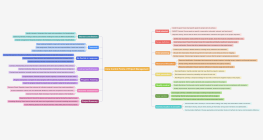
11 Pain Points in User Psychology of Copywriting
0 Report
This mind map explores the intricate psychology behind copywriting, focusing on 11 key pain points that influence user behavior. Understanding these psychological triggers, such as the desire to compensate oneself or others, the fear of falling behind, and the need for consistency, can significantly enhance the effectiveness of copywriting. By addressing dilemmas, leveraging ideal identities, and activating emotions like guilt or superiority, marketers can craft compelling messages that resonate with consumers. This framework provides valuable insights into creating persuasive content that aligns with users' psychological motivations, ultimately driving engagement and conversion.
Related Recommendations
Other works by the author
Outline/Content
See more
compensate oneself
If someone feels they have given too much for others or long-term goals, they will want to compensate and reward themselves (provide reasons for consumers to indulge).
compensate others
If a person feels that others have given him a lot while he has given little in return, he will feel guilty towards others and thus have the motivation to compensate them.
backward mentality
We all don't want to fall behind, especially those who are similar to us and close to us,
If something "people have me not", I am easy to stimulate action (stimulate the jealousy in my hand)
If something "people have me not", I am easy to stimulate action (stimulate the jealousy in my hand)
dilemma
Users often have to make a difficult choice between two goals they both want to achieve. If your proposal allows them to have their cake and eat it too, making them no longer have to make a difficult choice, they are more likely to make a change and choose your product (set up a "bait product" and provide a "reference system" for decision-making).
Consistency psychology
Everyone wants to maintain the consistency of their different behaviors. If a user's two consumption behaviors conflict, they are more likely to change their consumption behavior to maintain the consistency of their actions (the principle of commitment consistency).
Integrative psychology
Users feel they have spent a lot of effort to achieve a certain goal, but just missed it, so it's easy to take action to make changes (binding mating goals, etc.)
evade identity
Users have people they don't want to be, and if something they did in the past (such as not buying your product) happens to be a characteristic of the kind of person they don't want to be, they are more likely to buy and use your product (avoiding the group).
Ideal Identity
Users must have the person they want to be, if you let him do this, it just happens to be a feature of the kind of person he wants to be, he will be very easy to do (yearning for the group)
Acquisition of experience
If others feel that they have failed in the same thing once, they will take action (activate guilt, regret emotions) because they don't want to fail a second time.
Optimal mindset
Two choices are before you,if the cost, time, etc. are the same, one choice obviously looks more reasonable, and users will choose this (provide a more powerful "reference system" for their own sales)
Superiority complex
If I can obtain something that others find difficult to get, I am more likely to take action (activating vanity, showing off, feelings of superiority, and identity recognition)
Collect
Collect

0 Comments
Next Page