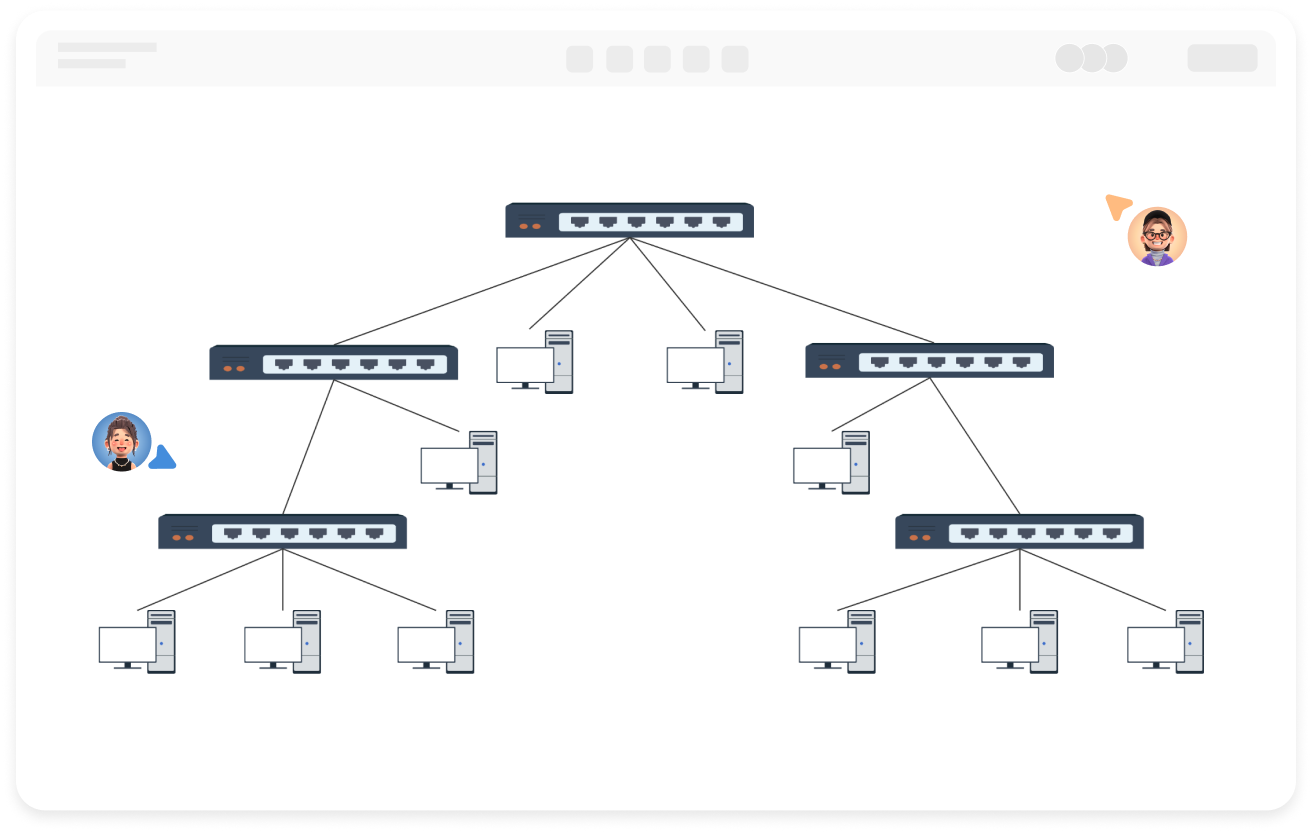
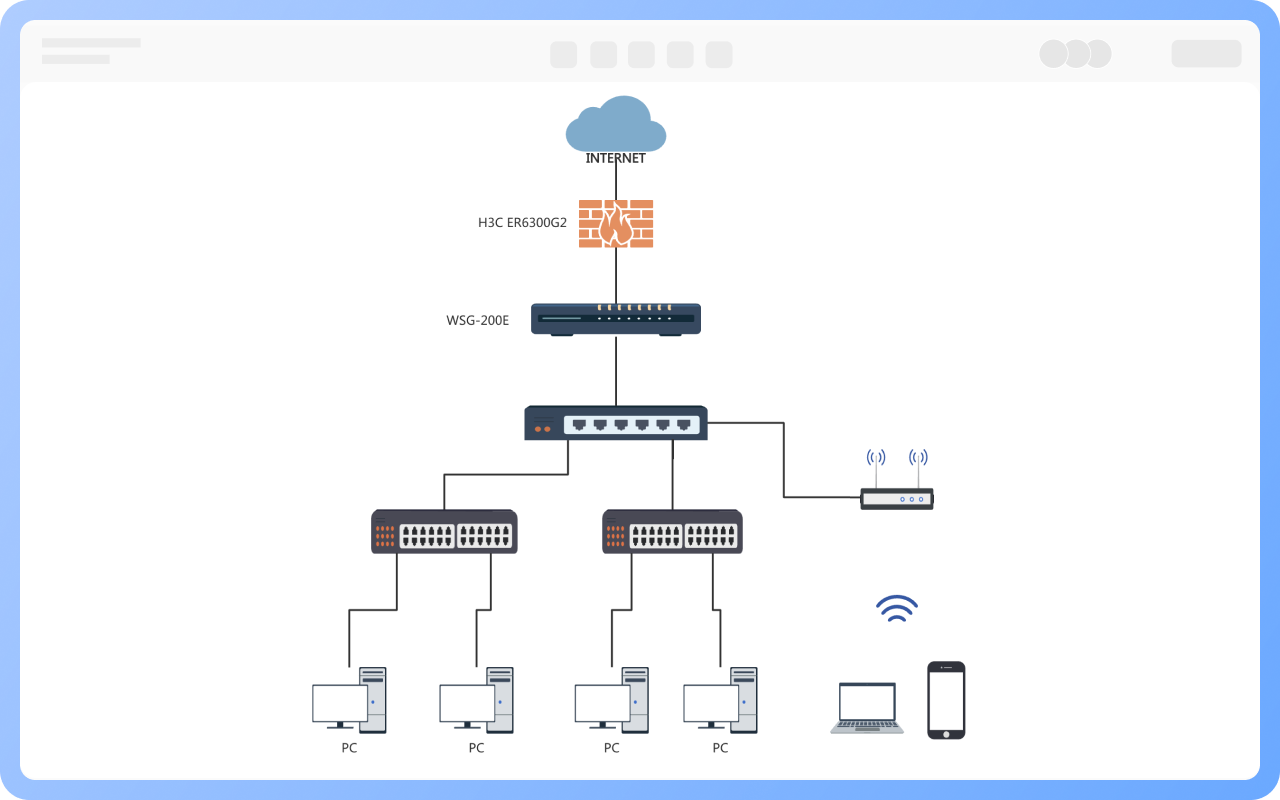
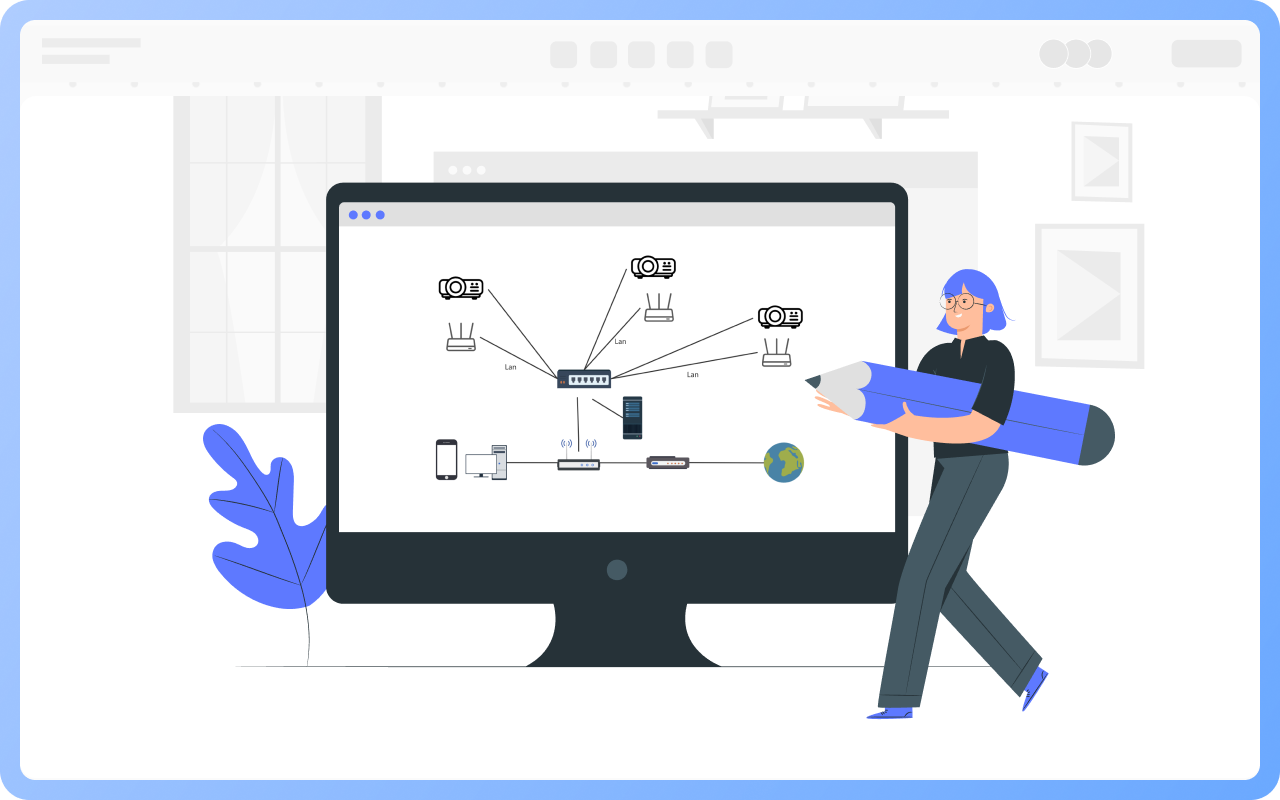
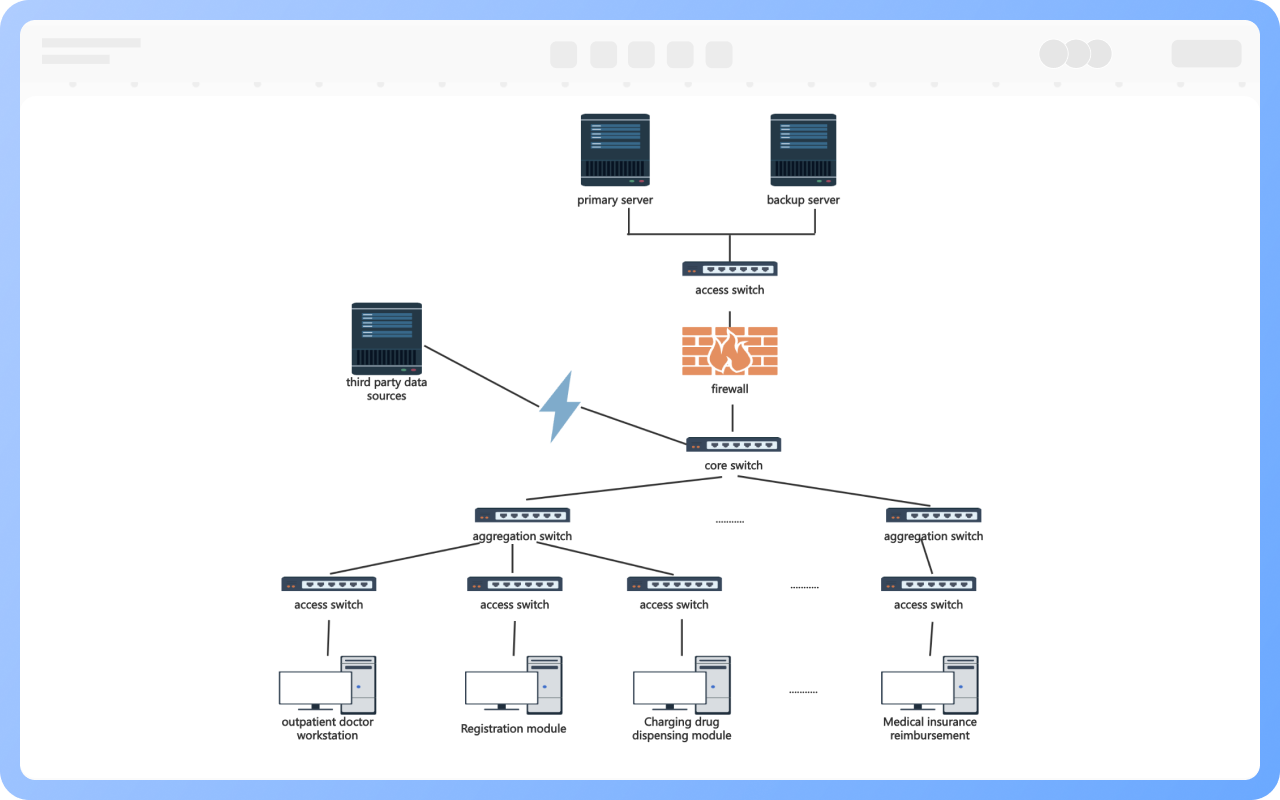
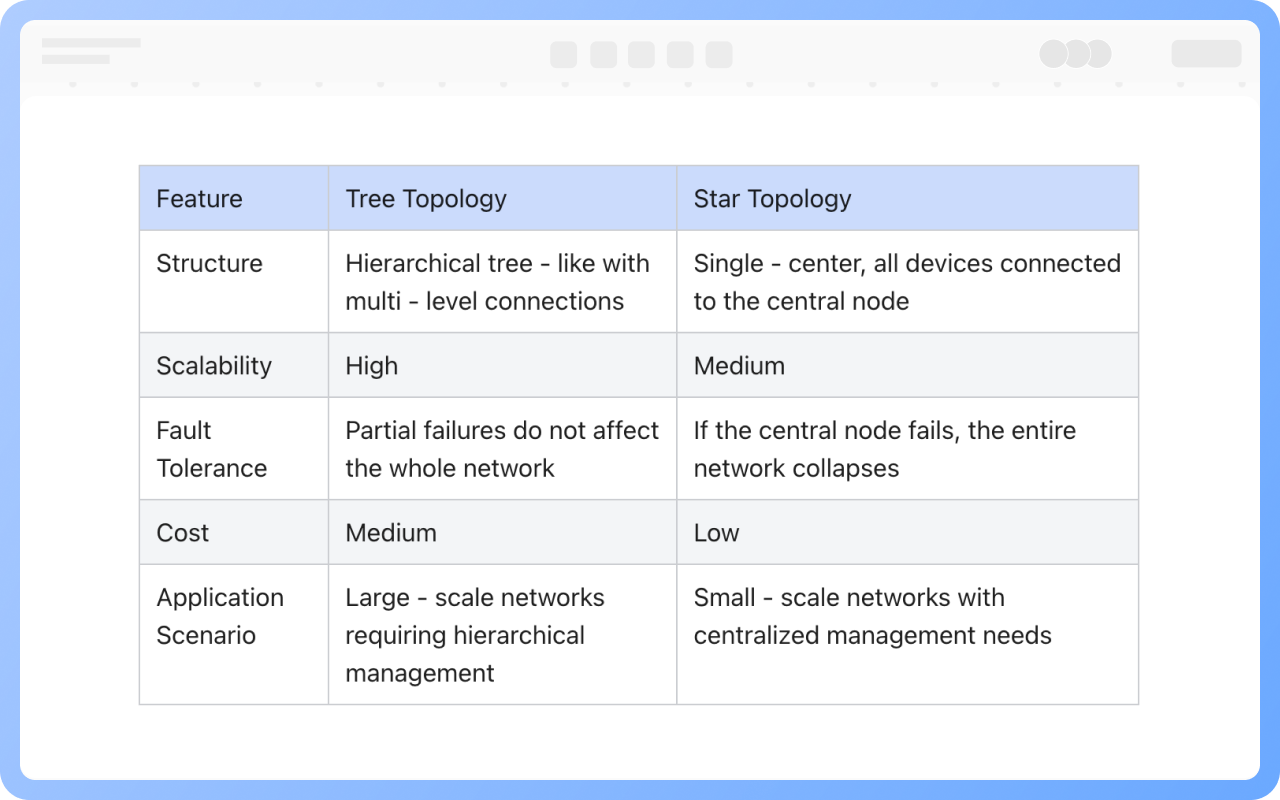
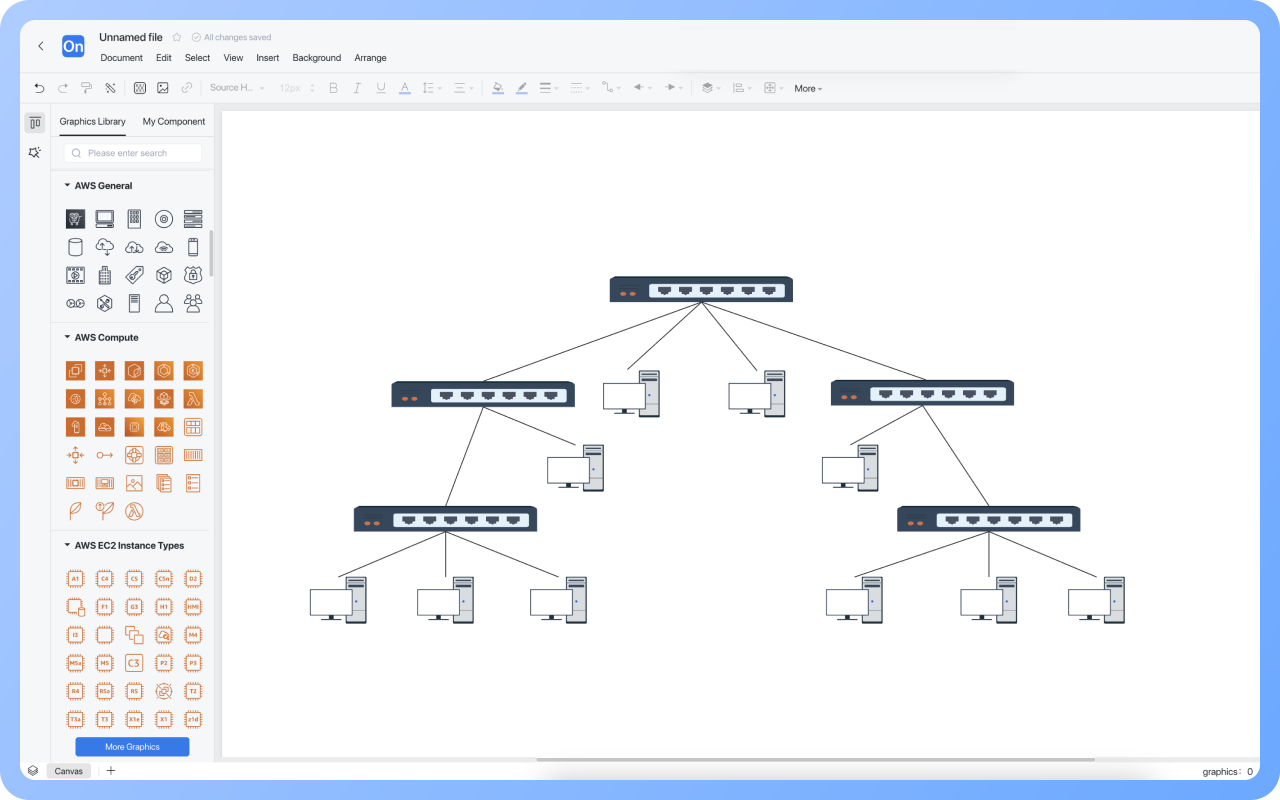
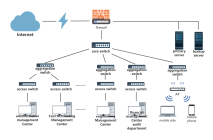
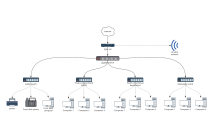
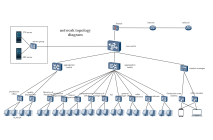
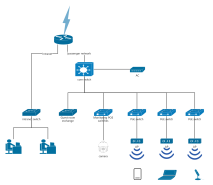
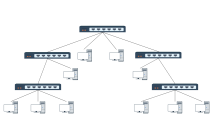
Clear hierarchy: The network extends downward from the root node (such as the main switch) into multiple branches, each of which can be further subdivided, forming a hierarchical structure similar to a family tree.
Unidirectional connection: Data usually flows in the "parent node → child node" direction, but some protocols support bidirectional communication.
No loops: There is only a unique path between any two nodes, preventing broadcast storms caused by data loops.