

Mind mapping is an effective tool that can help us clearly present complex ideas. Whether in study, work, or daily life, mind mapping can achieve twice the result with half the effort.
For beginners, it is not difficult to master the skills of drawing mind maps. This article will start from scratch and gradually guide you to master the basic concepts of mind maps, drawing methods, and how to apply these skills in real life, so that your thoughts can be clearly seen.
Mind Map is a graphical tool for displaying and organizing information. Its core concept is to structure complex information for better understanding and memory. Mind Maps usually start with a central theme and expand branches in all directions. Each branch represents a sub-item related to the theme, and the branches can be further refined to form a hierarchical structure.
Red Green Mind Map Style Template
The main features of mind mapping:
1. Visualization: Make information more intuitive through images, colors and symbols.
2. Hierarchy: Starting from the central theme, break down the information layer by layer.
3. Associativeness: Promotes the brain's associative ability and helps stimulate creativity and inspiration.
1. Determine the central theme
First, make sure you have a clear theme for your mind map. This theme will be the core of the entire mind map. The central theme is usually a word or phrase, which can be a problem you want to solve, a point of knowledge that needs to be sorted out, or anything that interests you.
2. Draw the center node
Draw a circle in the center of the paper or electronic device and write the central theme. Make sure this central node is eye-catching enough to highlight its importance by using different colors, fonts or icons.
3. Add a main branch
Draw several main branches radiating from the central node. Each branch represents a sub-topic closely related to the central topic. Label the corresponding sub-topic keywords at the end of each branch. These keywords should be concise and clear, and be able to summarize the core content of the sub-topic.
4. Expand secondary branches
Continue to refine each major branch and add secondary branches. Secondary branches can represent more specific content or further analysis under the subtopic. In this way, you can continue to refine until each branch fully expresses the information you want to present.
5. Add images and symbols
To make the mind map more visual, you can add relevant images, symbols or colors to each branch node. This will not only enhance the visual effect, but also help you better remember and understand the information.
6. Inspection and adjustment
After completing the preliminary drawing, check whether the structure of the entire mind map is reasonable and whether the information is complete. If necessary, you can adjust the branches to make the mind map more logical and organized.
1. Use keywords
When drawing a mind map, try to use keywords instead of complete sentences. Keywords help improve the efficiency of information transmission and are easier for the brain to remember and understand.
2. Color classification
Using different colors to identify different branches or levels can help distinguish the priority and category of information. Colors can not only make the mind map more beautiful, but also enhance the visibility and memory of information.
3. Image assistance
Images are an indispensable element in mind mapping. The brain's memory of images is much stronger than that of text, so inserting images in appropriate locations can greatly improve the effect of mind mapping.
4. Keep it simple
Although the branches of a mind map can be expanded infinitely, be careful not to make the structure too complicated. Too many branches may confuse people and fail to effectively convey information. Keeping it concise and clear is an important principle of mind mapping.
5. Use symbols appropriately
Symbols can quickly convey information, and using some common symbols (such as arrows, asterisks, question marks, etc.) in mind maps can enhance the effect of expression. For example, arrows can be used to indicate the flow of information, and question marks can be used to indicate problems that require further thinking or resolution.
1. Study and review
Mind maps are widely used in learning. Students can structure knowledge points and form a knowledge framework by drawing mind maps. Especially in the review stage, mind maps can help students quickly review and organize what they have learned and improve review efficiency.
2. Project Management
In project management, mind maps can be used to plan all aspects of a project. Project managers can use mind maps to clearly display project goals, tasks, time arrangements, and resource allocation, which helps improve team collaboration efficiency.
3. Brainstorm
Mind mapping is an ideal tool for brainstorming. Through mind mapping, various ideas and creativity of team members can be effectively organized to discover potential solutions and innovative ideas.
4. Problem Solving
When solving complex problems, mind maps can help us analyze various aspects of the problem, find the key points, and develop solutions. Through the hierarchical structure of mind maps, the root cause of the problem and its solution path can be clearly shown.
5. Personal planning
For individuals, mind mapping is also a powerful tool for making plans and goals. Whether it is a work plan, a study plan, or a life goal, mind mapping can help us better organize and manage our time and tasks.
With the development of technology, more and more electronic tools can help us draw mind maps more conveniently.
ProcessOn is an online mind mapping tool that supports real-time online collaboration among multiple people. It provides a variety of preset themes and can be converted into outlines, Word, PPT, Excel, etc. with one click. ProcessOn supports the following structured mind mapping .
1. Ordinary mind map
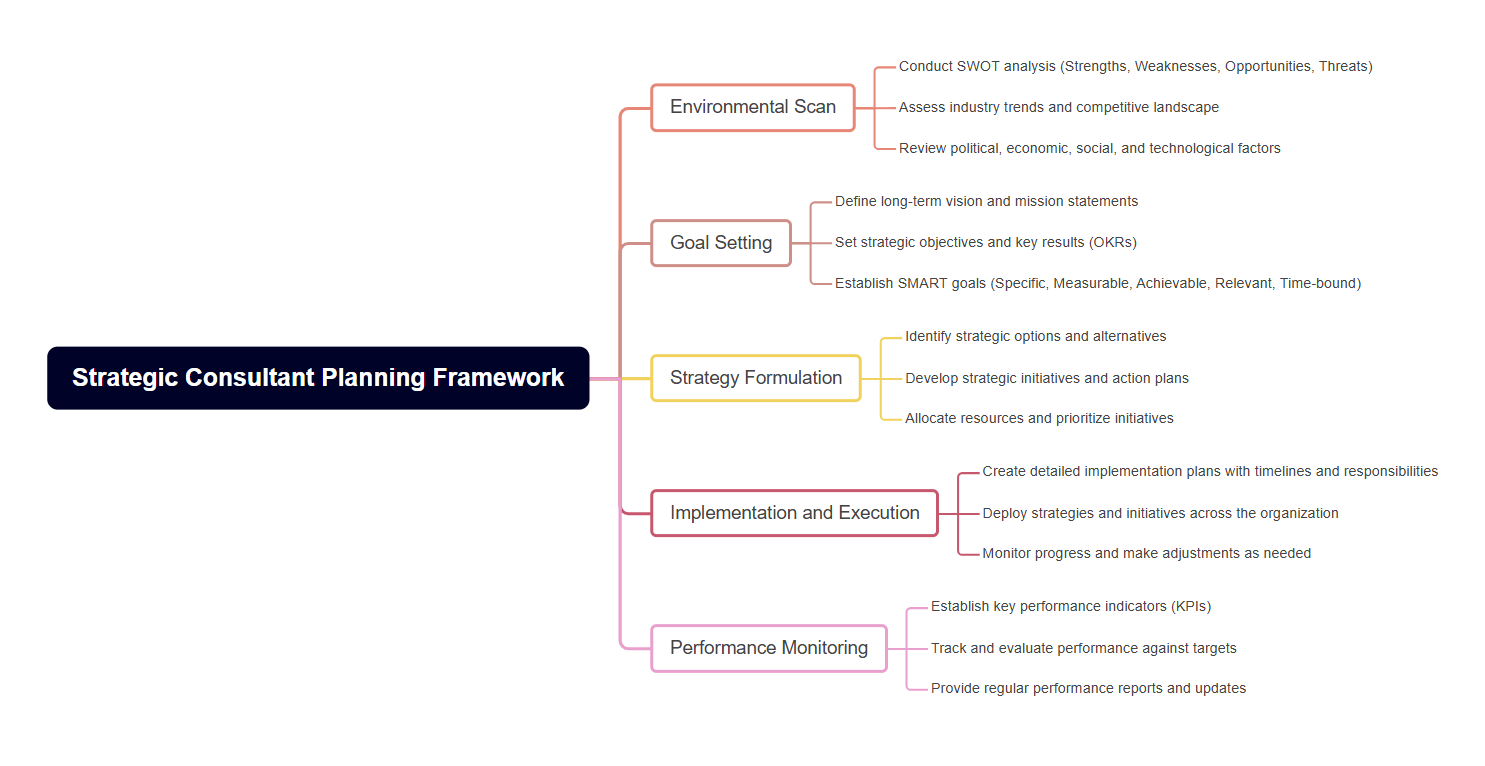
Strategic Consultant Planning Framework
2. Tree structure diagram
Trendy Purple Tree Org Chart Style Template
3. Organizational Chart
4. Treemap
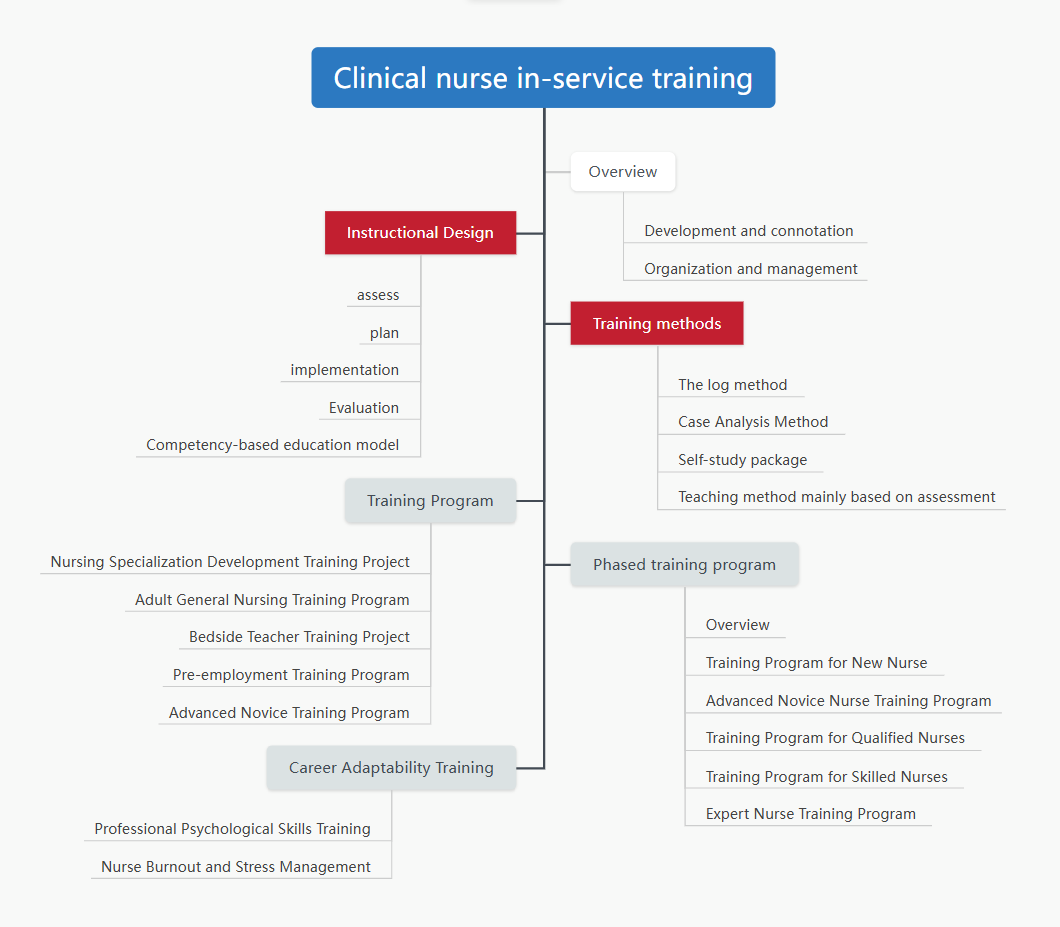
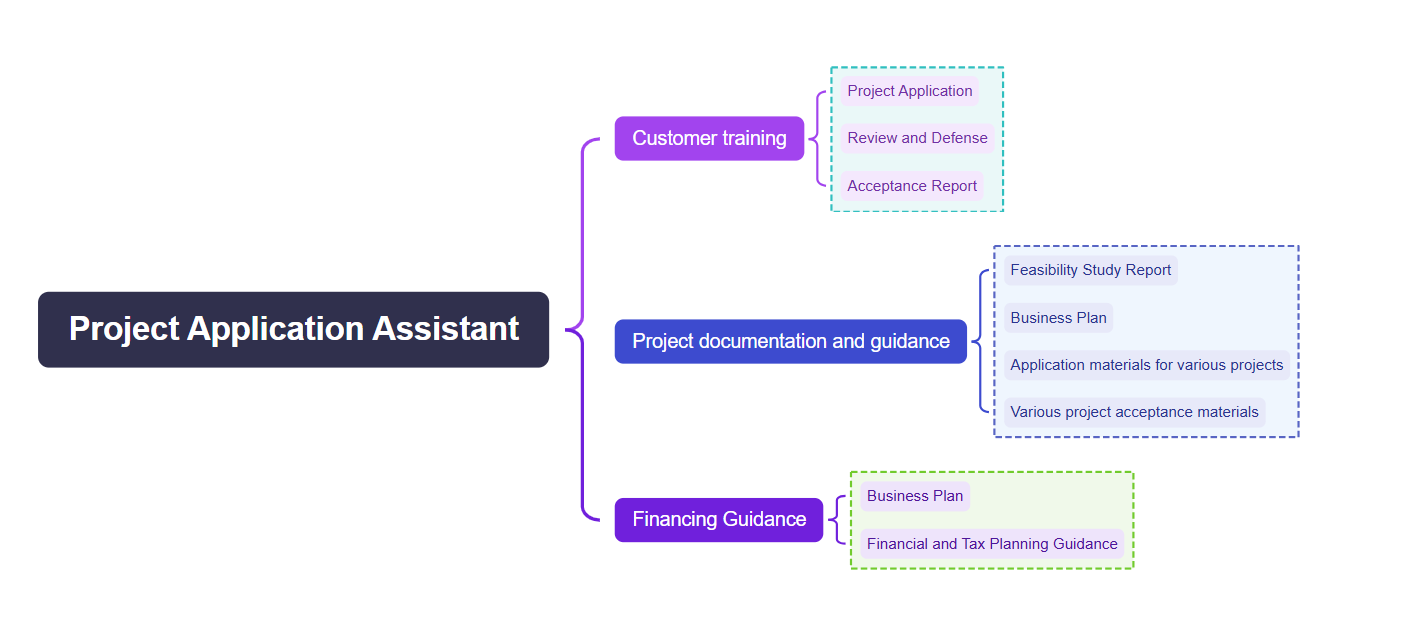
Project Application Assistant Responsibilities Bracket Chart
6. Fishbone diagram
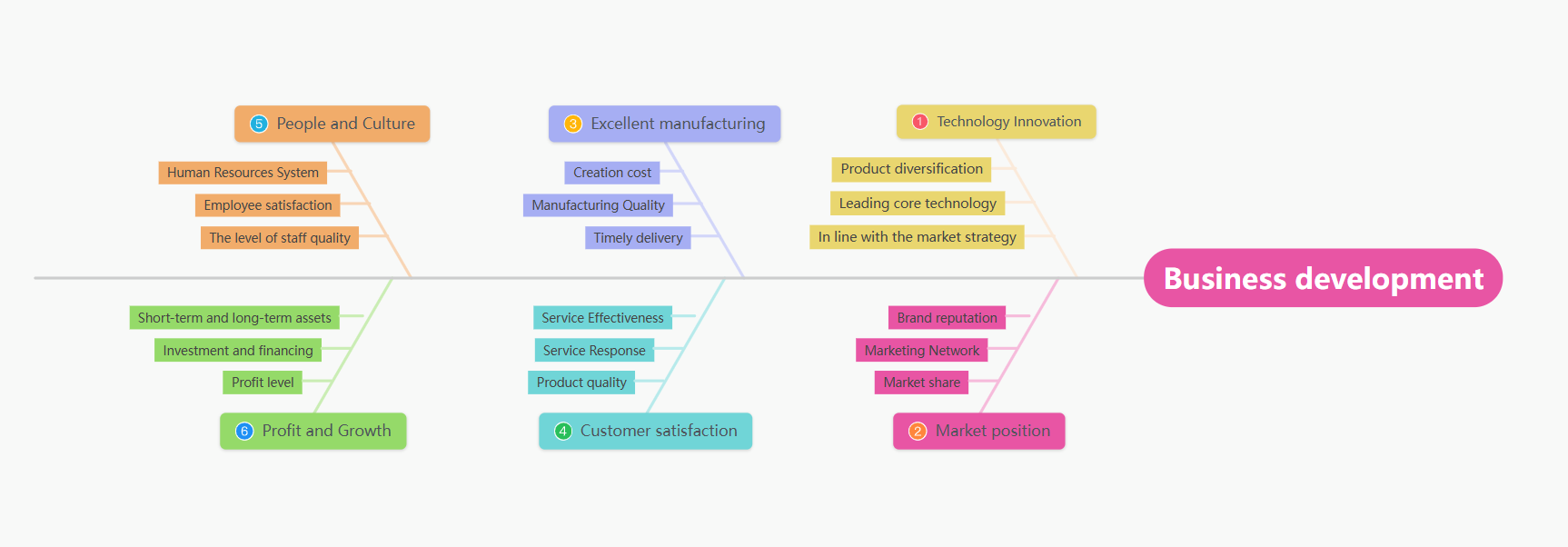
Enterprise development fishbone diagram
Mind mapping is a powerful tool that can help us better organize our thoughts, structure information, and stimulate creativity.
For beginners, it is not difficult to master the skills of drawing mind maps. Just follow the steps introduced in this article, start from scratch, practice and apply step by step, and you can easily master this skill. If you need to draw a mind map, come to ProcessOn !