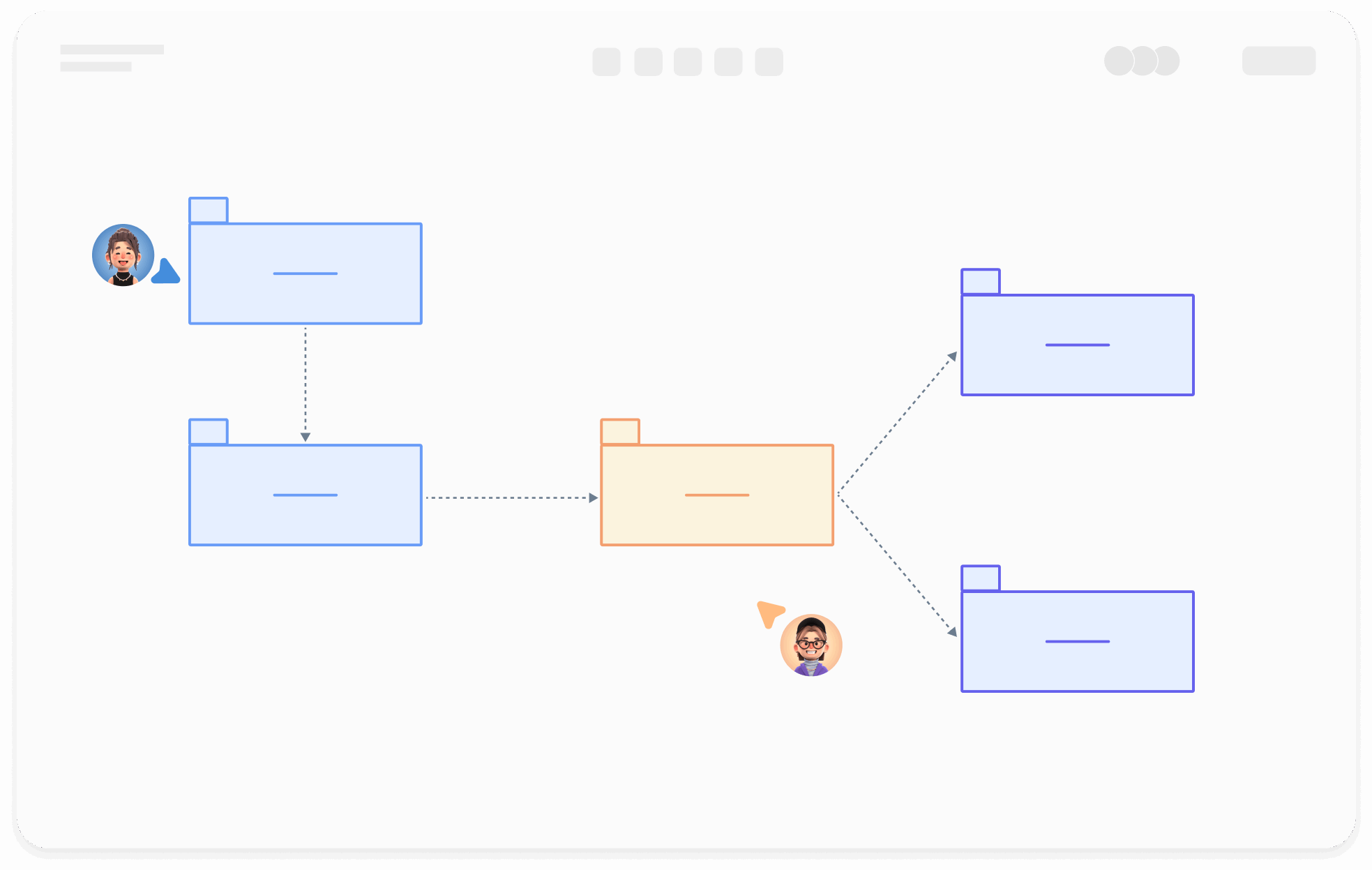
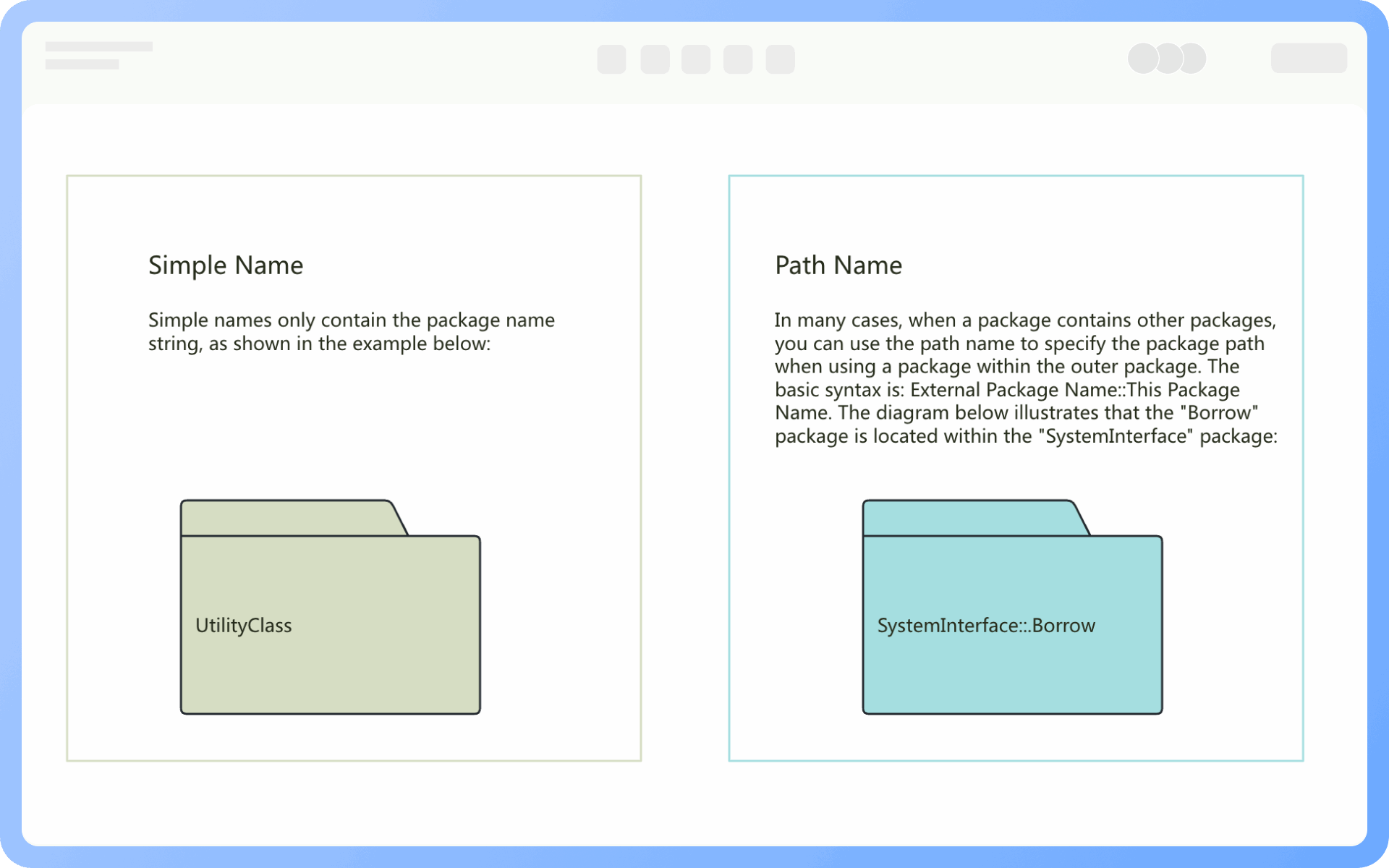
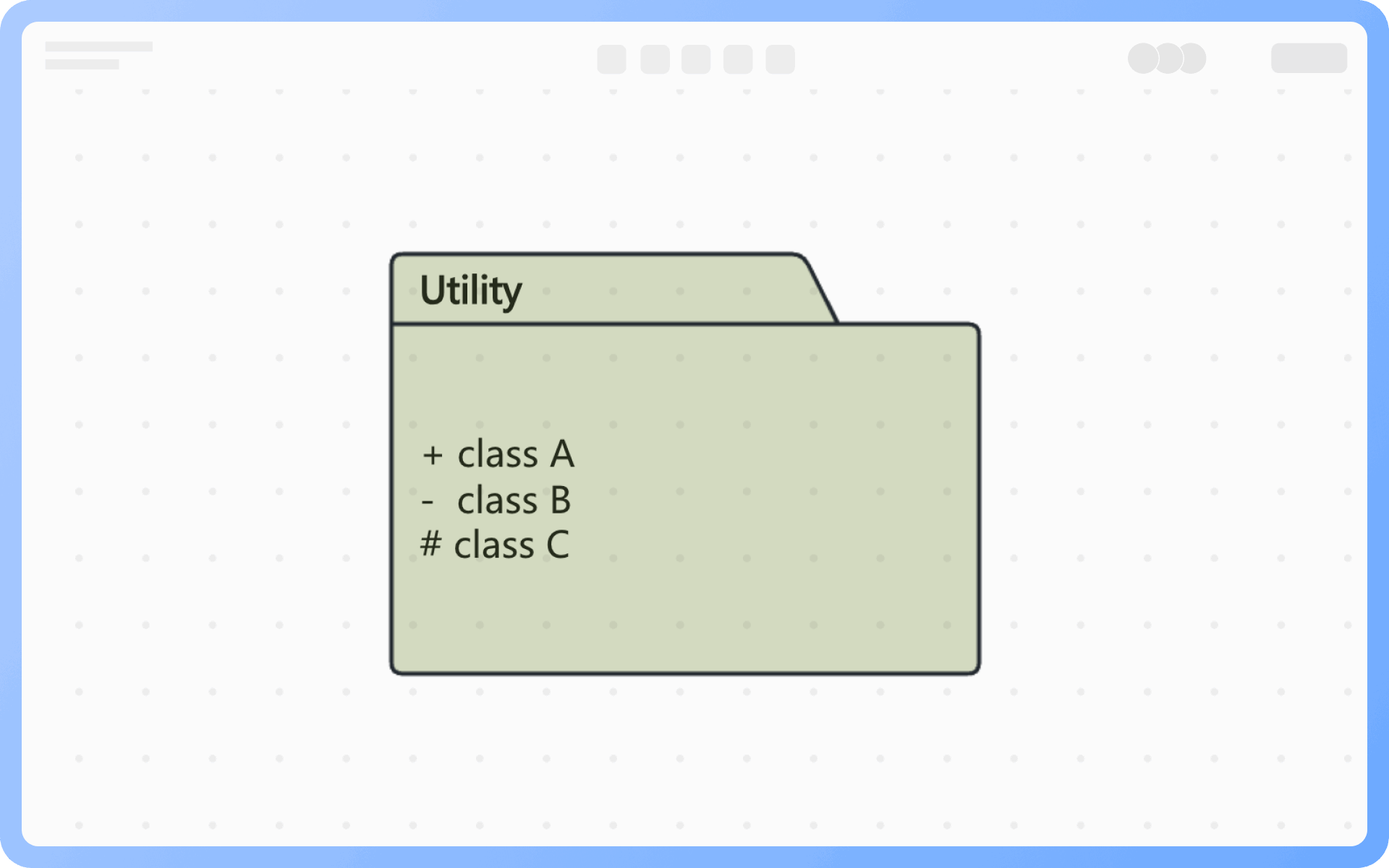
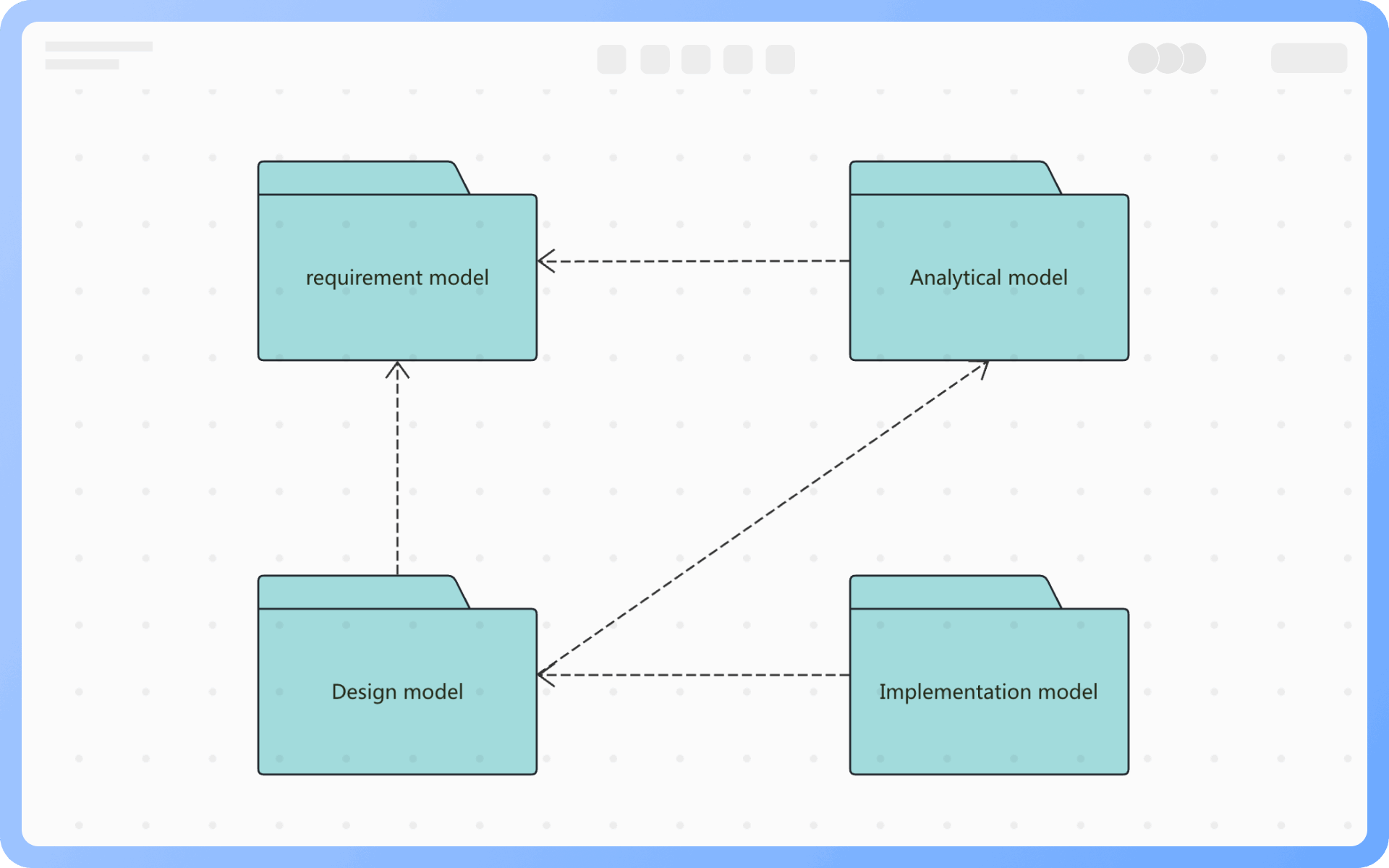
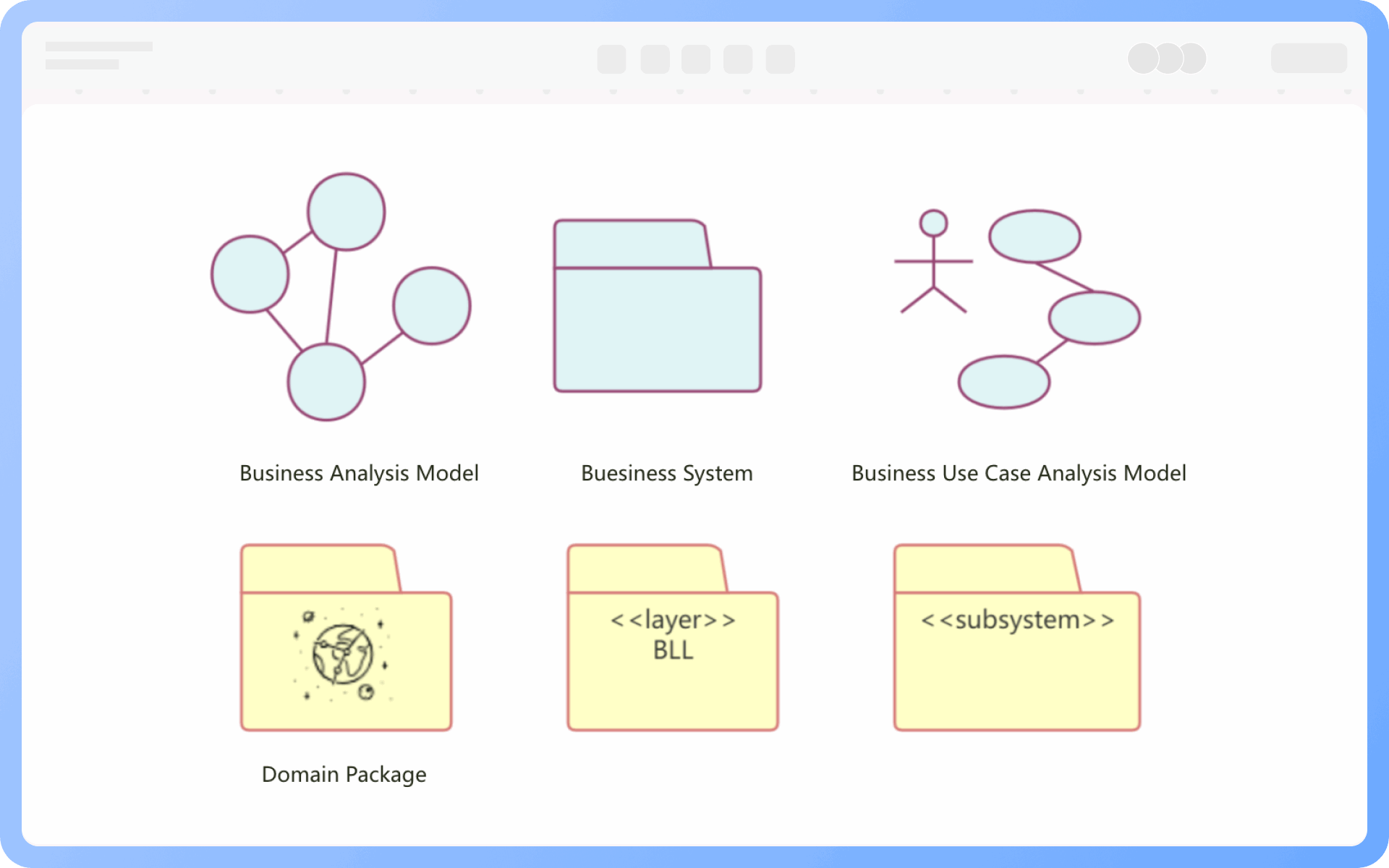
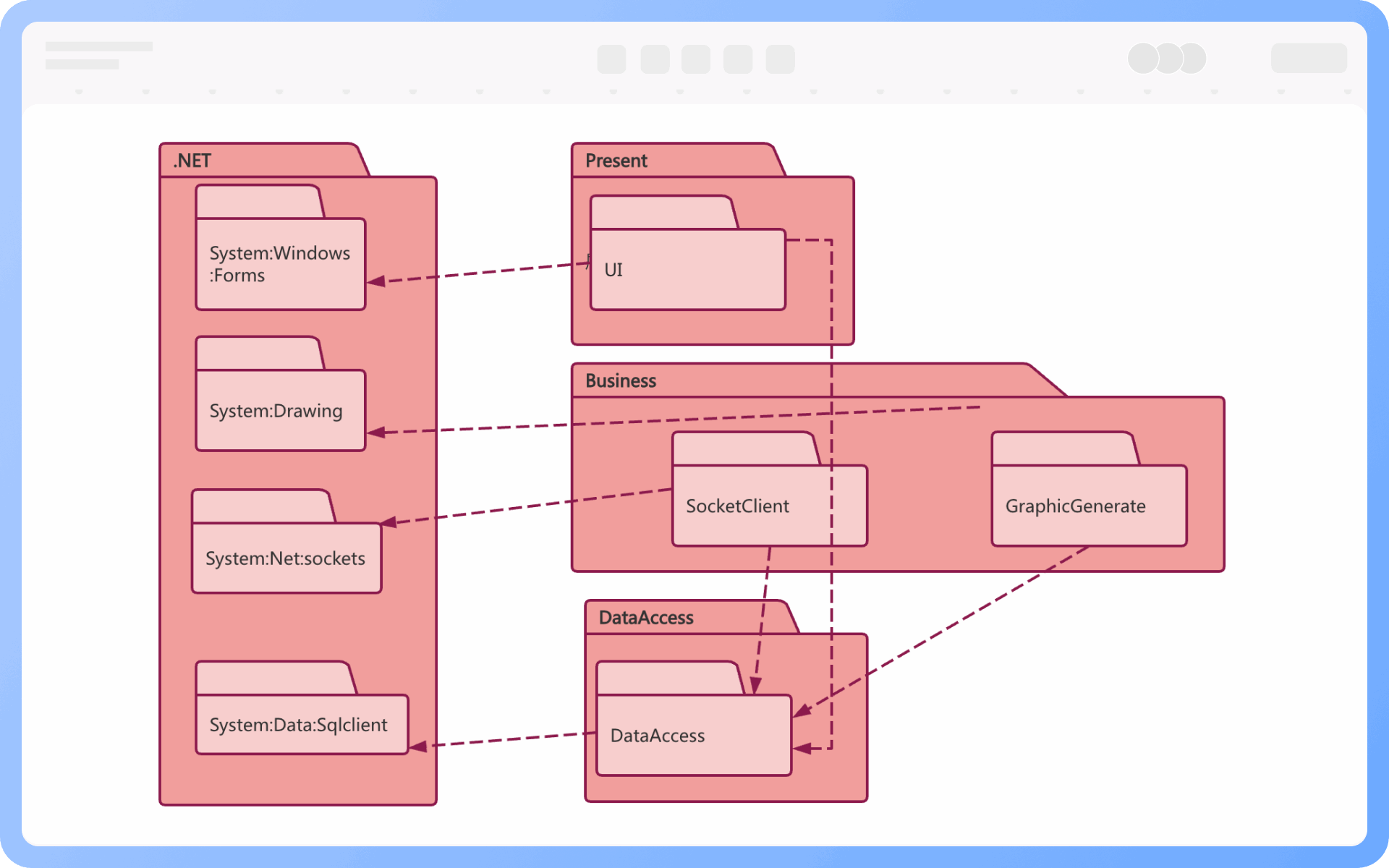
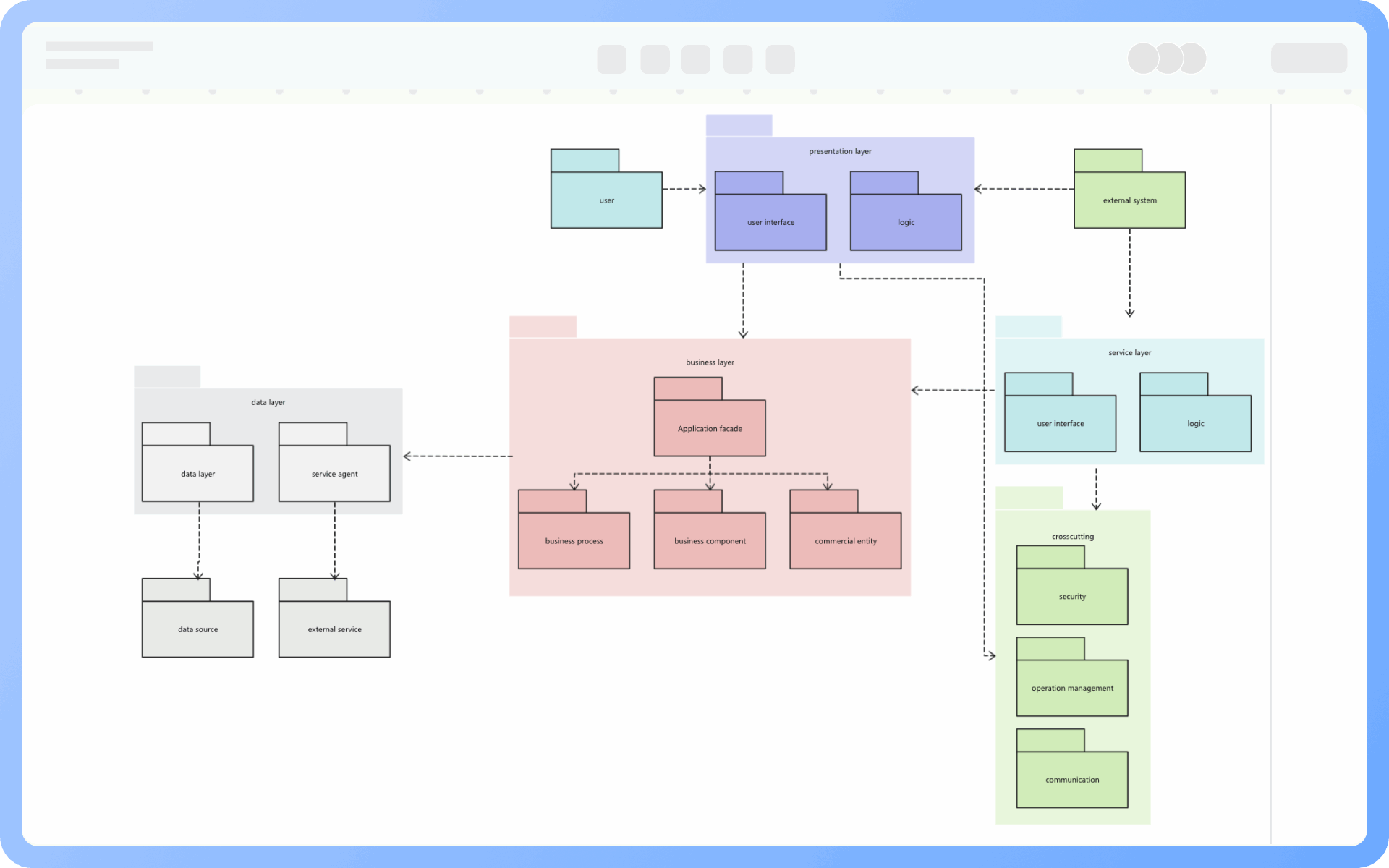
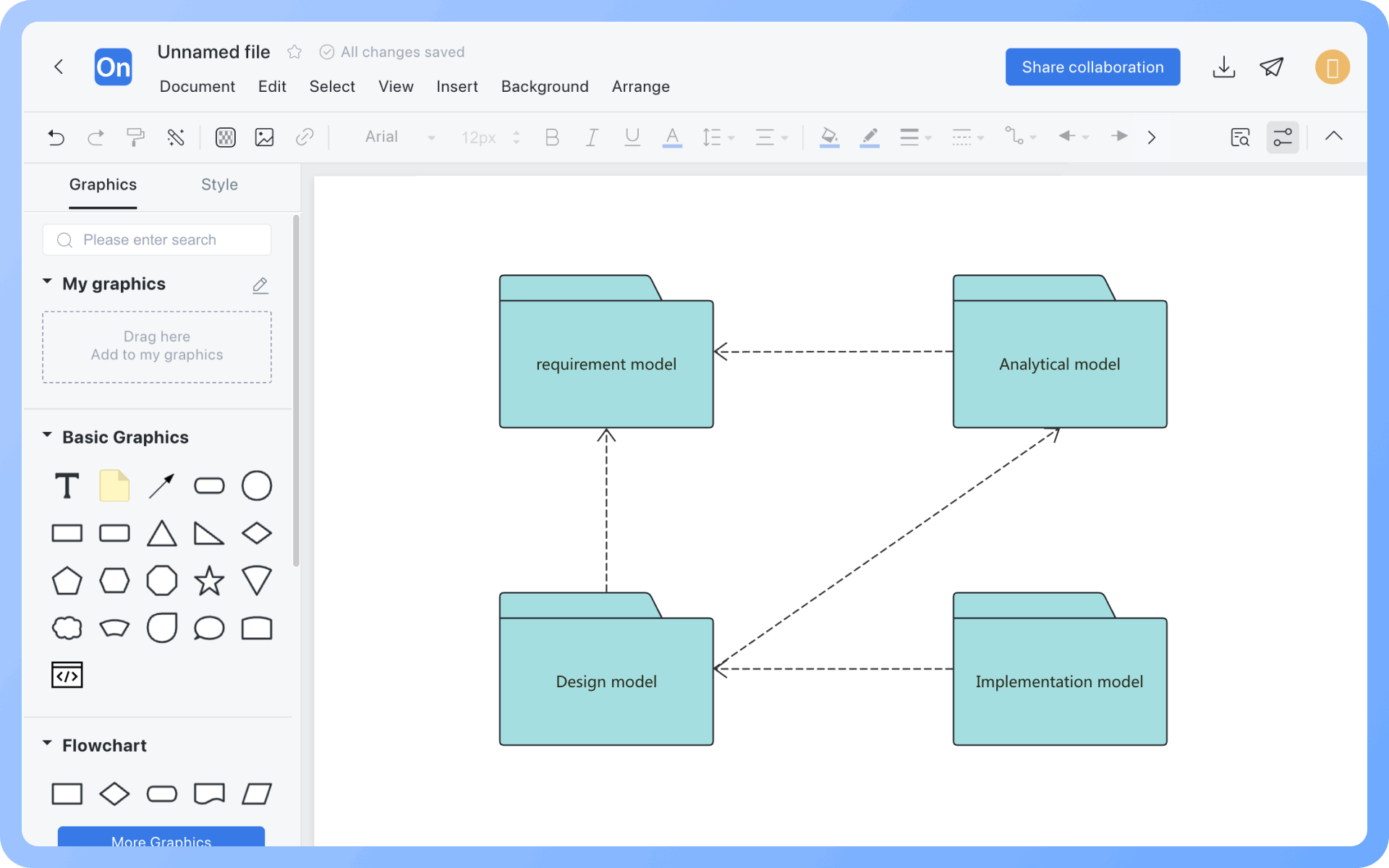
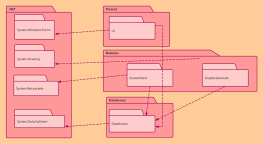
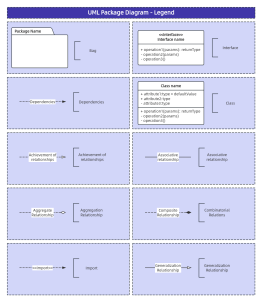
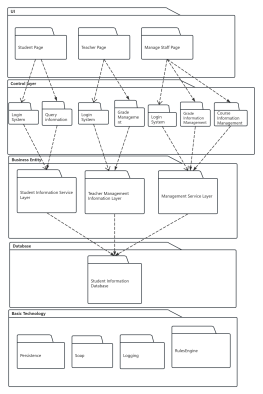
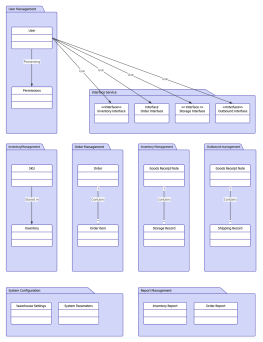
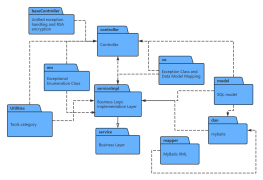
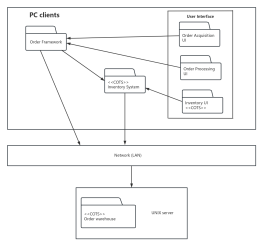
At the same level, each package should have a unique name different from other packages. Package names come in two forms:
Simple name: A simple name uses only the package's name string;
Path name: In many cases, a package contains other packages, so the outer package name is used to indicate the package path. The basic syntax is: [Outer Package Name::This Package Name].