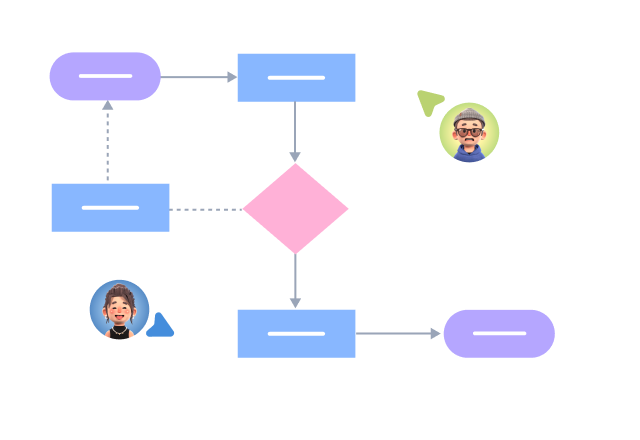
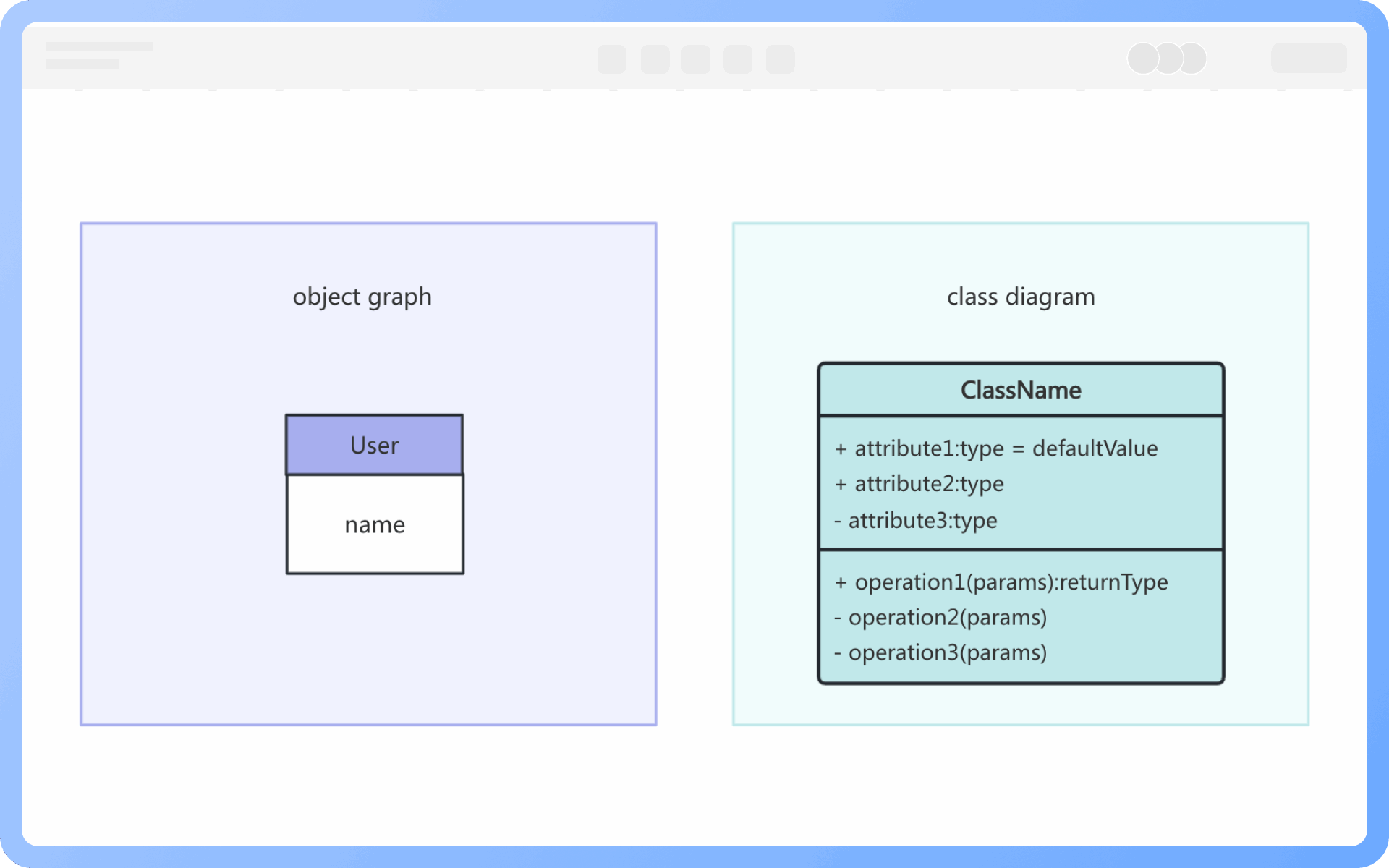
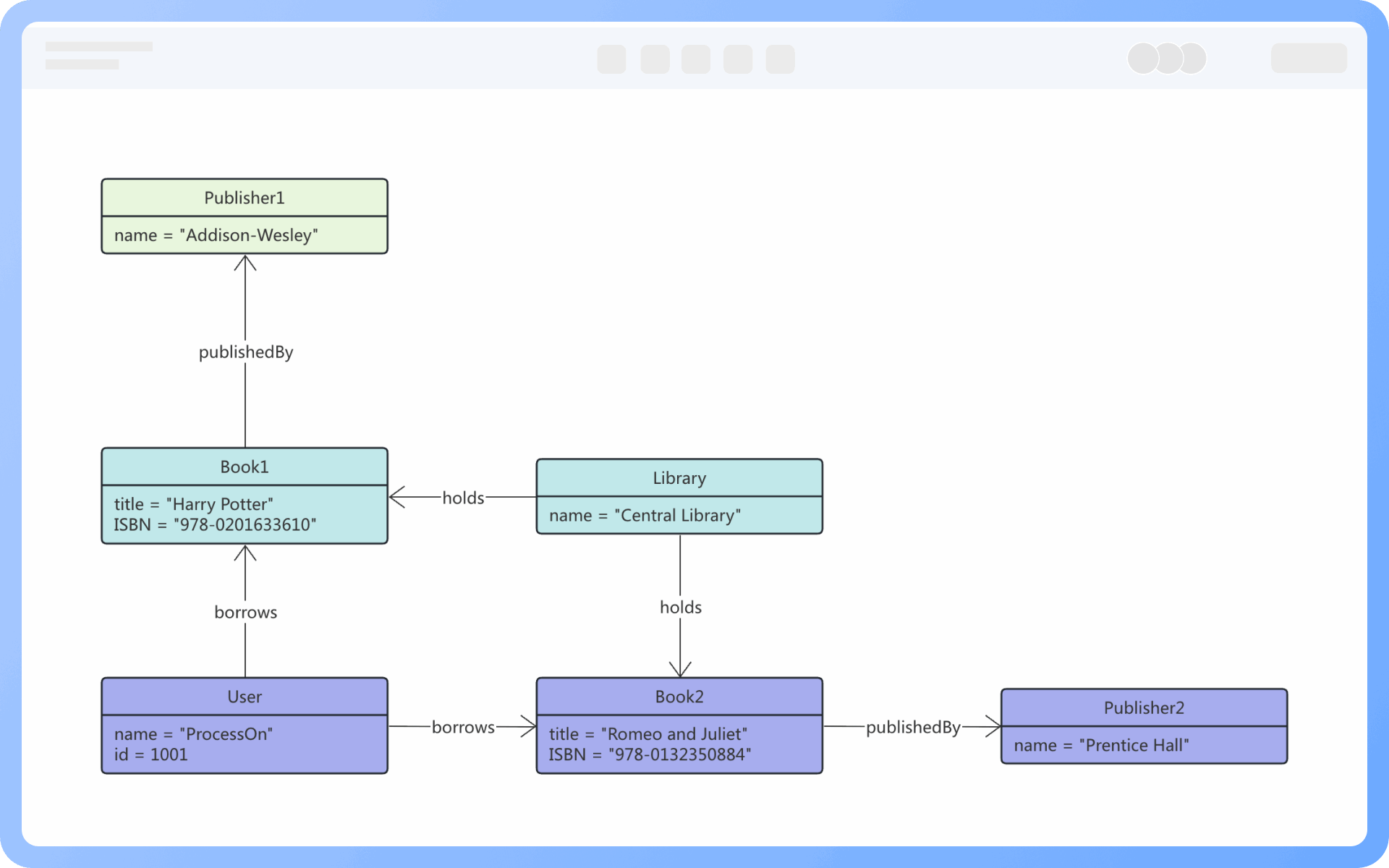
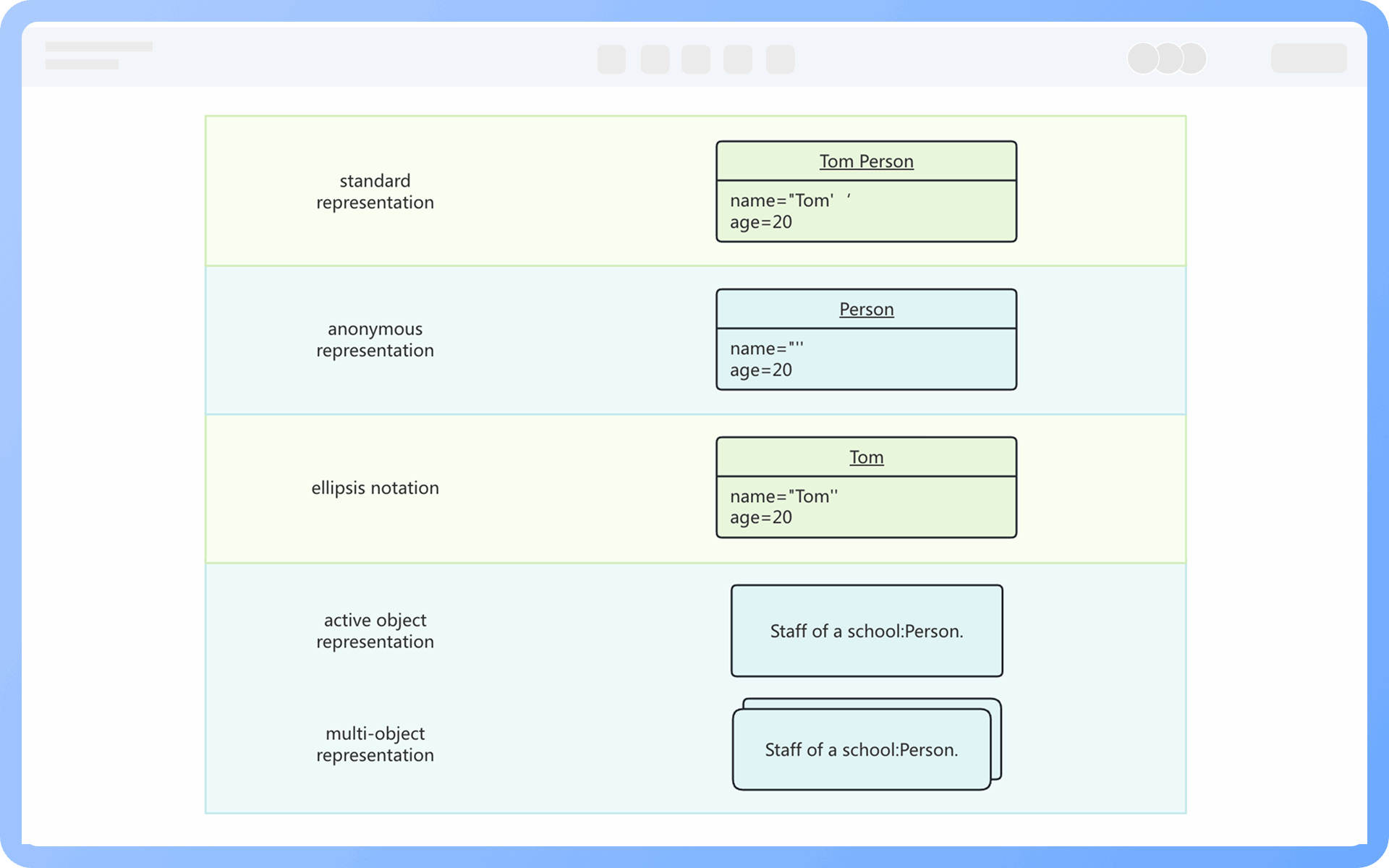
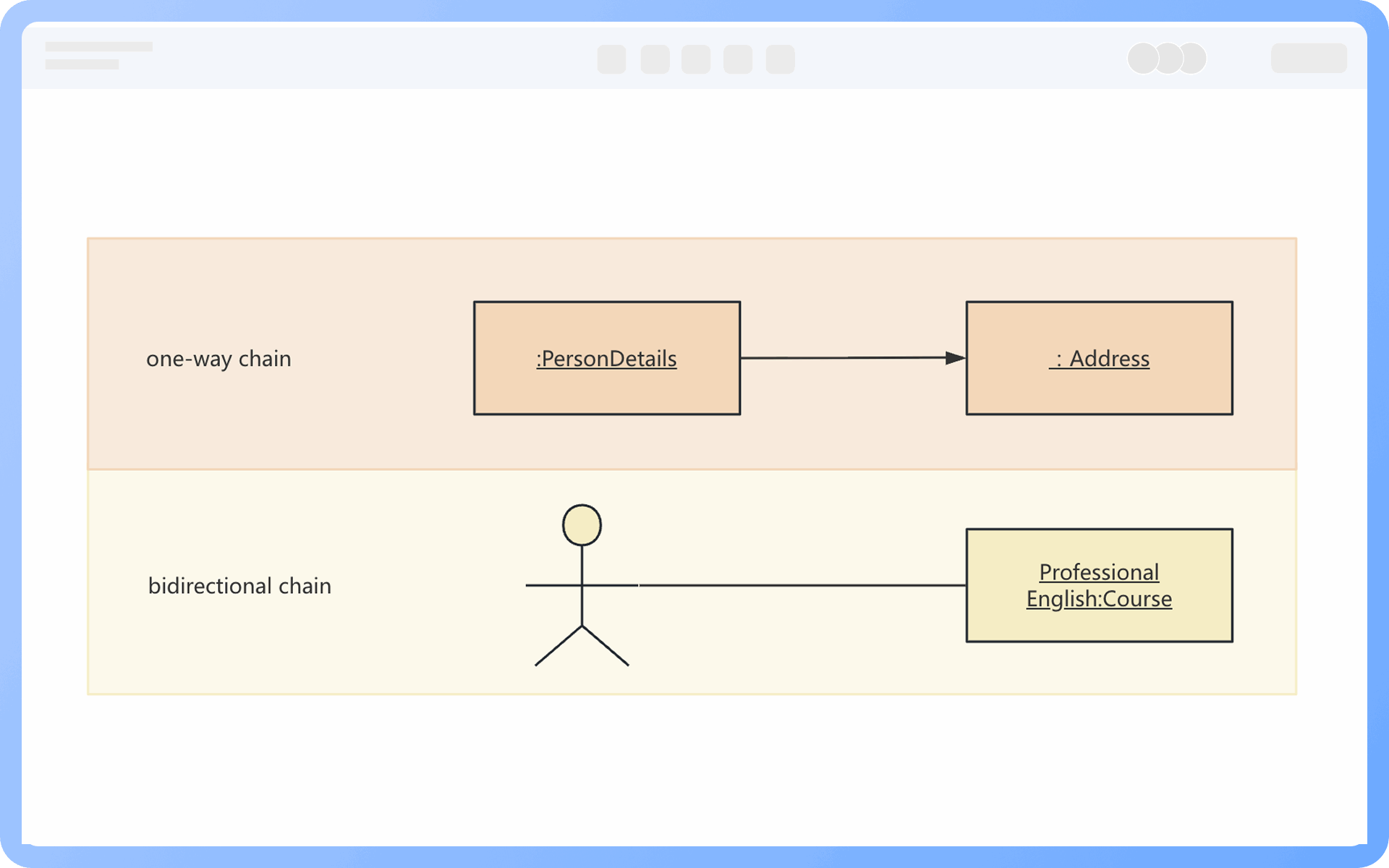
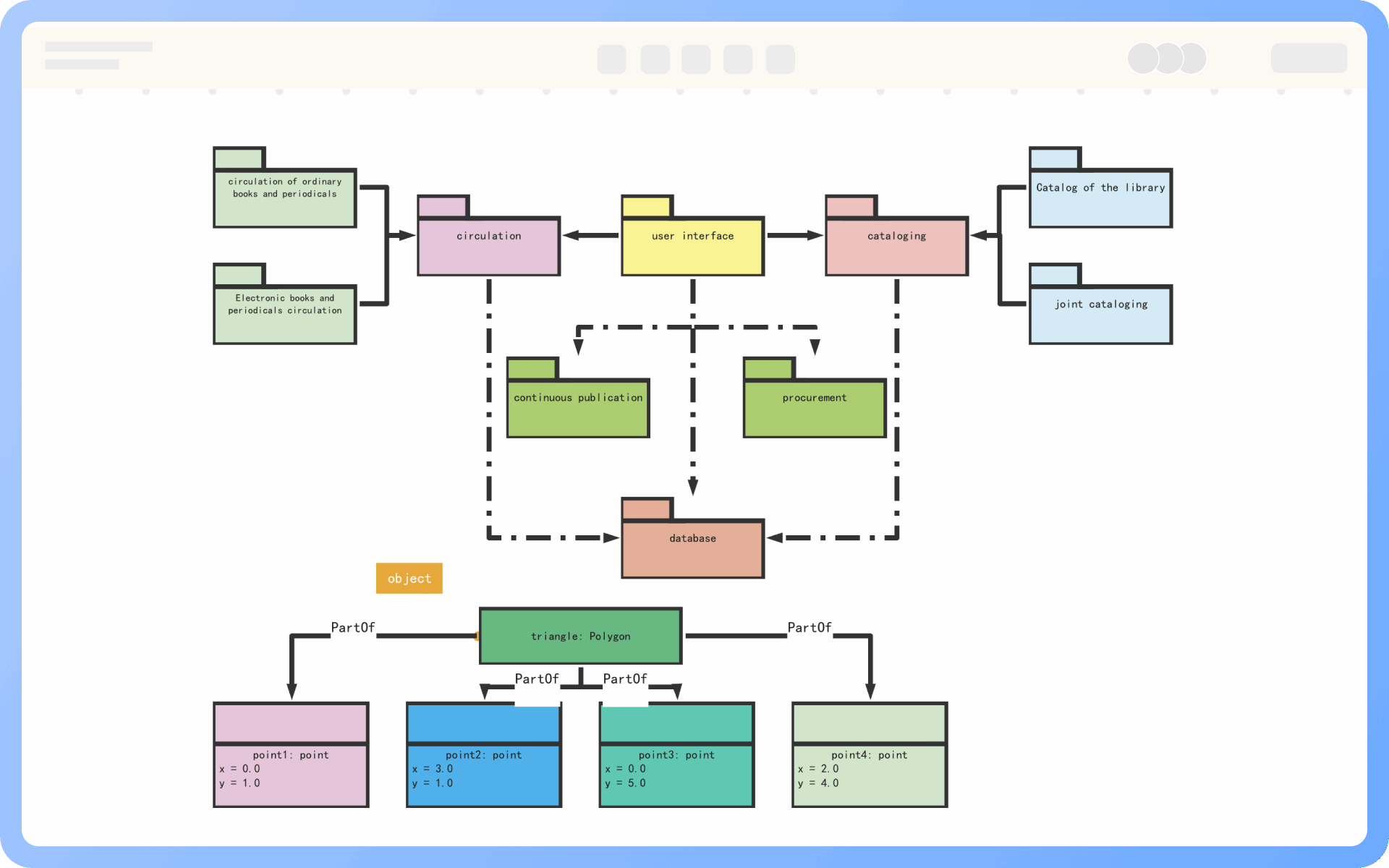
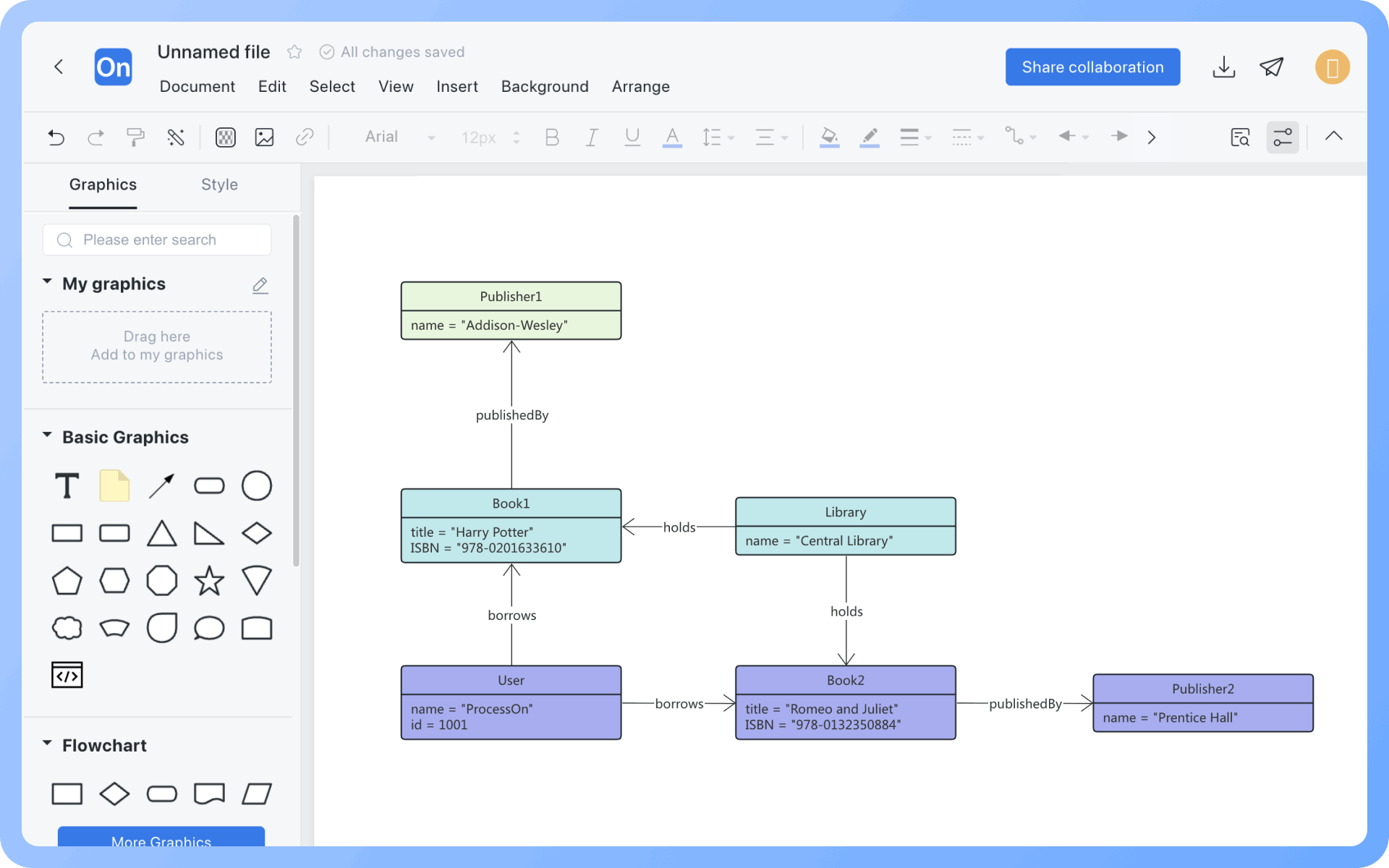
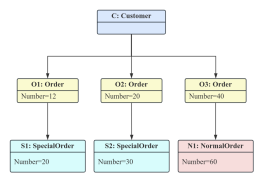
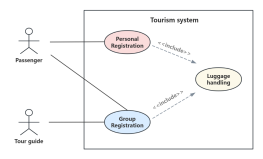
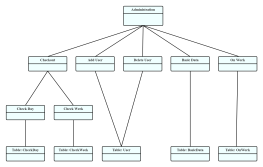
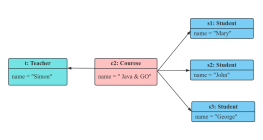
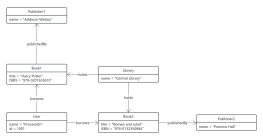
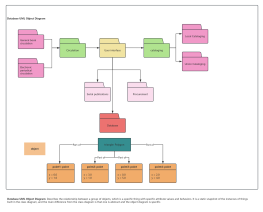
1. The model established by a class diagram describes general situations, while the model established by an object diagram describes specific situations.
2. A class diagram can completely describe the object structure of a system, whereas an object diagram cannot.
3. A class in a class diagram may correspond to multiple objects in an object diagram.