BPMN is a graphical standard for business process modeling. It provides a set of intuitive and easy-to-understand symbols and syntax so that business processes can be clearly represented and understood. The main purpose of BPMN is to facilitate the visualization, analysis and optimization of business processes and improve the efficiency and quality of business processes.
In today's complex and ever-changing business environment, efficient process management is crucial to the success of an enterprise. As a widely used process modeling standard, Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) provides enterprises with powerful tools to visualize, analyze and optimize business processes.
BPMN is a graphical standard for business process modeling. It provides a set of intuitive and easy-to-understand symbols and syntax so that business processes can be clearly represented and understood. The development of BPMN can be traced back to 2004, when it was initiated by the Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI) to provide a common language for business process management. Over time, BPMN has continued to develop and improve, and has now become a widely accepted process modeling standard worldwide.
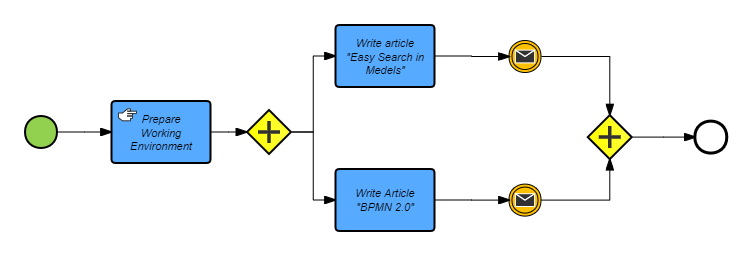
For example, when many companies are reengineering their business processes, they use BPMN to describe and analyze existing processes and identify problems and opportunities for improvement. By using BPMN, companies can better understand the nature of business processes and improve process transparency and manageability.
1. Activity
is one of the most basic elements in BPMN. It represents a specific task or operation in a business process. Activities can be manual or automatic, such as filling out a form, sending an email, performing a database query, etc.
For example, in an order processing process, activities may include receiving orders, reviewing orders, arranging shipments, etc. Each activity has clear inputs and outputs, as well as corresponding execution rules and time requirements.
2. Events
An event is a trigger point or result in a business process. It can be a start event, an intermediate event, or an end event. An event can be triggered by external factors or generated by the satisfaction of conditions within the process.
For example, in a customer complaint handling process, the customer submitting a complaint can be a start event, and sending a feedback email after the process is completed can be an end event. Intermediate events can include timeout events, error events, etc., which are used to handle abnormal situations in the process.
3. Gateway
Gateway is used to control the flow of the process. It determines the branching and merging of the process according to specific conditions. Gateways can be of different types such as exclusive gateways, parallel gateways, and inclusive gateways.
For example, in an approval process, you can use an exclusive gateway to decide whether the process should continue or terminate depending on the approval result. In a parallel task processing process, you can use a parallel gateway to start multiple tasks at the same time.
4. Swimlanes
Swimlanes are used to divide the activities in a business process according to different participants or departments, making the process clearer and easier to understand. Swimlanes can be horizontal or vertical, representing different organizational levels or business areas.
For example, in a cross-departmental collaboration process, swimlanes can be used to distinguish the responsibilities and tasks of different departments to avoid unclear responsibilities and duplication of work.
1. Visual
BPMN uses a graphical approach to represent business processes, making them more intuitive and easy to understand. Through visual flowcharts, companies can better understand the structure and logic of business processes and discover potential problems and opportunities for improvement.
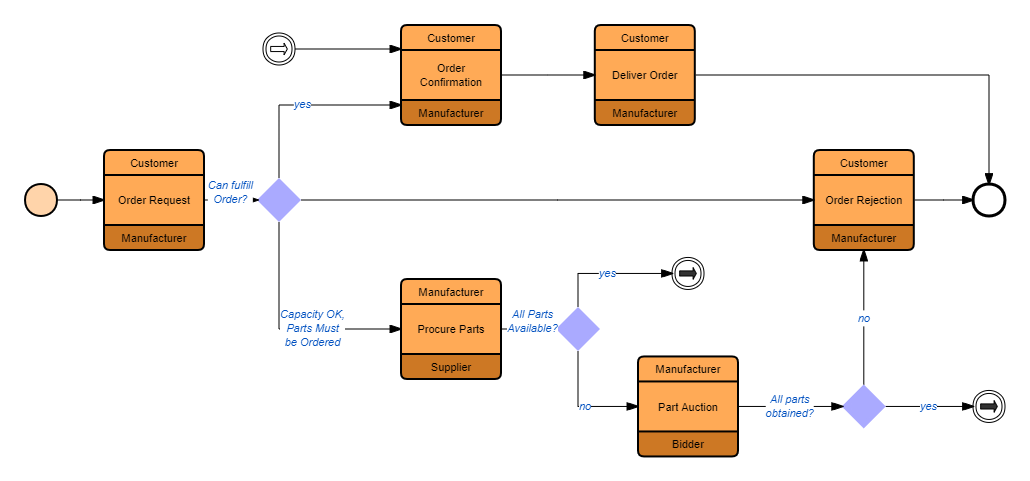
For example, companies can use BPMN tools to draw process diagrams, and then discuss and analyze with relevant personnel to jointly identify bottlenecks and optimization points in the process.
2. Standardization
BPMN is a standardized process modeling language that provides a unified set of symbols and syntax, allowing processes between different companies and departments to be compared and communicated. Standardized process models also facilitate enterprise process integration and automation.
For example, enterprises can use BPMN models to connect processes with suppliers and partners to improve business collaboration efficiency. At the same time, standardized models also make it easier for enterprises to use process automation tools to achieve automated execution and monitoring of processes.
3. Scalability
BPMN has good scalability and can be customized and expanded according to the specific needs of the enterprise. Enterprises can add their own symbols and rules based on BPMN to meet specific business process requirements.
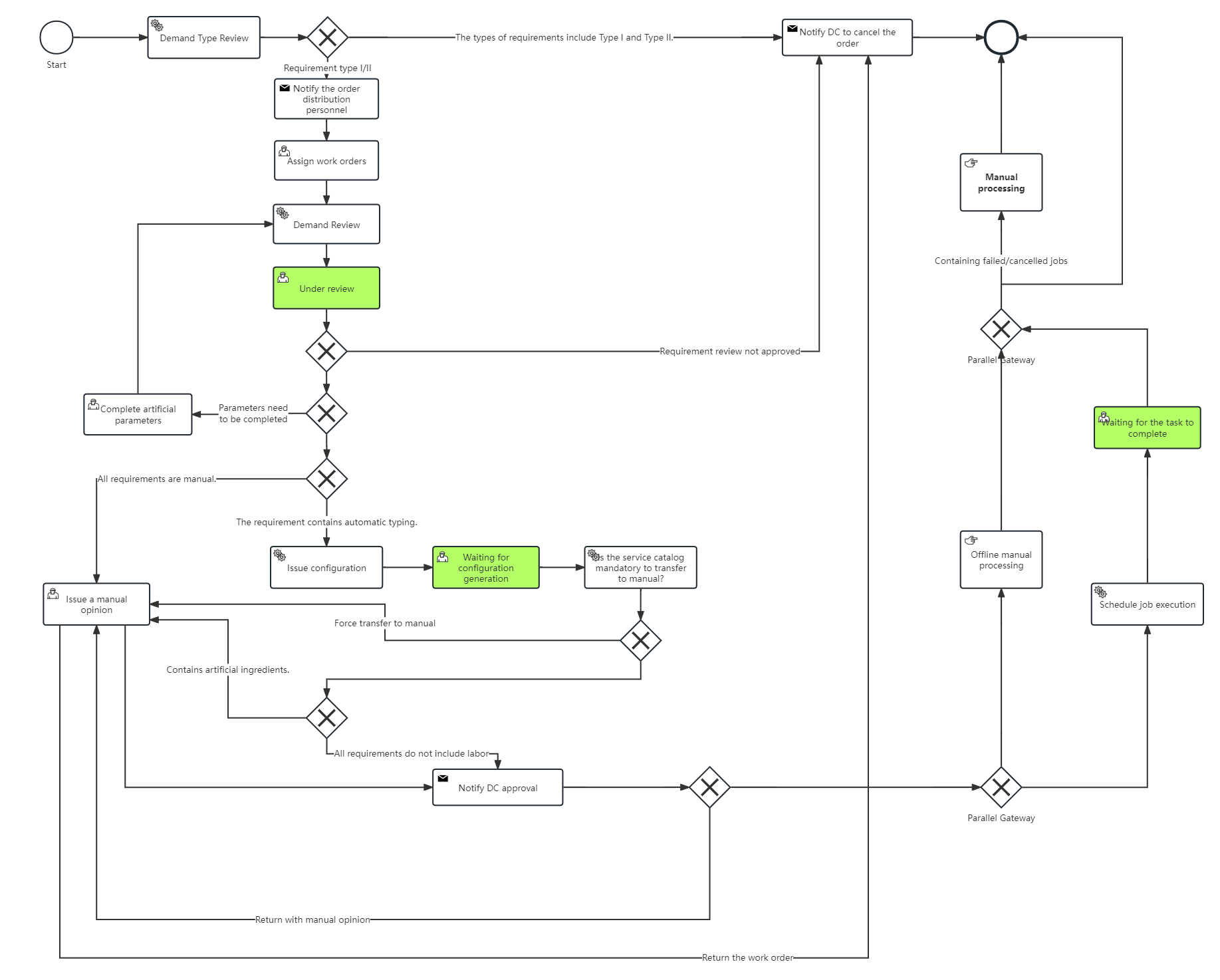
For example, enterprises can add custom activity types, event types, and gateway types to BPMN models to adapt to specific business scenarios. At the same time, BPMN also supports integration with other process modeling standards and technologies, such as UML, XML, etc.
4. Analysis and Optimization
BPMN can not only be used for process modeling and visualization, but also for process analysis and optimization. By analyzing the BPMN model, enterprises can find out the bottlenecks, redundant links and risk points in the process, and then take corresponding measures to optimize it.
For example, enterprises can use process analysis tools to simulate and analyze BPMN models to identify performance bottlenecks and optimization opportunities of the process. At the same time, enterprises can also adjust and improve the process based on the analysis results to improve the efficiency and quality of the process.
1. Business Process Reengineering
Business process reengineering is a fundamental redesign and optimization of existing business processes in order to improve competitiveness and efficiency. BPMN can be used as an important tool for business process reengineering to help companies clearly describe existing processes, identify problems and opportunities for improvement, and then design new process models.
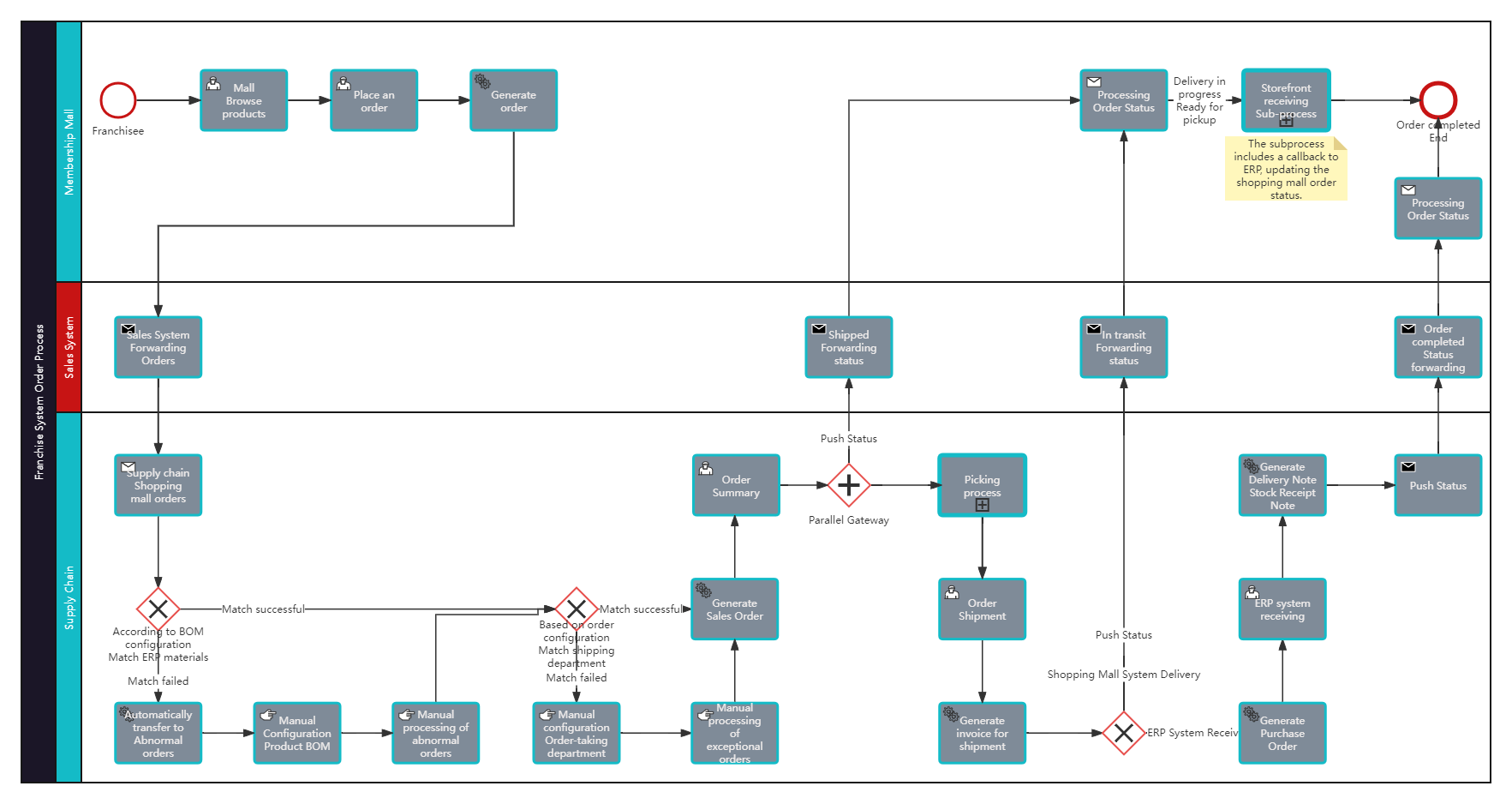
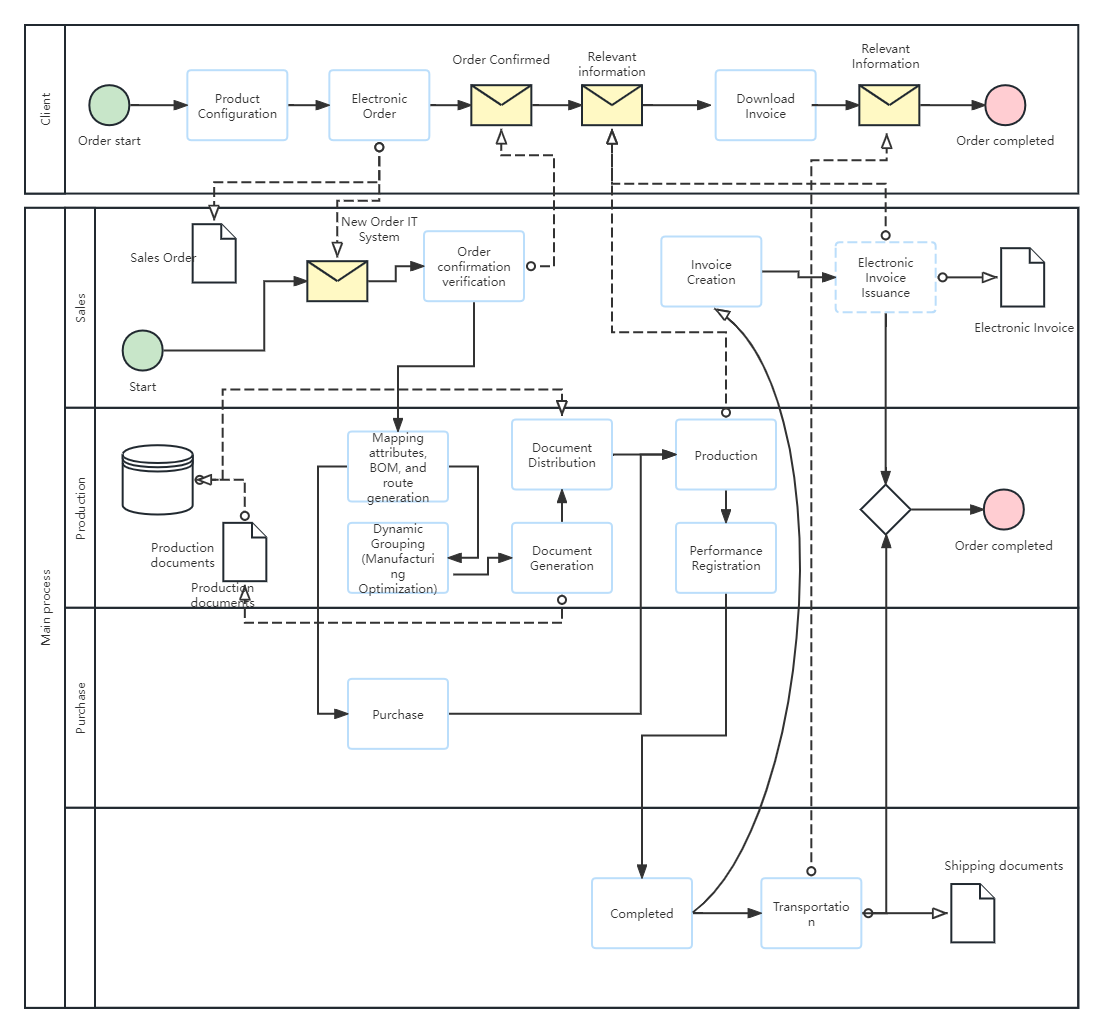
BPMN-Franchisee System Order Process
For example, companies can use BPMN tools to model and analyze existing processes, and then reengineer processes based on the analysis results. By redesigning the process, companies can eliminate unnecessary links and improve process efficiency and quality.
2. Process Automation
Process automation is the use of information technology by enterprises to automate and monitor business processes. BPMN can serve as the basis for process automation, helping enterprises design process models that can be automated, and then automate processes through process automation tools.
For example, an enterprise can use a BPMN model to describe a business process, and then use a process automation tool to convert the model into executable code to automate and monitor the process. Through process automation, an enterprise can improve the efficiency of process execution, reduce human errors, and reduce costs.
3. Project Management
Project management is the process of planning, organizing, executing and controlling projects to achieve specific goals. BPMN can be used as a project management tool to help companies describe project processes and activities, clarify project phases and milestones, and the responsibilities and tasks of each participant.
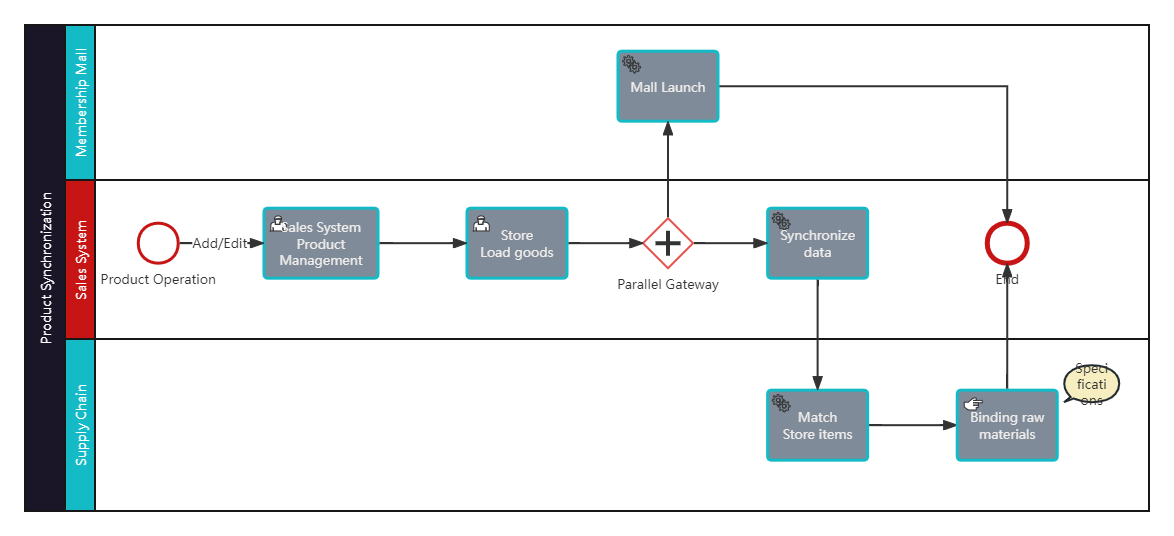
BPMN-Product Synchronization Process
For example, enterprises can use BPMN models to describe the process and activities of a project, and then develop project plans and schedules based on the model. At the same time, enterprises can also use BPMN models to monitor and control projects, identify problems in a timely manner, and take appropriate measures.
4. Enterprise architecture design
Enterprise architecture design is the process of overall planning and design of the enterprise's business, data, applications and technologies in order to achieve strategic goals. BPMN can be used as a tool for enterprise architecture design to help enterprises describe business processes and information flows and clarify the interaction and integration relationships between various business systems.
For example, enterprises can use BPMN models to describe business processes, and then design the functions and interfaces of business systems based on the models. At the same time, enterprises can also use BPMN models to evaluate and optimize enterprise architecture to ensure the rationality and effectiveness of enterprise architecture.
1. Training and education
Since BPMN is a relatively new technology, employees within the enterprise may not be familiar with it. Therefore, when implementing BPMN, the enterprise needs to provide adequate training and education to enable employees to understand the basic concepts, symbols and syntax of BPMN, as well as how to use BPMN for process modeling and analysis.
For example, companies can organize internal training courses, seminars and workshops, and invite professional trainers to give lectures and guidance. At the same time, companies can also provide online learning resources and documents so that employees can learn and master BPMN technology independently.
2. Tool selection
There are many different BPMN tools available on the market. Enterprises need to consider their own needs and budget when choosing tools. Different tools may have different functions and features. Enterprises need to choose the right tool according to their actual situation.
For example, enterprises can evaluate the features, ease of use, price, and support services of different tools, and then choose the tool that best suits them. At the same time, enterprises can also consider using open source BPMN tools to reduce costs and increase flexibility.
3. Process culture construction
The implementation of BPMN is not only a technical issue, but also involves the process culture construction of the enterprise. The enterprise needs to establish a process-oriented cultural atmosphere, let employees realize the importance of process management, and actively participate in the optimization and improvement of the process.
For example, companies can encourage employees to put forward suggestions and plans for process improvement through publicity, training and rewards. At the same time, companies can also establish an organizational structure and institutional system for process management to ensure the smooth implementation of process management work.
4. Integration with other systems
When implementing BPMN, enterprises may need to integrate with other systems, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, etc. Therefore, enterprises need to consider the integration capabilities of BPMN tools with other systems to ensure the smooth operation of the process.
For example, enterprises can choose BPMN tools with good integration capabilities, or achieve integration with other systems through customized development. At the same time, enterprises also need to establish data exchange and interface standards to ensure data consistency and accuracy between different systems.
In summary, BPMN, as a powerful process management tool, provides enterprises with visualization, standardization, scalability, and analytical optimization capabilities. When implementing BPMN, enterprises need to fully recognize its advantages and challenges and take corresponding measures for training, tool selection, process culture construction, and system integration to ensure the successful implementation of BPMN. Through the application of BPMN, enterprises can improve the efficiency and quality of processes, enhance competitiveness, and achieve sustainable development.
As an excellent online drawing tool, ProcessOn provides a convenient and efficient platform for drawing BPMN flowcharts. By using ProcessOn to draw BPMN, enterprises can visualize, analyze and optimize business processes, improve collaboration efficiency, reduce costs and enhance competitiveness. When using ProcessOn to draw BPMN, users need to be familiar with BPMN symbols and syntax, reasonably select templates and elements, and focus on multi-person collaboration and communication to ensure that the drawn flowcharts are accurate, clear and easy to understand. Come and experience it for free !