Have you ever wondered how the network can accurately transmit massive amounts of information to our devices when we use computers to connect to the Internet and browse web pages and download files easily? In an enterprise network, how can hundreds of computers and devices achieve efficient and stable communication? In fact, all of this is inseparable from a key network topology structure - star topology.
With its unique connection mode and operation mechanism, it provides a solid guarantee for the normal operation of the network. Next, let us have a deeper understanding of the star topology .
Star topology is a mesh structure with a central node as the core and all peripheral devices connected to it through independent links. Its physical form is like a wheel, with the central node as the "hub" and each "spoke" node connected through star-shaped radiating links. This architecture achieves controllable allocation of network resources through centralized management and has become one of the mainstream solutions for modern local area networks (LANs).
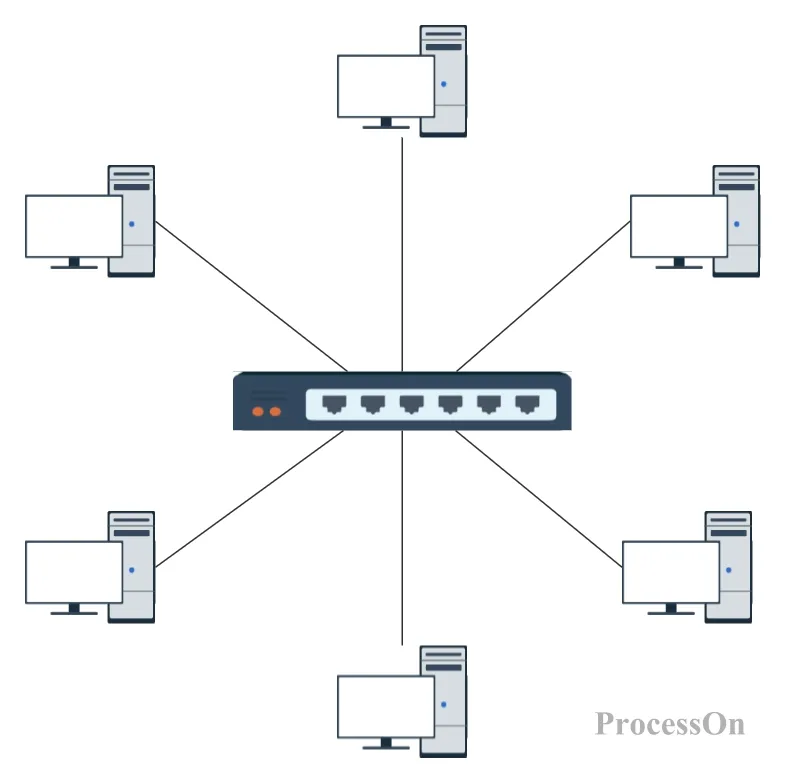
All data flows must pass through a central node (such as a switch or hub) to achieve unified traffic monitoring, access control, and security policy deployment. This design allows network administrators to manage all network devices through a single console.
The failure of a single node or link will not affect the operation of other devices. For example, if the network card of a PC is damaged, only that device will be offline, while the remaining devices can still communicate normally, significantly reducing system-level risks.
New nodes only need to be connected to the central device without changing the existing links. This "plug and play" feature makes it particularly suitable for scenarios that require frequent capacity expansion, such as growing enterprises or temporary exhibition networks.
The processing capacity of the central node becomes the ceiling of network throughput. Although high-performance enterprise-class switches can alleviate bottlenecks, their procurement costs may account for 30%-50% of the overall network investment.
Core device: Usually a switch or hub, serving as the central hub of the network.
Function: Responsible for centralized data processing, forwarding and network traffic control. All peripheral device data transmission must pass through the central node.
Terminal devices: such as computers, servers, printers, IP phones, etc. These devices are connected to the central node through independent links.
Features: Each peripheral device is directly connected to the central node and does not communicate directly with other peripheral devices.
Physical link: A physical line used to connect the central node and peripheral devices, such as twisted pair cables (Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, Cat7, etc.), optical fiber, etc.
Selection basis: The choice of transmission medium depends on the needs of the network, including transmission distance, bandwidth requirements, cost and other factors.
Communication rules: such as IEEE 802.3 Ethernet protocol, which ensures the correct transmission and reception of data in a star topology.
Function: Network protocols define rules such as data format, transmission rate, error detection and correction to ensure the normal operation of the network.
| Dimensions | Bus topology | Star topology |
| structure | Linear shared bus, high risk of single point failure | Centralized hub/switch, single point failure controllable |
| reliability | If the bus breaks, the entire network will be paralyzed | Central node failure only affects local |
| Scalability | Simple but limited by bus length and number of devices | Flexible, the central node supports a large number of branches |
| Cost | Low (only backbone cable required) | Higher (needs central equipment and more cables) |
| Applicable scenarios | Small temporary networks, laboratories | Enterprise-level network, data center |
Case 1 : High-availability architecture in the financial industry
A stock exchange adopts a dual-star redundant design: two core switches form a logical single device through virtualization technology, and the access layer switch is dual-uplinked to the two cores. When the primary link fails, the STP protocol can complete the link switch within 50ms, ensuring zero interruption of the trading system.
Case 2 : Expansion of the Medical Internet of Things
A tertiary hospital manages 500+ APs through wireless controllers based on a star-shaped backbone network, achieving unified access to medical equipment, electronic medical record systems, and smart terminals. The central switch is configured with DHCP Snooping and DAI defense to effectively block access by illegal devices.
ProcessOn is an online drawing tool that supports drawing various types of network topology diagrams, provides a large number of network topology diagram templates, and supports multi-person online collaborative editing.
1. Log in to ProcessOn , go to the Personal Files page, and select Create New Flowchart.
2. Click "More Graphics" in the lower left corner and select the network topology icon type according to enterprise needs.

3. Drag device icons ( switch, computer, server, etc.) to the canvas and connect them with cables . Add connected devices and use colors to distinguish different device roles.
4. completing the topology map , click the "Export" button in the upper right corner of the page, select the appropriate export format (such as PNG, JPEG, PDF, etc.), and save the topology map to your local computer. You can also click the "Share" button to generate a sharing link to share the map with colleagues or customers .
The following are some star topology diagram templates shared in the ProcessOn template community .
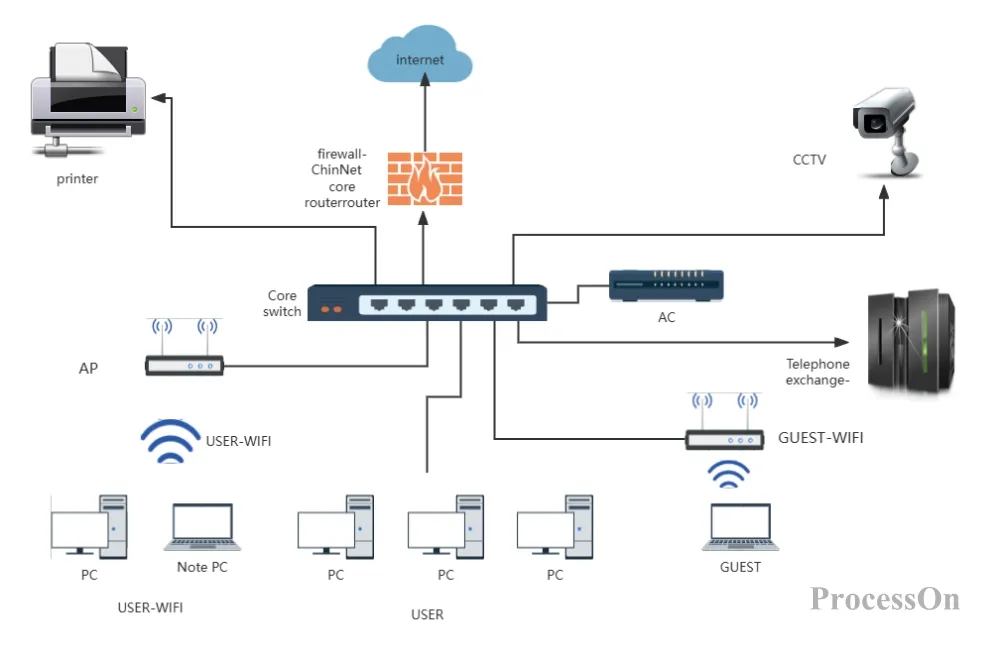
Enterprise basic network topology diagram-star topology
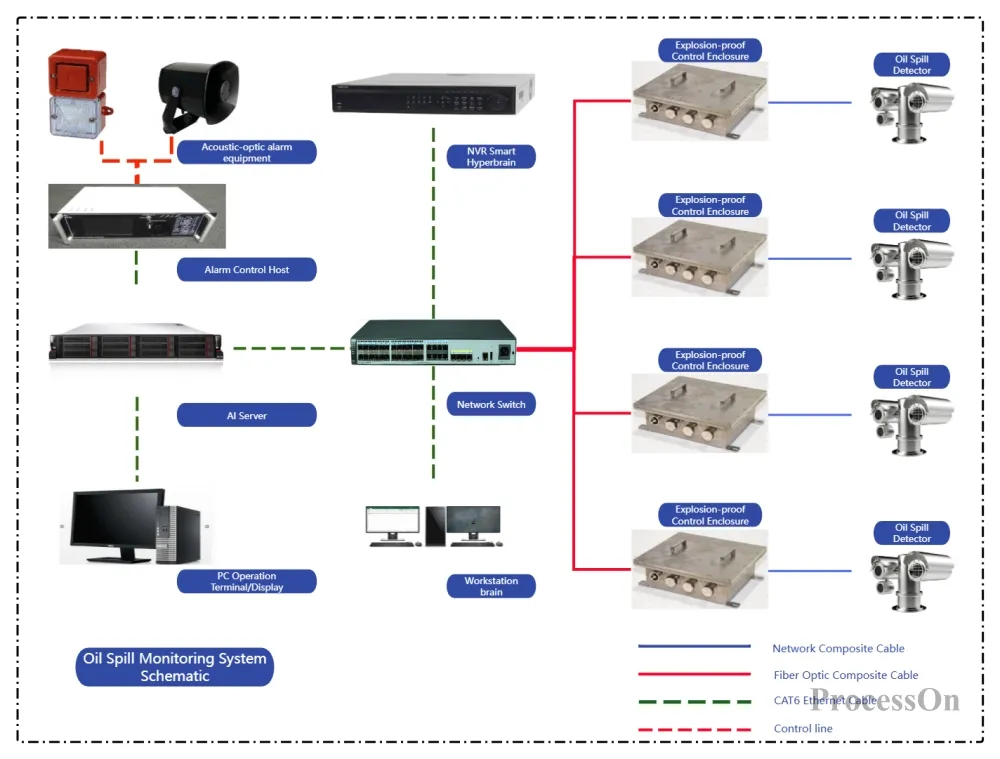
Video surveillance topology diagram - star topology
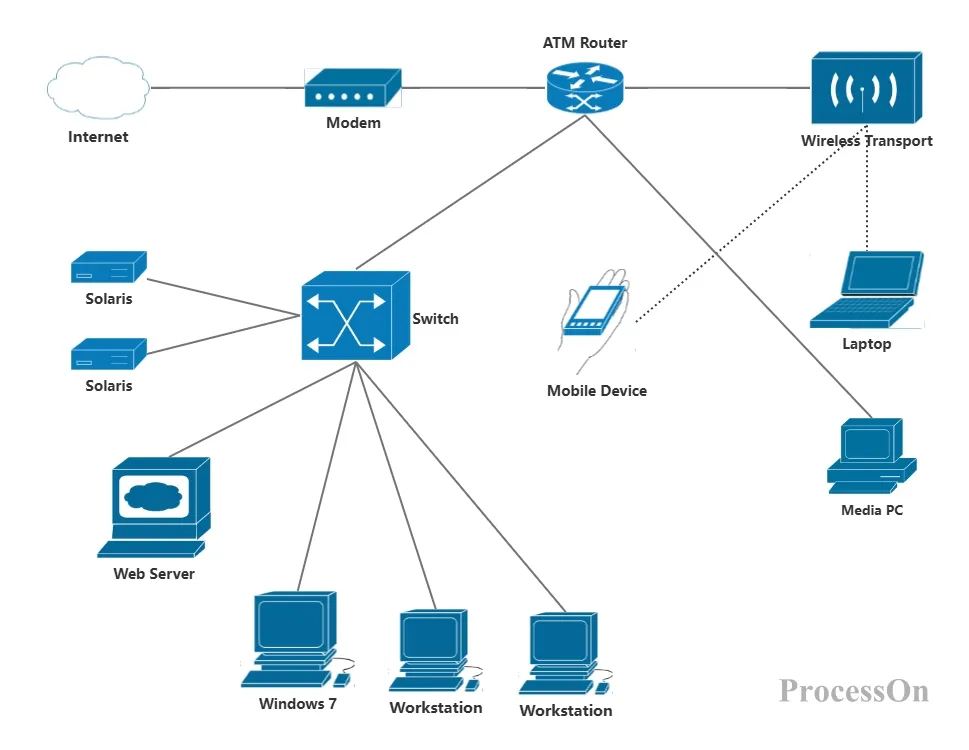
Cisco Network Topology Diagram - Star Topology
As the wave of digitalization continues to advance, the star topology continues to play a pivotal role in the field of network architecture with its unique advantages. Its centralized management, high reliability, and flexible expansion capabilities make it one of the preferred solutions for modern network design.