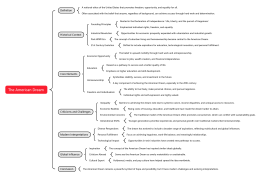
The American Jobs Act Mind Map
1 Report
This mind map provides an overview of 'The American Jobs Act,' proposed by President Barack Obama in 2011 to address the lingering effects of the 2008 financial crisis and the slow recovery in the labor market. With an estimated cost of $447 billion, the Act aimed to reduce unemployment and stimulate economic growth through targeted investments and tax cuts. Key components included payroll tax cuts, business incentives, infrastructure investments, and support for the unemployed. Despite facing legislative challenges and mixed public reception, the Act sparked ongoing debates about economic policy and influenced future infrastructure investments.
Related Recommendations
Other works by the author
Outline/Content
See more
Legislative Challenges
Opposition from Congress
Republicans opposed large government spending and the proposed tax hikes on the wealthiest Americans
Disagreements on whether the proposed tax cuts would be effective in stimulating growth
Some Democrats criticized the Act for not going far enough to address poverty or long-term unemployment
Concerns Over the National Debt
Republicans and fiscal conservatives raised concerns about the impact of the Act on the national deficit
Debate over the long-term sustainability of increased government spending
Disagreements about the economic theory behind using deficit spending to stimulate growth
Effectiveness and Impact Debate
Questions about whether the proposed measures would significantly reduce unemployment
Mixed opinions on whether the tax cuts would lead to sustainable business investments
Debates about the extent to which government spending can offset the private sector's slow recovery
Public Reception
Support from Economists and Policy Experts
Many economists praised the Act for its focus on creating jobs through infrastructure investment
Proponents of Keynesian economics saw it as a necessary response to the economic crisis
Supporters argued that government intervention was crucial in addressing unemployment and stimulating demand
Opposition from Fiscal Conservatives
Critics argued that the Act was a temporary fix and would not lead to long-term job creation
Some believed the focus on government spending would lead to greater economic inefficiencies
Fiscal conservatives feared the Act would exacerbate the national debt
Mixed Reception from the Public
Public support varied by region, with some areas particularly benefiting from infrastructure investments
Concerns about whether the measures would reach those most affected by the recession, such as low-income communities
Legacy and Impact
Some Provisions Passed Separately
Key aspects, such as tax cuts for businesses and extended unemployment benefits, were passed as part of other bills
While the Act itself did not pass in full, elements of it shaped future economic policies
Highlighted Ongoing Debates About Economic Policy
The Act sparked ongoing discussions about the role of government spending in stimulating economic recovery
The debate over tax cuts, infrastructure investments, and deficit spending continues to shape U.S. fiscal policy
Set the Stage for Future Infrastructure Investments
The American Jobs Act helped bring attention to the aging infrastructure of the U.S.
Subsequent administrations continued to push for large-scale infrastructure projects as a means to drive job creation
Overview
Proposed by President Barack Obama in 2011
Introduced in response to the lingering effects of the 2008 financial crisis and the slow recovery in the labor market
Aimed to reduce unemployment and stimulate economic growth through targeted investments and tax cuts
Estimated cost: $447 billion
Included a variety of measures designed to create jobs, boost consumer spending, and improve infrastructure
Philosophy behind the Act
Key focus on immediate job creation and stimulating demand in the economy
Use of government spending to fill in for the private sector's slower recovery
Key Components
Tax Cuts
Payroll Tax Cuts for Workers and Employers
Temporary reduction in the payroll tax paid by workers (from 6.2% to 4.2%)
Employer payroll tax cut aimed at encouraging businesses to hire new employees
Tax relief targeted to low and middle-income households to boost consumption
Business Incentives
Tax credits for businesses that hire workers and invest in new facilities or technologies
Temporary deduction for businesses to write off the cost of hiring new workers
Small business tax cuts to encourage investment and expansion
Infrastructure Investments
Public Infrastructure Projects
Funds for modernizing transportation systems (roads, bridges, public transit)
Renovating schools, public buildings, and improving energy efficiency
Investment in renewable energy infrastructure, such as wind and solar energy projects
Public works funding to improve the nation's infrastructure for long-term economic health
Job Creation through Infrastructure
Large-scale infrastructure projects expected to create thousands of jobs
Focus on repairing and upgrading aging infrastructure, contributing to long-term economic efficiency
Support for the Unemployed
Extension of Unemployment Benefits
Extended unemployment insurance for those who had exhausted their benefits
Increased access to job retraining programs to help displaced workers transition to new industries
Emergency unemployment compensation to provide financial stability during economic downturns
Job Training and Workforce Development Programs
Creation of job training programs targeted at high-demand industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and technology
Partnerships with educational institutions and private employers to offer skills training
Programs aimed at helping workers displaced by automation and outsourcing
Education and Workforce Development
Modernization of Public Schools and Colleges
Funding to upgrade facilities, technology, and resources in schools across the nation
Ensuring access to high-quality education in underfunded districts
Incentives to hire and retain high-quality teachers, reduce class sizes, and improve student outcomes
Preventing Teacher Layoffs
Grants to local school districts to prevent widespread teacher layoffs
Support for hiring additional staff to address rising student numbers
Job security for educators, particularly in struggling communities
Economic Goals
Boost Hiring and Reduce Unemployment Rates
Goal of creating an estimated 1.9 million jobs in the first two years
Focus on reducing the unemployment rate to pre-recession levels
Reduce joblessness through targeted job creation programs
Stimulate Economic Growth and Increase Consumer Spending
Using tax cuts and unemployment benefits to increase disposable income
Encouraging business investment through tax relief and incentives
Increasing demand for goods and services by boosting purchasing power
Strengthen Infrastructure and Public Services for Future Growth
Invest in infrastructure that can support long-term economic growth
Enhance public services such as education, healthcare, and transportation to improve quality of life
Prepare the workforce for the demands of a modern economy through education and training
Collect
Collect
Collect

Collect

0 Comments
Next Page