Productivity and production relations
0 Report
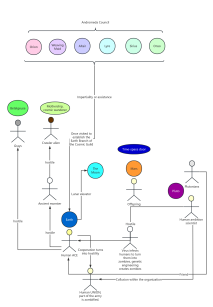
This mind map explores the intricate relationship between productivity and production relations, key concepts in understanding societal development. It delves into how productive forces, the human capacity to transform nature, resolve contradictions between humans and the environment. The map also examines production relations, the social dynamics formed during production, and their interaction with productive forces. By illustrating historical transitions, such as from primitive to capitalist societies, it highlights the evolution driven by technological advancements. Furthermore, it underscores the importance of aligning production relations with productive forces to foster societal progress, offering insights into Marxist theory and policy formulation.
Related Recommendations
Other works by the author
Outline/Content
See more
Productivity
The productive forces are the ability of people to actively transform the natural world and obtain material means of life from it, which represents the relationship between man and nature.
The productive forces resolve the contradiction between man and nature.
relations of production
The relationships formed among people during the production process
factors of production
Entity-level elements
means of production
labor object
Laborer
Manual laborer
Mental worker
Science and technology are the primary productive force.
The relationship between productive forces and production relations
The productive forces determine the production relations, what kind of productive forces there are, will give rise to what kind of production relations.
The productive forces determine the production relations, what kind of productive forces there are, will give rise to what kind of production relations.
The condition of productivity determines the nature of the production relations.
Example 1: Primitive tools → Primitive society
Example 2: Bronze Ware → Slave Society
Example 3: Iron tools → feudal society
Example 4: Steam engine → capitalist society
The development of productivity determines the transformation of production relations.
Original tools → Bronze tools → Iron tools → Steam machines
Primitive society → slave society → feudal society → capitalist society
Example 1: Primitive tools → Primitive society
Example 2: Bronze Ware → Slave Society
Example 3: Iron tools → feudal society
Example 4: Steam engine → capitalist society
Original tools → Bronze tools → Iron tools → Steam machines
Primitive society → slave society → feudal society → capitalist society
The relations of production exert a dynamic counteraction on the productive forces.
When the relations of production are in line with the objective requirements of the development of productive forces, they play a promoting role in the development of productive forces.
When the relations of production do not meet the objective requirements of the development of productive forces, they will hinder the development of productive forces.
The law of the contradiction between productive forces and production relations has extremely important theoretical and practical significance.
Denied the "moral preaching" as the thought system for judging the merits and demerits of historical events, for the first time scientifically established the development of productive forces as "the highest standard of social progress".
It is an important basis for Marxist political parties to formulate their lines, policies, and policies.
The law that the relations of production must be in line with the development of the productive forces
From the perspective of content, it summarizes the two aspects of the interaction between productive forces and production relations.
From the perspective of the process, this law manifests as the relationship between the mode of production and the productive forces always evolving from basically suitable to basically unsuitable, and then back to basically suitable.
Correspondingly, the relations of production also always change from relative stability to the replacement of the old and new, and then to relative stability.
Collect
Collect

0 Comments
Next Page