The functional organizational structure is a pyramid-shaped structure with professional division of labor as its core. Its core feature is to achieve management specialization through the division of functional departments. This structure originated from the practice of Henri Fayol, a French management scientist in the early 20th century. Its typical form is the U-shaped organization (Unitary Structure). Its operating logic is reflected in three levels:
Vertical chain of command: senior managers pass instructions to the grassroots through functional departments (such as R&D, production, and marketing), forming a clear hierarchical system;
Horizontal collaboration network: Functional departments act as advisory bodies to provide technical guidance and resource support to line departments;
Specialized division of labor: Each department focuses on specific functions, such as the Human Resources Department is responsible for recruitment and training, and the Finance Department is responsible for unified budget management.
This structure is particularly typical in manufacturing companies. For example, in the organizational structure of a certain electronic product company, the president is in charge of functional departments such as marketing, production, and R&D. Each department has project teams A/B/C, forming a three-level management framework of "president-functional department-project team".
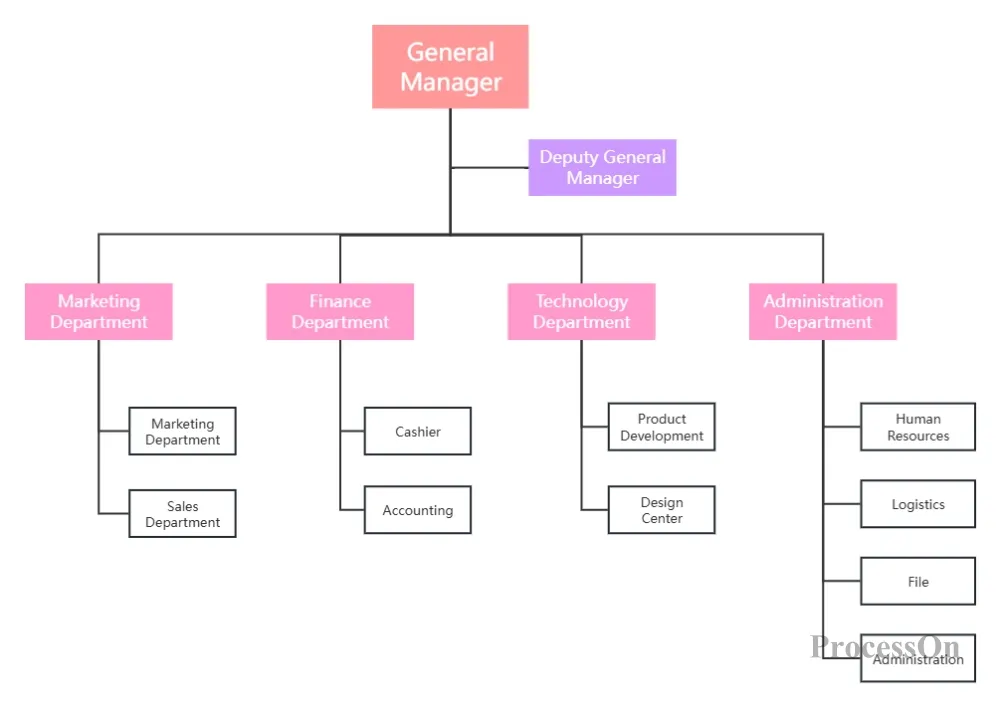
Startup company organizational chart
Decision-making level: General manager/president, who holds the final decision-making power;
Executive level: functional department managers (such as vice president of marketing, vice president of engineering), responsible for departmental strategy execution;
Professional level: technical experts and project coordinators, the former provide technical support, the latter are responsible for cross-departmental communication;
Operational level: Grassroots employees are assigned to specific project teams according to their functions.
adopts the "department contracting system". For example, a new product development project may be led by the R&D department and completed jointly with the production department and the quality inspection department. The staff deployment presents a "tidal effect": personnel are transferred from functional departments during the peak period of the project and return to their original positions after the project is completed.
Advantages of concentrated resources
Technology reuse effect: By concentrating experts in the same field (such as all electronic engineers in the R&D department), a knowledge sharing pool is formed to reduce technology redundancy. For example, a technology company uses a functional architecture to enable the AI algorithm team to serve multiple projects such as intelligent customer service and recommendation systems at the same time, increasing the technology reuse rate by 40%.
Improved professional efficiency: Employees form a "learning curve" within their functional departments, and as they accumulate experience, their work efficiency increases exponentially.
Talent team stability
Clear promotion channel: Functional departments provide a vertical development path of "specialist-supervisor-manager-director", employees have clear career expectations, and the retention rate of key positions is higher than that of project-based organizations.
Knowledge inheritance mechanism: The department uses mentoring, technology sharing sessions, and other means to ensure that core skills are not lost due to staff turnover.
Operational cost optimization
Equipment and resource concentration: For example, the precision instruments of the quality inspection department can serve all product lines of the company, and the equipment utilization rate is high.
The SOP (standard operating procedure) developed by functional departments can be quickly extended to new projects to reduce trial and error costs.
Departmental barriers and misaligned goals
KPI conflict: The marketing department pursues sales and may require the rapid launch of products with simplified functions; while the R&D department focuses on technological perfectionism, which leads to delays in product launch.
Resource wars: When resources are limited, departments may engage in “political games” to compete for budgets rather than allocating resources based on project priorities.
Delayed customer response
Demand transmission attenuation: Customer feedback needs to go through multiple layers of filtering from sales department → marketing department → R&D department, and key demands may be misinterpreted or ignored.
Insufficient customization capabilities: Standardized functional division of labor makes it difficult to quickly respond to personalized needs, and is at a disadvantage in the C2B (consumer to business) model.
Long decision-making chain
Approval marathon: A cross-departmental decision needs to go through multiple levels of approval from department manager → vice president → president, and the average decision-making cycle is longer than that of a flat organization.
Innovation inhibition effect: The creativity of grassroots employees needs to be reported up the chain of command, which may lead to "good ideas withering in the reporting process."
| Comparison Dimensions | Functional Organization | Linear organization |
| Distribution of decision-making power | Focus on senior management, and functional departments provide advisory opinions | Total focus on top management |
| Communication Path | Vertical + horizontal interweaving requires cross-departmental coordination | Single vertical chain, fast information transmission |
| Applicable scenarios | Mature business, standardized production, technology-intensive industry | Startups, simple businesses, and on-site operations organizations |
| Typical Cases | A convention and exhibition center project construction coordination leading group | Small processing plants, fast food chains |
ProcessOn is an online drawing tool that supports drawing various types of organizational charts, provides a large number of organizational chart templates, and supports multi-person online collaborative editing.
1. Log in to ProcessOn , go to the personal file page, and select Create a new mind map.
2. Click "Structure" on the right toolbar to switch to the organizational chart. Click the "+" outside the central topic to create topics of the same level, parent topics, and child topics. Double-click the topic to add role names to the organizational structure, such as Human Resources Department, Product Department, etc.
3. You can insert elements such as icons or pictures into the theme to increase the visibility of the organizational chart.
The following are some functional organizational chart templates shared in the ProcessOn template community.
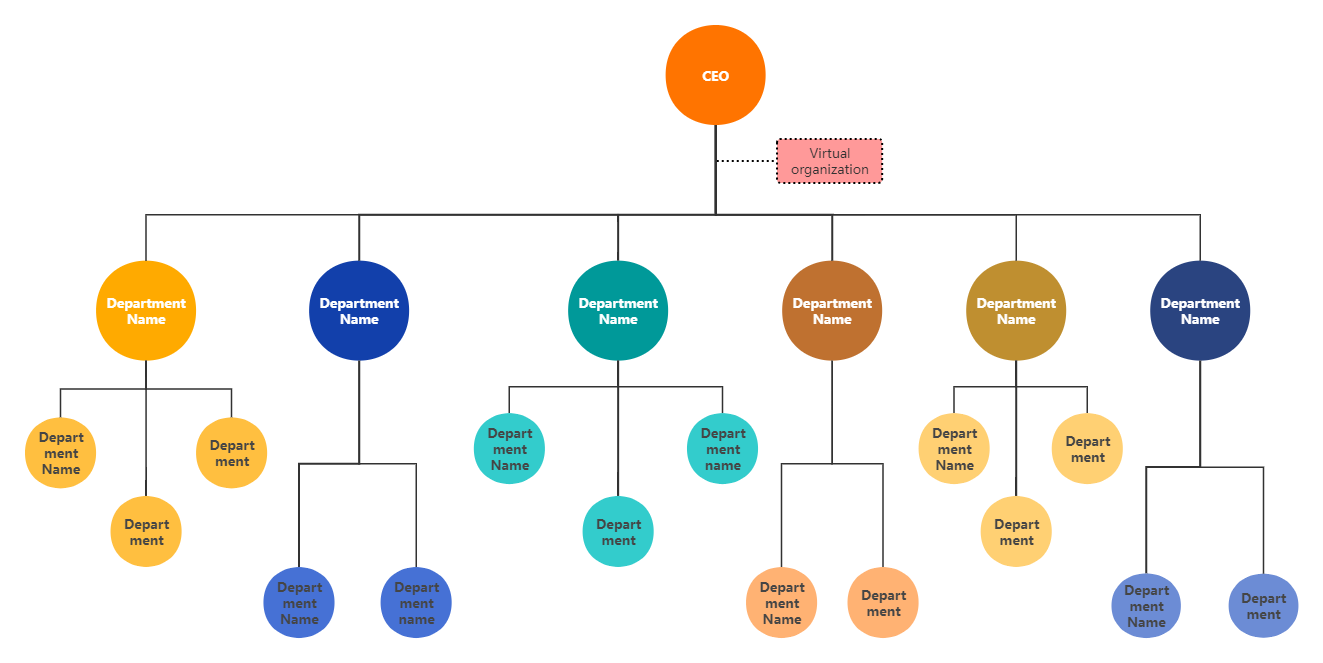
Functional Organization Chart Template
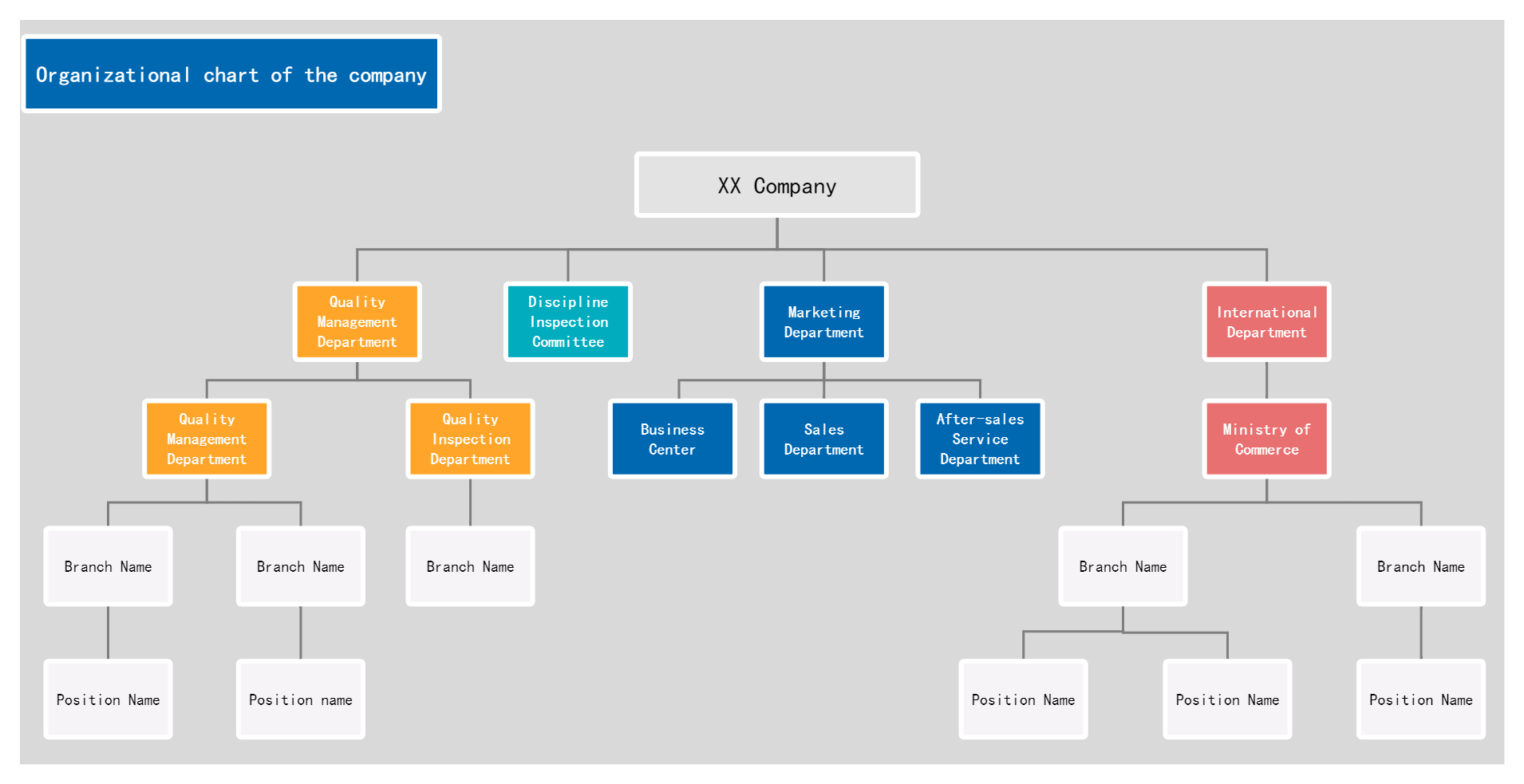
Enterprise functional organization chart
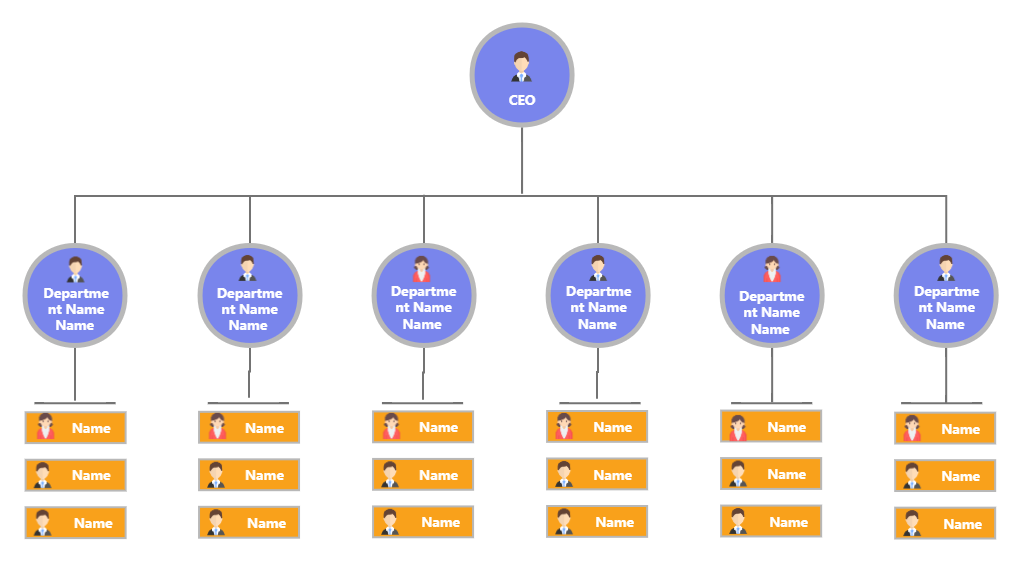
Company Organization Chart - Flowchart
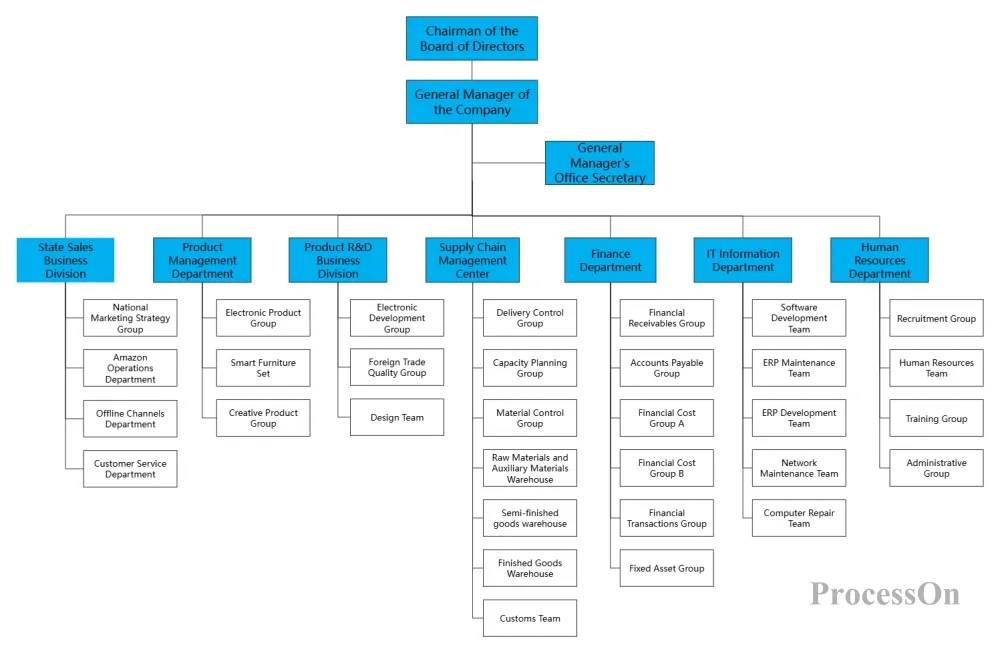
E-commerce company organizational structure - functional
The functional organizational structure can realize the specialized division of labor in the enterprise. Employees in each department focus on work in a specific field, can delve into professional knowledge, and continuously improve their professional skills. The enterprise can concentrate limited resources on various functional departments to achieve optimal allocation of resources. However, we must also realize that the functional organizational structure is not a one-time solution. In actual application, enterprises need to adjust and optimize the organizational structure in a timely manner according to their own development stage, business characteristics and changes in the market environment. Only in this way can the advantages of the functional organizational structure be fully utilized and its possible disadvantages be avoided.