Cold War Timeline and Key Events
0 Report
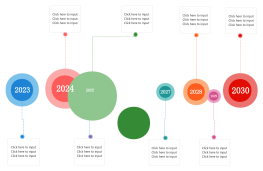
This mind map outlines the 'Cold War Timeline and Key Events,' highlighting significant moments and themes from the Cold War era, spanning from the 1940s to the 1990s. Beginning with the origins of the Cold War in the 1940s, it examines pivotal events such as the Truman Doctrine, Berlin Blockade, and the establishment of NATO. The mind map traces the escalation of tensions through the Korean War, Cuban Missile Crisis, and the Space Race, before moving to the period of détente in the 1970s. It concludes with the fall of the Berlin Wall and the Soviet Union's collapse, marking the Cold War's end.
Related Recommendations
Other works by the author
Outline/Content
See more
1940s: Origins of the Cold War
1945: Yalta and Potsdam Conferences
Divisions between the Allies on post-war Europe began to emerge.
Agreements on dividing Germany and Berlin into occupation zones.
1947: Truman Doctrine
Policy of containment aimed at preventing the spread of communism.
U.S. aid pledged to Greece and Turkey to counter Soviet influence.
1948: Berlin Blockade and Airlift
Soviet Union blocked access to West Berlin, aiming to force Allies out.
Western Allies launched a massive airlift to supply the city, lasting nearly a year.
1949: NATO Established
Creation of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization as a military alliance.
Counterbalance to Soviet influence in Europe.
1949: Soviet Atomic Bomb Test
Soviets successfully tested their first nuclear weapon, ending U.S. monopoly.
Escalated the arms race between the superpowers.
1950s: Heightening Tensions
1950-1953: Korean War
Proxy war between communist North Korea (backed by China and USSR) and capitalist South Korea (supported by UN and U.S.).
Ended in a stalemate, solidifying the division of Korea.
1955: Warsaw Pact
Soviet response to NATO; alliance of Eastern Bloc countries.
1956: Hungarian Revolution
Anti-Soviet uprising in Hungary brutally crushed by Soviet troops.
Exposed the limits of Soviet tolerance for dissent within its sphere of influence.
1957: Space Race Begins
Soviet Union launched Sputnik, the first artificial satellite.
Triggered U.S. investment in space exploration and education.
1960s: Crisis and Confrontation
1961: Bay of Pigs Invasion
Failed U.S.-backed invasion of Cuba aimed at overthrowing Fidel Castro.
1961: Berlin Wall Constructed
Physical barrier dividing East and West Berlin, symbolizing Cold War divisions.
1962: Cuban Missile Crisis
Soviet deployment of nuclear missiles in Cuba brought the world to the brink of nuclear war.
Crisis ended with a negotiated withdrawal of missiles from Cuba and U.S. missiles from Turkey.
1968: Prague Spring
Reform movement in Czechoslovakia advocating political liberalization.
Crushed by Warsaw Pact invasion, reasserting Soviet control in Eastern Europe.
1970s: Détente
1972: SALT I Treaty
Strategic Arms Limitation Talks led to agreements on limiting nuclear weapons.
1973: U.S. Withdrawal from Vietnam
Marked the end of direct U.S. involvement in the Vietnam War.
1979: Soviet Invasion of Afghanistan
Soviet forces intervened to support a communist government facing internal rebellion.
Triggered U.S. support for Afghan mujahideen, further escalating tensions.
1980s: Renewed Confrontation
1980: Solidarity Movement in Poland
Independent trade union became a significant anti-communist force.
1983: Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI)
U.S. missile defense program dubbed 'Star Wars,' aimed at countering Soviet threats.
1985: Gorbachev's Reforms
Mikhail Gorbachev introduced glasnost (openness) and perestroika (restructuring) to reform the Soviet Union.
1989: Fall of the Berlin Wall
Symbolic end of Cold War divisions as East and West Germany began reunification.
1990s: End of the Cold War
1991: Collapse of the Soviet Union
Dissolution of the USSR marked the definitive end of the Cold War.
Former Soviet republics gained independence, reshaping global geopolitics.
Key Themes and Legacies
Ideological Conflict
Capitalism vs. Communism defined global alignments and policies.
Proxy Wars
Conflicts in Korea, Vietnam, and Afghanistan showcased superpower competition.
Nuclear Arms Race
Continuous buildup of nuclear arsenals raised global fears of annihilation.
Impact on Decolonization
Cold War rivalries influenced the independence movements in Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
Space Race and Technology
Accelerated advancements in space exploration and military technology.
Collect
Collect
Collect

0 Comments
Next Page