Amidst the wave of digital transformation, business process modeling (BPM) has become a core tool for enterprises to optimize efficiency and reduce communication costs. As a globally recognized process modeling standard, BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation), with its intuitive symbology and rigorous logical expression, has become the "lingua franca" of business analysts, product managers, and IT teams. However, many beginners are often intimidated by BPMN due to confusing symbols, unclear logic, and lack of proficiency in tool usage. This article will guide you through the fundamentals of BPMN, from the classification and usage of basic symbols to practical flowchart drawing techniques, common pitfalls, and optimization suggestions. Combining case studies with practical tool implementations, this article will help you quickly get started and produce professional-level business process diagrams, making complex processes crystal clear.
BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) is a standardized graphical language used to describe business processes within an enterprise or organization. Developed by the Object Management Group (OMG), it aims to unify the understanding of processes among business personnel, process analysts, and developers, enabling seamless integration of business and IT languages.
(1) Events: Indicates what happens in the process, represented by circles.
Start event (hollow circle): starting point of the process.
End event (solid circle): the end point of the process.
Intermediate events (double circles): such as timed events and message events (triggering subsequent actions).
(2) Activities: Indicates tasks that need to be performed and are represented by rounded rectangles.
Task: Atomic operation (such as "send email").
Sub-Process: A nested complex process (expandable/collapsed).
Call Activity: References other process templates.
(3) Gateways: Control flow branches, represented by diamonds.
Exclusive Gateway: A binary choice (e.g., “Are you a member?” → Yes/No branch).
Parallel Gateway: Triggers multiple paths simultaneously (e.g., "payment" and "shipping" in parallel).
Inclusive Gateway: Multiple branches that meet the conditions (such as "Select express delivery method: Standard/Expedited").
(1) Sequence Flow: Flow objects are connected with solid arrows to indicate the execution order.
(2) Message Flow: Use dotted arrows to connect different process pools to indicate cross-system/departmental communication.
(3) Association: Use a dotted line to connect activities and data objects to indicate data reference.
(1) Pool: represents an independent process participant (such as a department or system).
(2) Lane: A subdivided role within a pool (e.g., the “pre-sales team” and “after-sales team” within the pool’s “customer service department”).
(1) Data input/output: represented by a folded rectangle, defining the data required or generated by the activity.
(2) Data Store: A cylinder with open ends represents persistent storage (such as a database).
(1) Text Annotation: Use a folded-corner rectangle to add explanatory text.
(2) Group: Use dotted boxes to logically group related elements (without affecting the execution order).
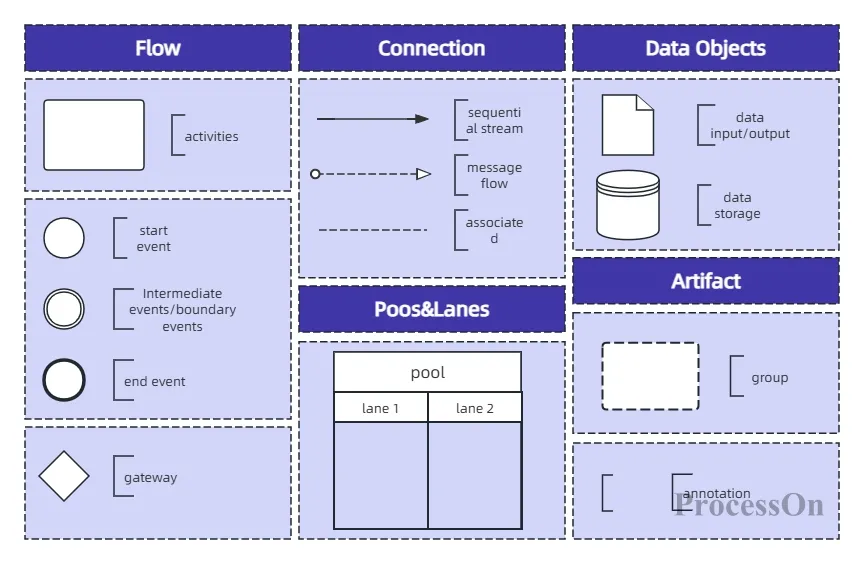
BPMN business process notation
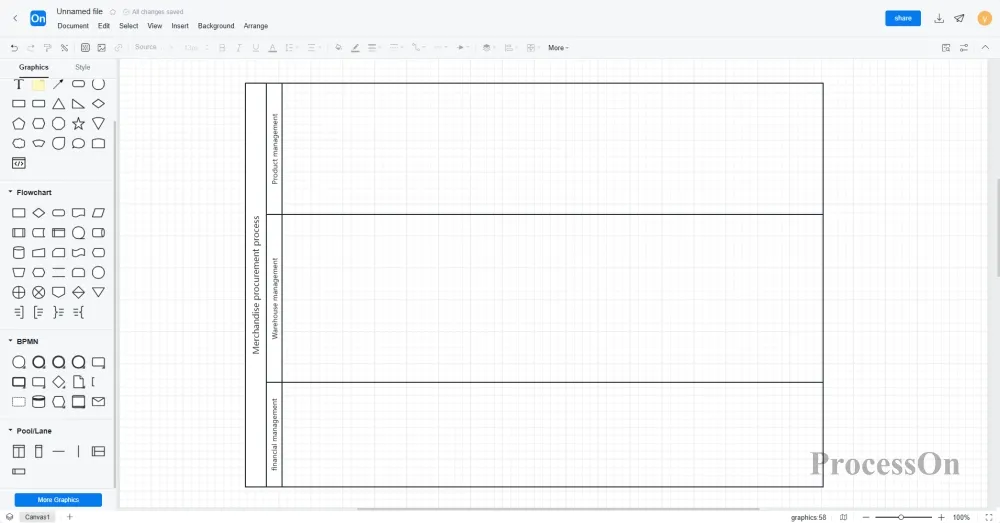
1. After logging in to ProcessOn, go to your personal files page, click "New File" and select "Processchart." Then, under More Diagrams, add BPMN to the Diagram Library. If you need to draw a pool or swimlane, you can also add the Pool/Swimlane diagram type to the Diagram Library.
2. Create process pools and swimlanes, and divide roles within the pools.
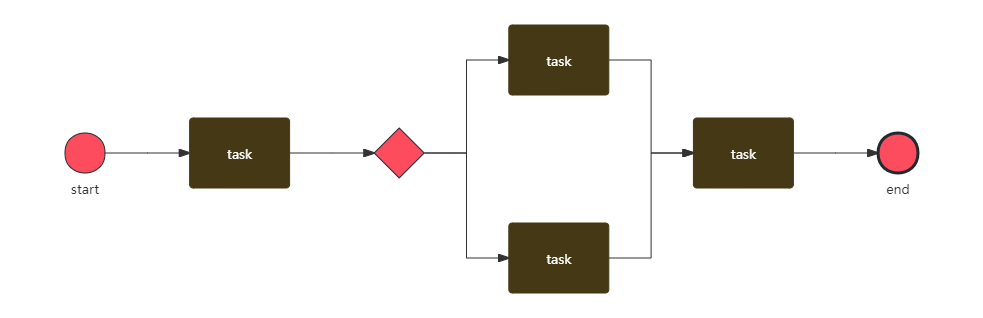
3. Define start and end events, add activities (Tasks) and sub-processes, and design branching logic. Use solid arrows to connect flow objects (events, activities, gateways) to indicate the execution order.
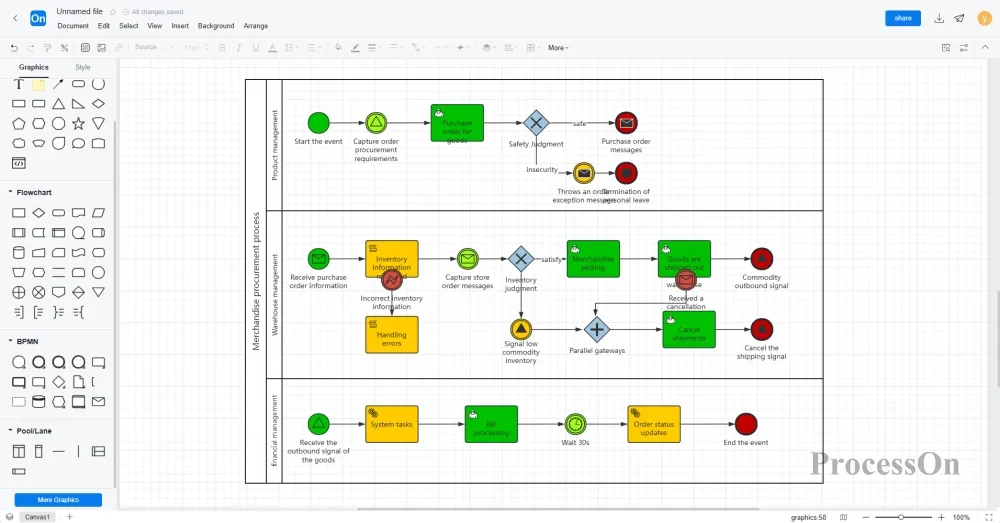
4. After you've finished drawing, export it as an image or PDF, which you can then insert into company documents and share with your team. You can also directly share your circuit diagram with colleagues or clients, allowing them to view or edit it online.
Main process diagram: retain only the core path (such as "order → payment → delivery"), and use sub-processes or call activities to hide complex details.
Sub-process diagram: retain only the core path (such as "order → payment → delivery"), and use sub-processes or call activities to hide complex details.
To avoid crossing lines, you can adjust the element position or set the crossing lines to be displayed at the intersection.
Use different colors to distinguish roles (e.g. blue = customer, green = system).
Add labels to key activities (e.g., “High Priority,” “Automation Triggered”).
Overly complex: A gateway branch has no more than 5 paths.
Fuzzy gateway: Clearly mark the gateway type to avoid ambiguity in gateway type and the resulting branch logic ambiguity.
Missing exceptions: Add intermediate events to handle timeouts or errors (such as a "payment failed" branch).
Go through the process from beginning to end to ensure there are no dead loops or missed nodes.
The ProcessOn template community includes a wealth of BPMN templates for reference, and supports copying to improve drawing efficiency. Below are some templates shared.
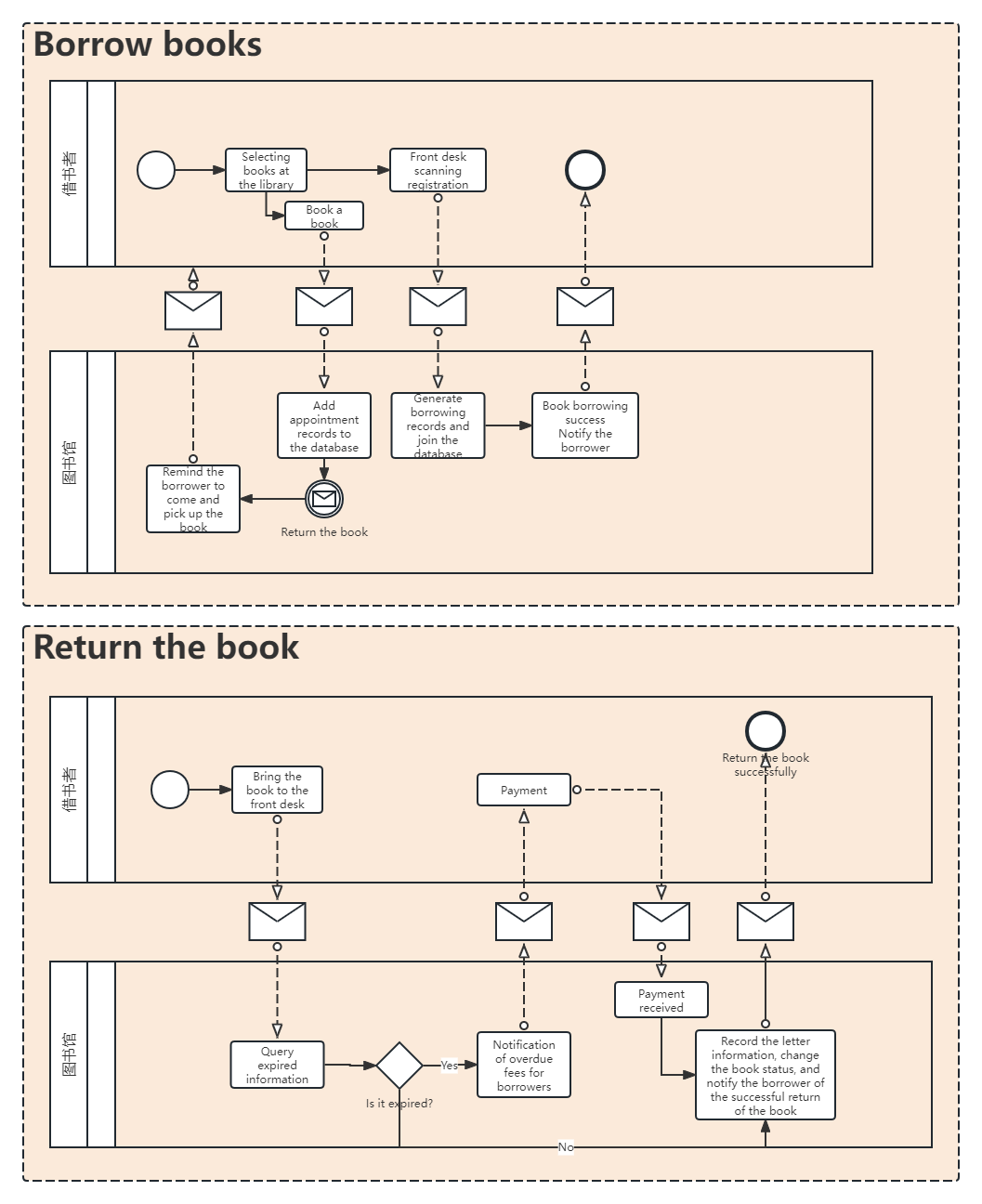
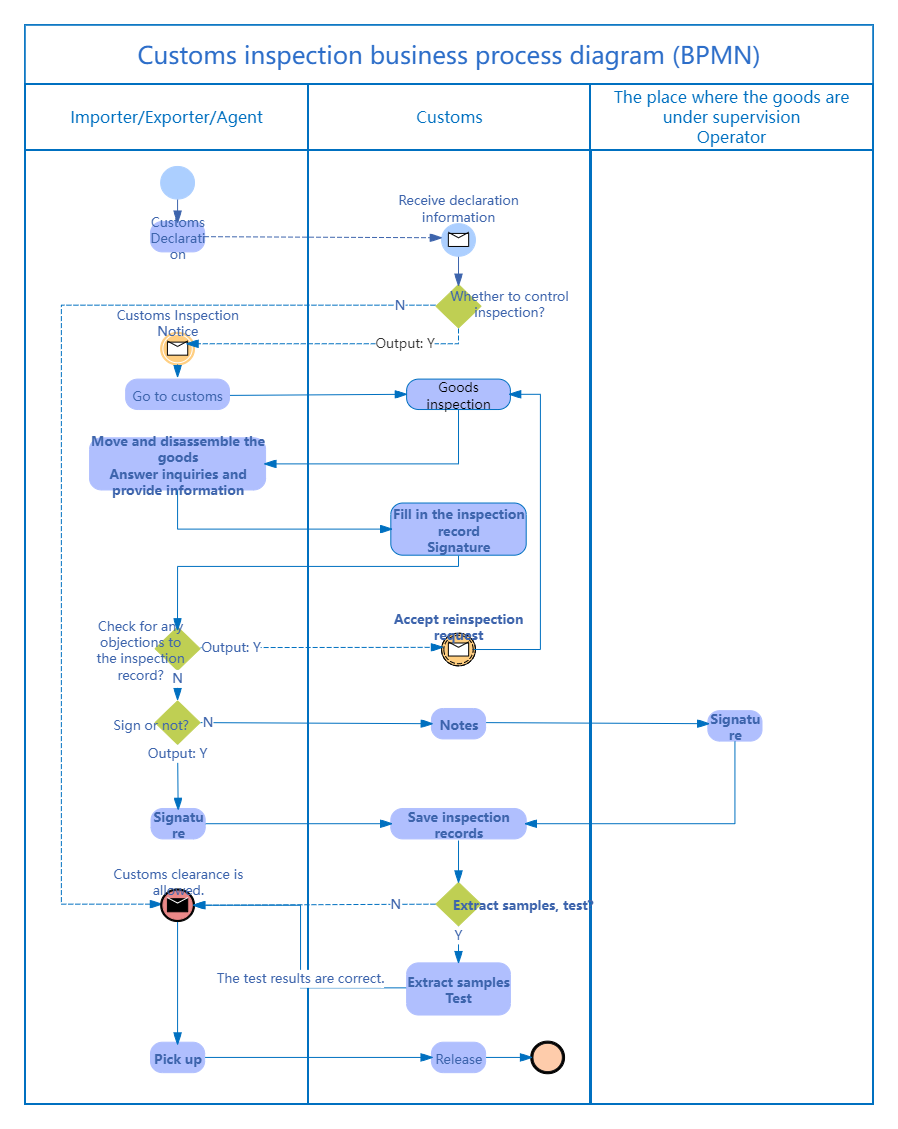
Customs Inspection Business Process Diagram (BPMN)
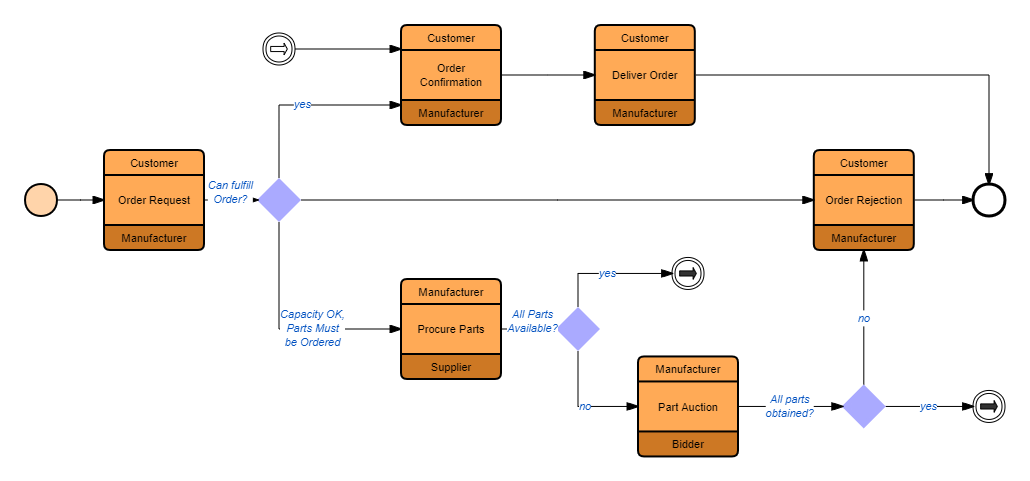
BPMN-Franchisee System Order Process
The core of drawing BPMN diagrams is structured thinking : first define the boundaries, then break down the steps, and finally express the logic with symbols. Now, open ProcessOn and follow the steps in this article to try drawing your first BPMN diagram!